Dynamics 365 Tutorials, Supply Chain and Logistics Management
Learn How Direct Deliveries in Dynamics 365 Can Assist You Overcome the Challenge of Excessive Stocking in Warehouse

Inventory Management with Direct Deliveries in Dynamics 365
Over Stocking | Reduce Cost | Cost Management | Vendor Managed Inventory | Warehouse Solutions
What is Inventory Management?
Inventory management is a critical component of every company supply chain. Keeping a close eye on inventory movement may make or break a firm, which is why entrepreneurs usually emphasize the need for proper inventory management. But, unfortunately, while some company owners appreciate the need and criticality of inventory monitoring daily, others do not, allowing their firm to slide through unnoticed holes.
Inventory management cannot be overstated, much more so for ecommerce and online retail enterprises. Accurate inventory monitoring enables firms to respond quickly and correctly to customer demands. In addition, inventory management in organizations must increase in lockstep with the company’s growth. Businesses may obtain several inventory management advantages by implementing a strategic plan of action that improves the process of supervising and managing inventory, including real-time data on inventory conditions and levels.
Learn more about our courses that provide you with the fundamental skills to achieve six-figure employment opportunities in the sector.
SUMMARY
Inventory management is critical for every business, but it is essential for eCommerce and online retail companies. Accurate inventory tracking helps businesses to react promptly and accurately to client requests. In addition, companies may benefit from various inventory management benefits by developing a strategic plan that streamlines the process of monitoring and controlling inventory.
What Do Inventory Management and Warehouse Management Have in Common?
Inventory management and warehouse management are similar disciplines, as both aids in moving inventory from the supplier to the end consumer efficiently and effectively. Each involves storing, shipping and reordering stock. In addition, they share the following features:
Both use software, radio frequency identification (RFID), and barcode tools to improve efficiency and accuracy. In addition, both provide visibility into all stock, either for one warehouse or the entire company.
SUMMARY
Although inventory management and warehouse management are two very distinct professions, they have a great deal in common. Both increase productivity and accuracy via software, radio frequency identification (RFID), and barcode equipment. Both enable insight into all stock, whether at a single warehouse or throughout the organization.
What is Stock Control?
Stock control sometimes referred to as inventory control and is used to demonstrate how much stock you have on hand at any one moment and how you manage it.
It applies to all items used to manufacture a product or service, from raw materials to completed products. It encompasses stock at every step of the manufacturing process, from acquisition and delivery through use and reordering.
Stock control efficiency enables you to keep the correct inventory quantity in the right location at the right time. It prevents money from being stranded needlessly and safeguards production in the event of supply chain disruptions. Everything you utilize to manufacture your goods, deliver your services, and manage your firm is considered inventory.
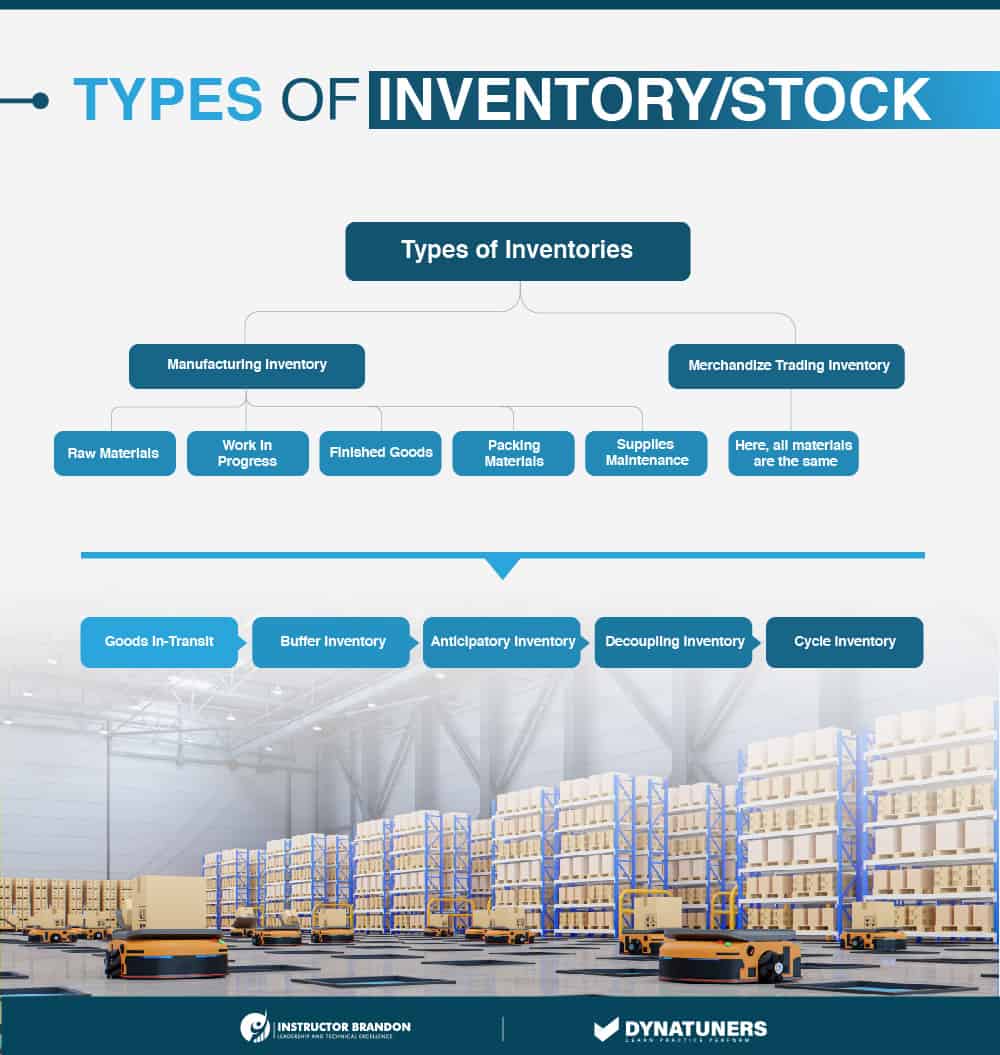
Stock is classified into four broad categories:
- Ready-to-use raw materials and components
- Work in progress – inventories of incomplete manufactured items
- Ready-to-sell completed items
- Consumables, such as gasoline and stationery
SUMMARY
All items utilized in manufacturing a product or service are considered stock. It includes stock at every stage of the production process, from purchase and delivery through usage and replenishment. Stock is divided into four major categories: (1) ready-to-use raw materials and components; (2) semi-finished raw materials and components; (3) ready-to-sell raw materials and components and (3) finished raw materials and components—finished products, including fuel, stationery and other consumables.
Stock Control Methods
There are various stock control systems, all of which are intended to give an efficient mechanism for determining what, when and how much to order.
You may use a single approach or a combination of two or more if you have a variety of stock.
-
Minimum stock level
You establish a minimum stock level and automatically reorder when that level is reached. This is referred to as the Re-ordering Level.
-
Stock review
You conduct frequent stock reviews. After each review, you place an order to restore stocks to a predefined level.
-
Just In Time (JIT)
This strategy tries to save expenses by minimizing inventory. Items are provided when required and promptly used. However, there is a risk of stock running out, so you must have confidence in your suppliers’ ability to meet demand.
These techniques may be used in conjunction with others to improve the stock control system. For instance:
-
Re-order lead time
Accounts for the time between placing and receiving an order.
-
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
This is a typical formula for determining the optimal stock level to maintain. However, because this is a somewhat sophisticated computation, you may find it simpler to utilize stock management software.
-
Batch control
It’s a term that refers to the process of controlling the production of commodities in batches. You must ensure that you have enough supply of components to last until the next batch arrives. If your demands are predictable, you may purchase a predetermined amount of stock each time you make an order, or you can regularly order, such as every week or month. In effect, you’re putting a standing order, which means you’ll need to keep an eye on the quantities and costs.
-
First in, first out
It’s a technique for effectively using perishable merchandise and preventing it from deteriorating. Stock is designated by the date of receipt and is processed in exact chronological sequence through each manufacturing step.
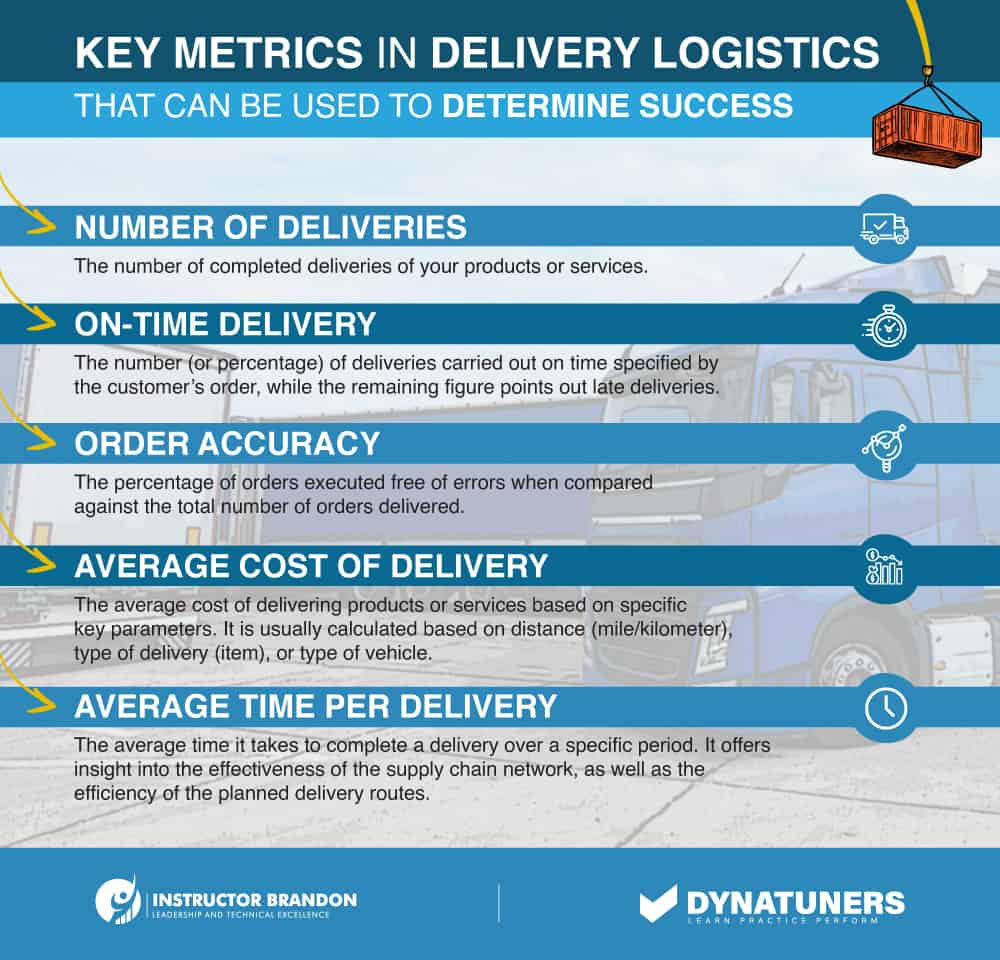
SUMMARY
Stock control systems are intended to give an efficient mechanism for determining what, when, and how much to order. You may use a single approach or a combination of two or more if you have a variety of stock. These techniques may be used in conjunction with others to improve the stock control system.
Direct Deliveries in D365
Direct deliveries shorten delivery times and save inventory costs since you do not store the items in your warehouse before shipping them to the consumer.
Direct deliveries may be created directly from the Sales order page. To begin, generate a sales order and associated order lines. Then, on the Sales order tab of the Action Pane, pick Direct delivery. Finally, define which lines must be handled directly. A connection is established between the direct delivery sales order lines and the related purchase order lines.
Packaging Slip
After you’ve established a direct delivery relationship between the lines of the sales order and the lines of the purchase order, you may amend the sales order using a packing slip. Update the packing slip or the invoice based on the purchase order. From the Sales order page, you must invoice-update the sales order. A sales order cannot have a quantity more significant than the amount documented as received due to an invoice update.
For instance, a sales order line may include ten items, but only five of those items have been updated through a packing slip. Suppose you pick All in the Quantity list when you invoice-update the sales order. In that case, only those products that have been physically received or updated by utilizing a packing slip are invoice-updated. The whole line of sales orders is not updated.
Learn more about our courses that provide you with the fundamental skills need to achieve six-figure employment opportunities in the sector.
SUMMARY
Direct deliveries shorten delivery times and save inventory costs since you do not store the items in your warehouse before shipping them to the consumer. From the Sales order page, you must invoice-update the sales order. For example, update the packing slip or the invoice based on the purchase order.
Things to Look out for when Creating Direct Deliveries in Dynamics 365
When you alter the Requested receipt date field on a sales order line, the associated purchase order line’s Delivery date field is likewise updated. Similarly, when you edit the Confirmed field on a buy order line, the accompanying sales order line’s confirmed receipt date and established ship date values are updated as well.
The delivery address for a purchase order is typically the company’s address. On the other hand, when creating a direct delivery, you enter the customer’s address as the delivery address. Therefore, if you edit the delivery address on a buy order line with the direct delivery type, the related sales order line’s delivery address is likewise changed. Similarly, if the delivery address on the sales order line is changed, the delivery address on the buy order line is updated.
Direct delivery results in a dialogue box stating that the line is tied to purchase order lines. If the sales order line has been partly delivered, you can’t remove the line or the purchase order lines related to it.
Direct delivery means that the things you never sell physically arrive at your facility. However, a warehouse must still be specified on the sales order line. Similarly, selection criteria may be provided for an item’s item model group. Because the products are never physically delivered to your warehouse, these standards are bypassed when a sales order is a direct delivery.
SUMMARY
Direct delivery means that the things you never sell physically arrive at your facility. If you edit the delivery address on a buy order line with the direct delivery type, the related sales order line’s delivery address is likewise changed. The delivery address for a purchase order is typically the company’s address.
Functional Walkthrough of Direct Deliveries in Dynamics 365
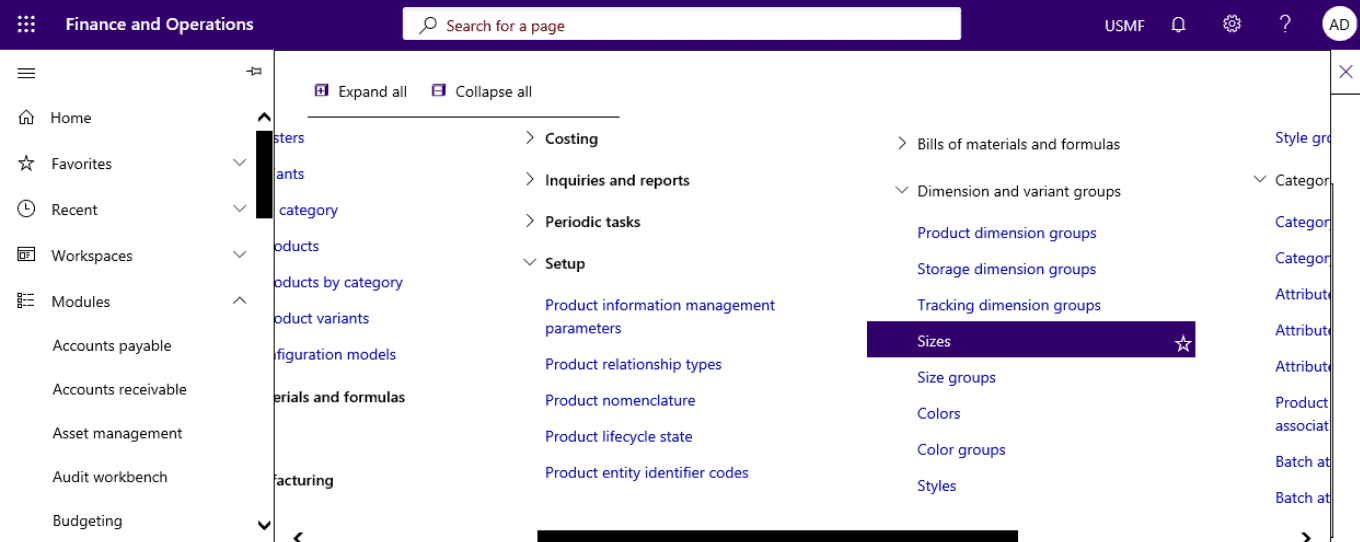
Step 1
Open Product information management > Setup > Dimension and variant groups > Sizes.
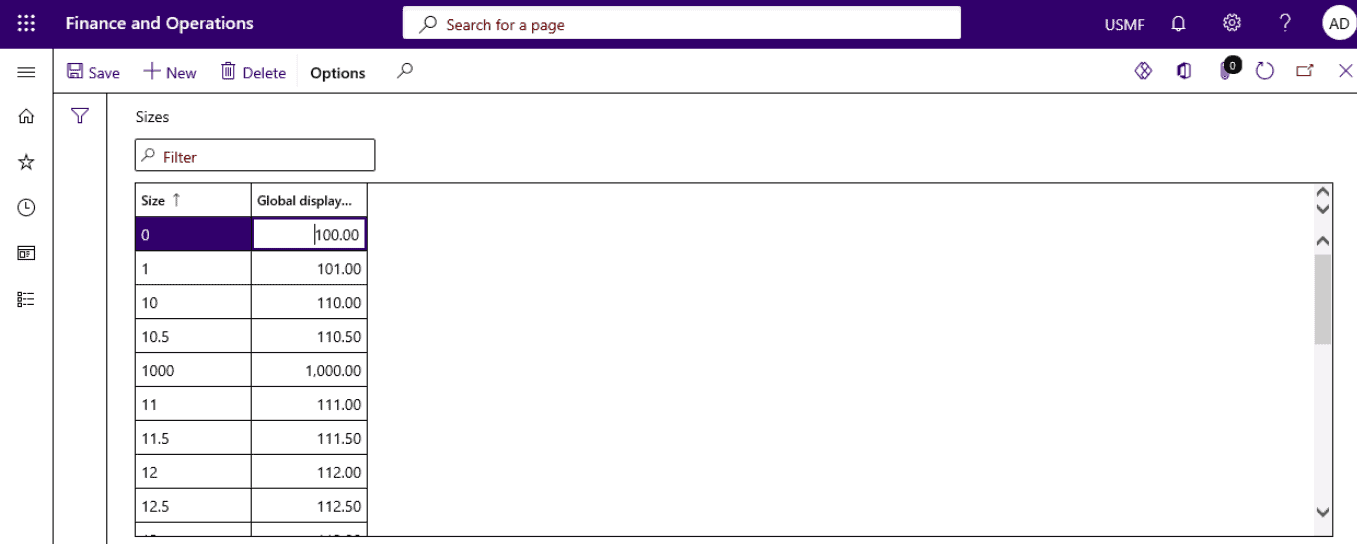
Step 2
Select New.
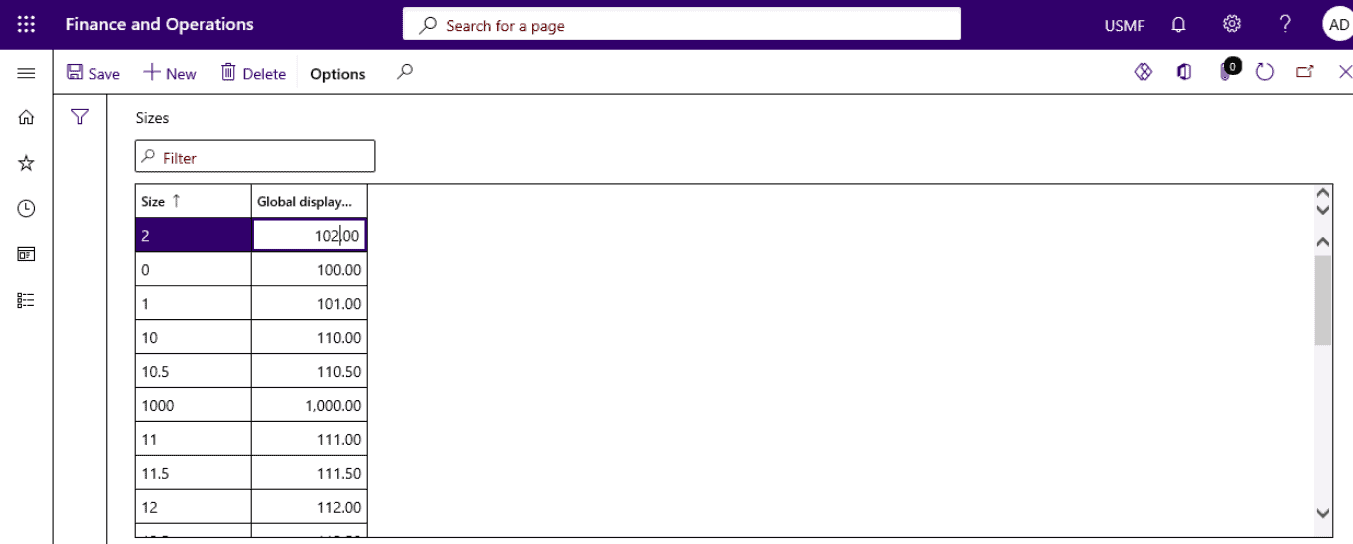
Step 3
Enter New size.
Step 4
- Open Product information management > Setup > Dimension and variant groups > Colors.
- Select New.
- Enter new color.
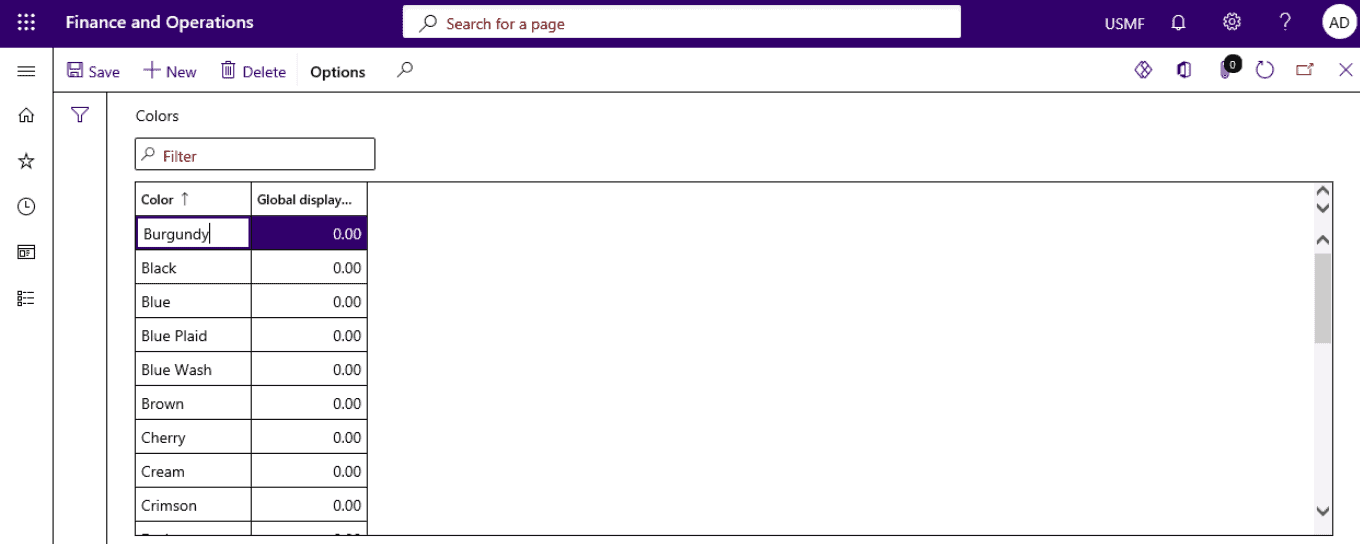
Step 5
- Open Product information management > Setup > Dimension and variant groups > Styles.
- Select New.
- Enter New Style.
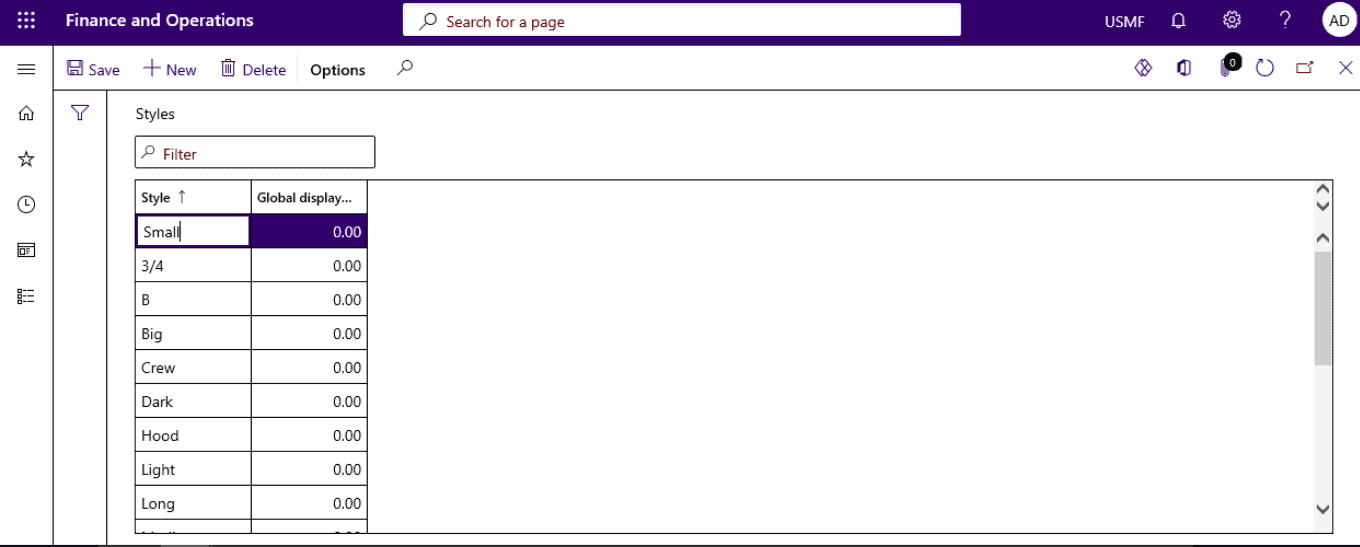
Product Dimensions
Product dimensions can also be created and maintained on the Product dimensions page, which can be accessed from different locations:
Step 1
Open Product information management > Products > Product masters.
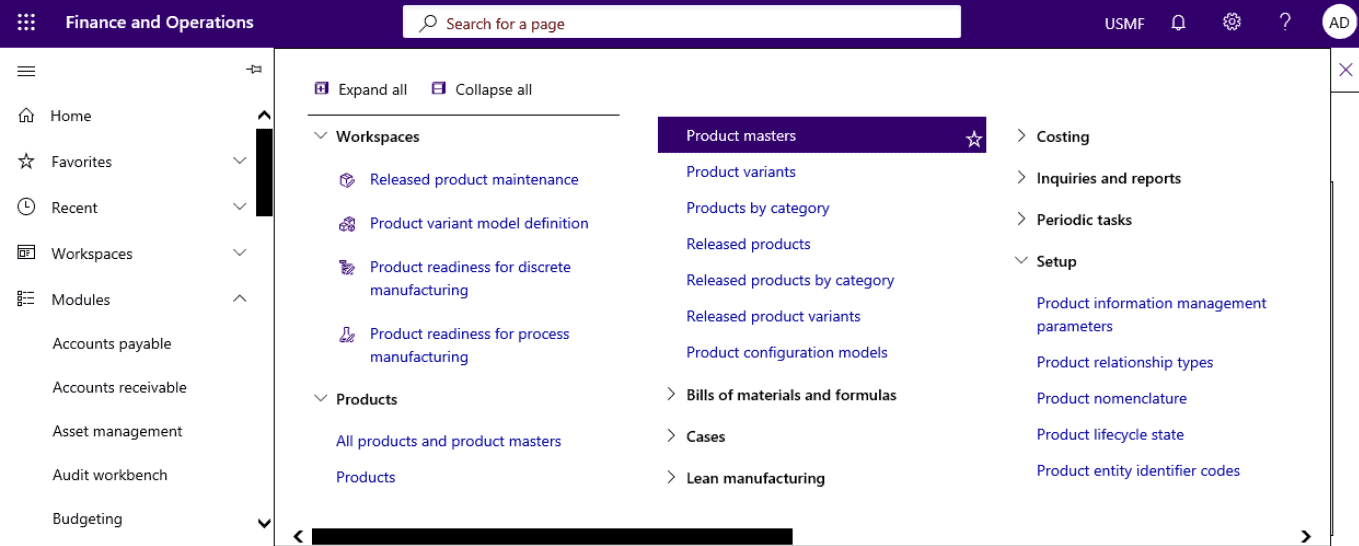
Step 2
On the Action Pane, select Product dimensions.
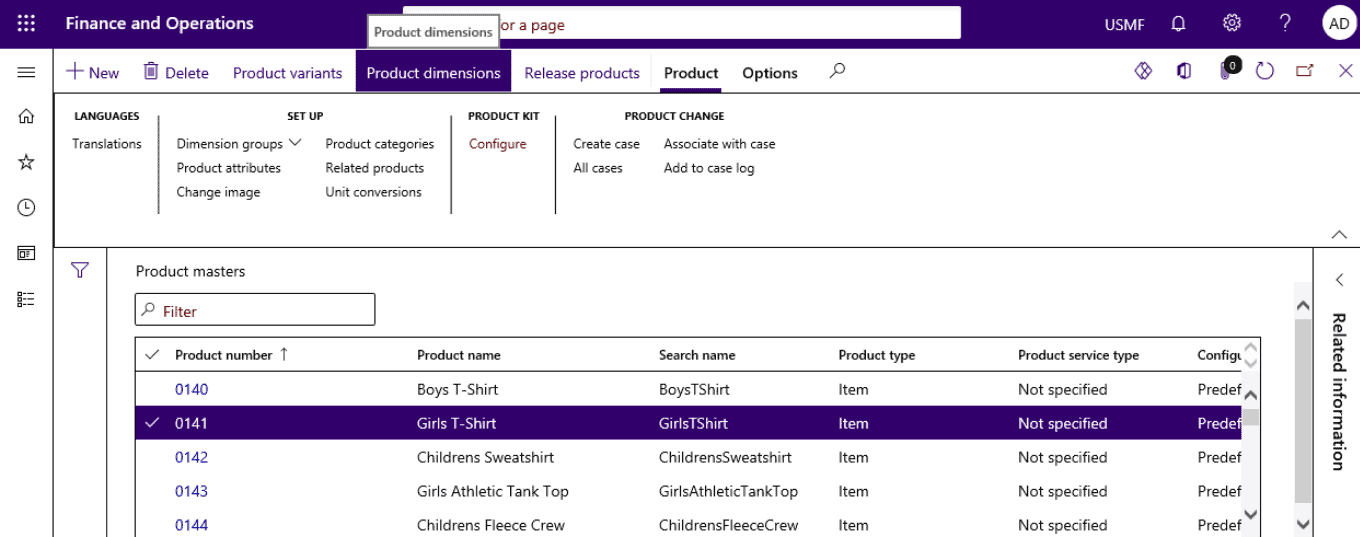
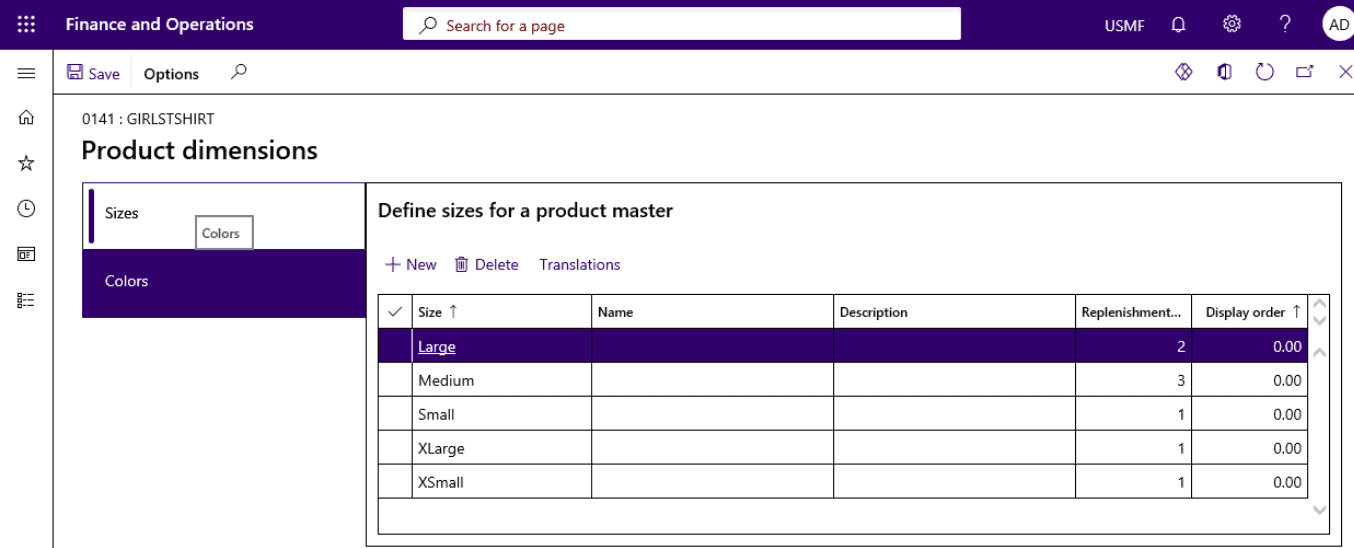
Step 3
Open Product information management > Products > All products and product masters.
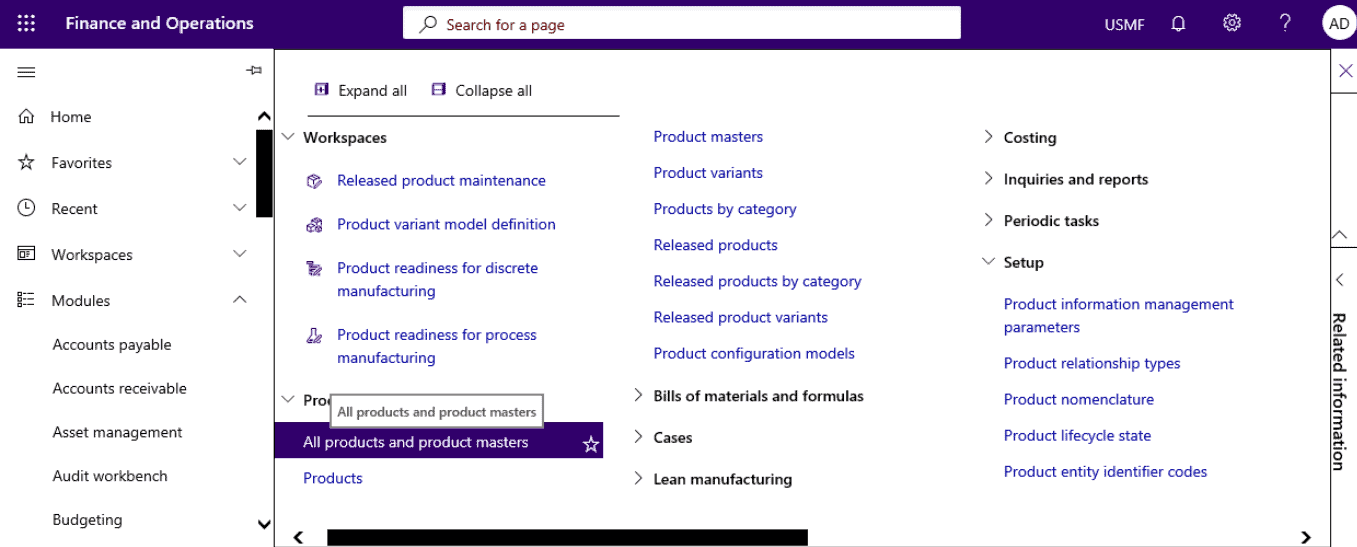
Step 4
Select a product master on the Action Pane, select Product dimensions.
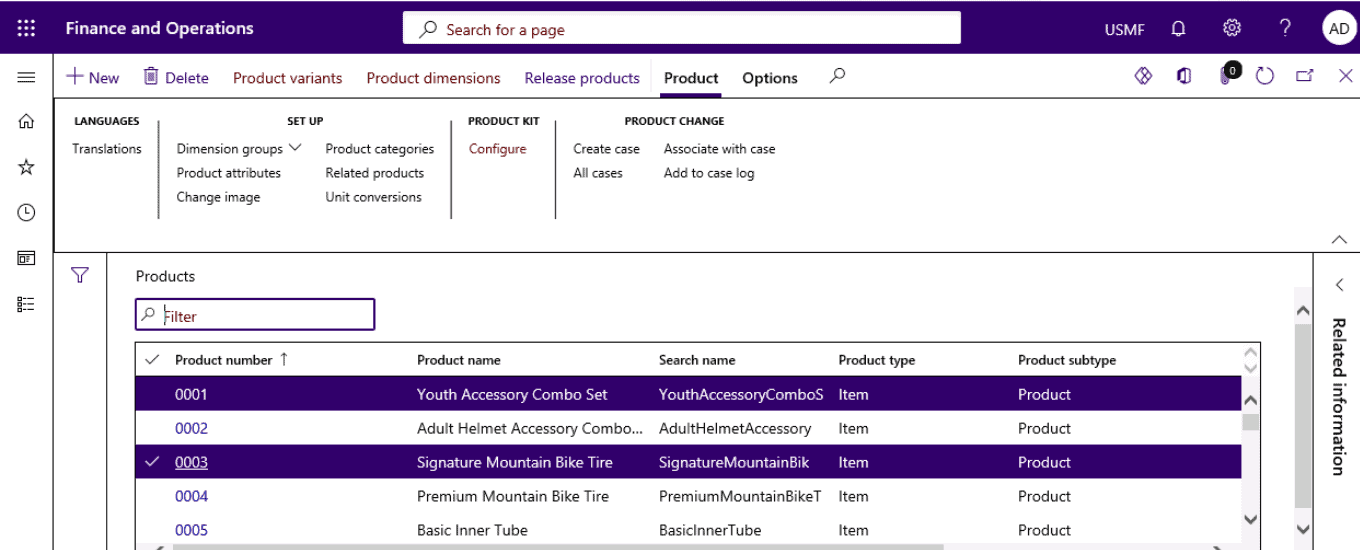
Step 5
Go to Product information management > Products > Released products.
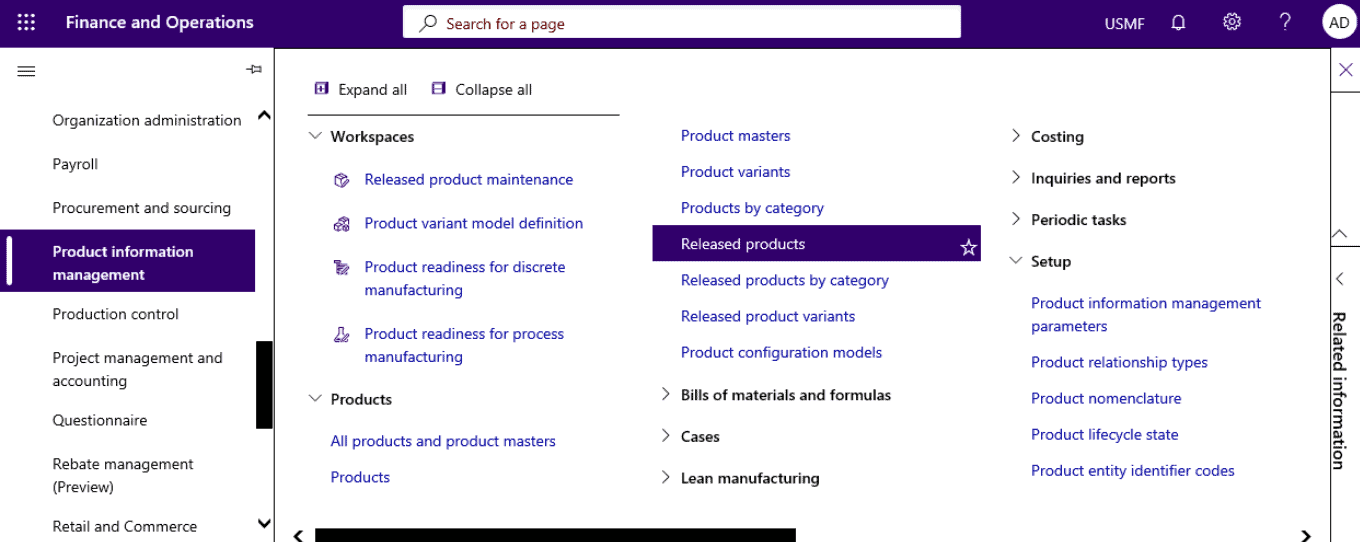
Step 6
On the Action Pane, select Product dimensions in the Product tab in the Product master group.
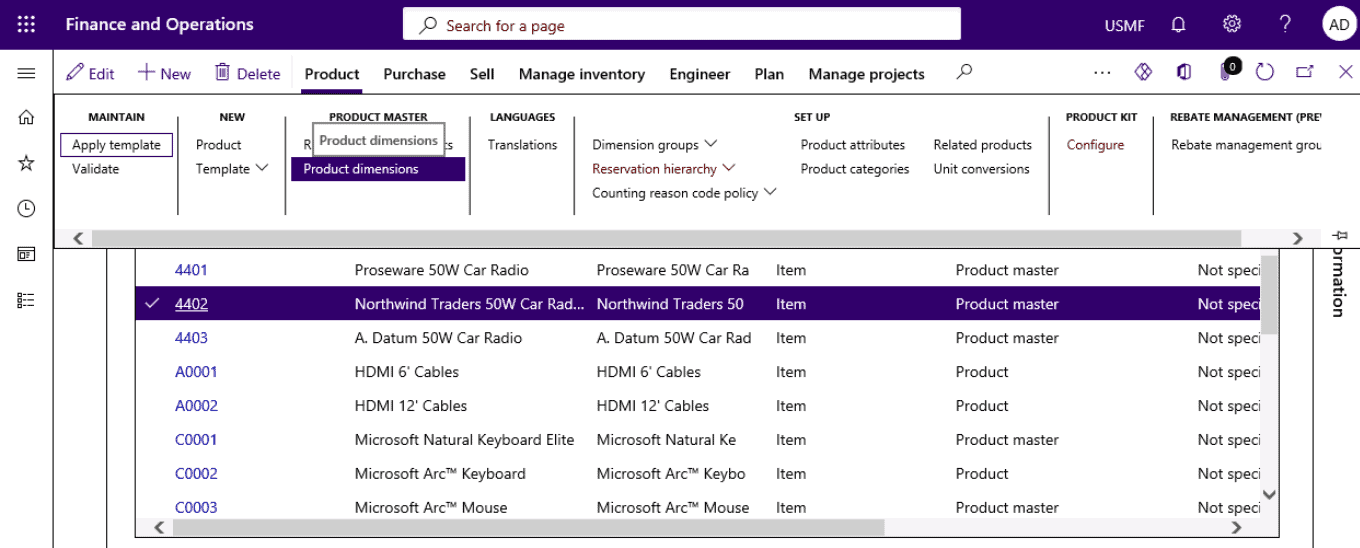
Step 7
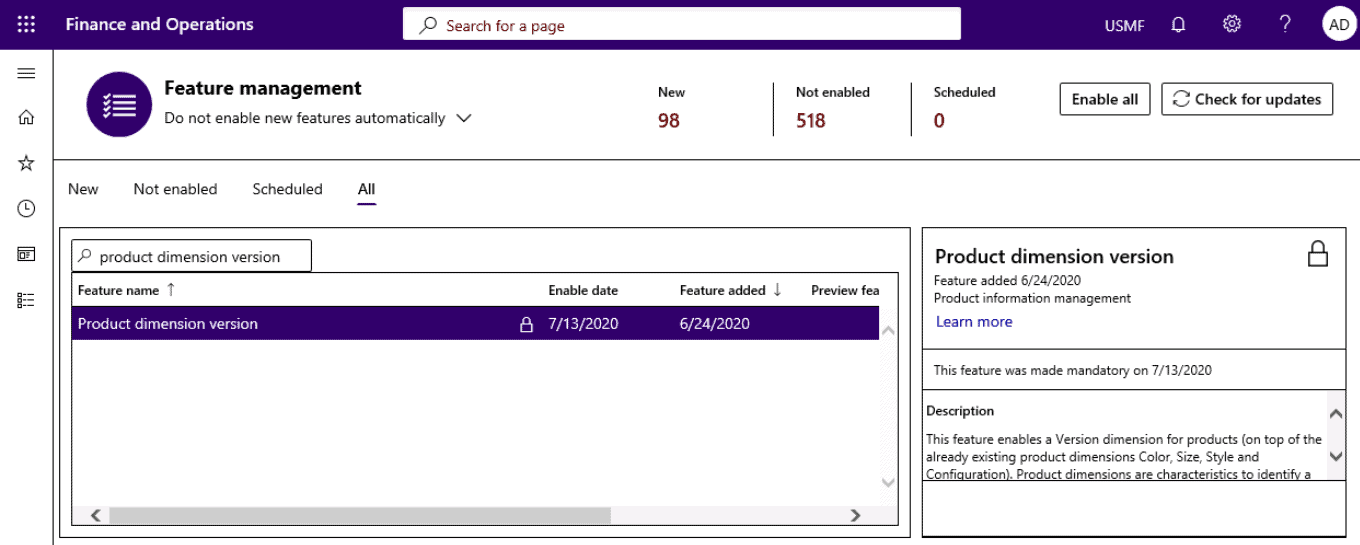
Open System administration > Feature management workspace.
Step 8
Enable packaging product dimensions by clicking on Enable now.
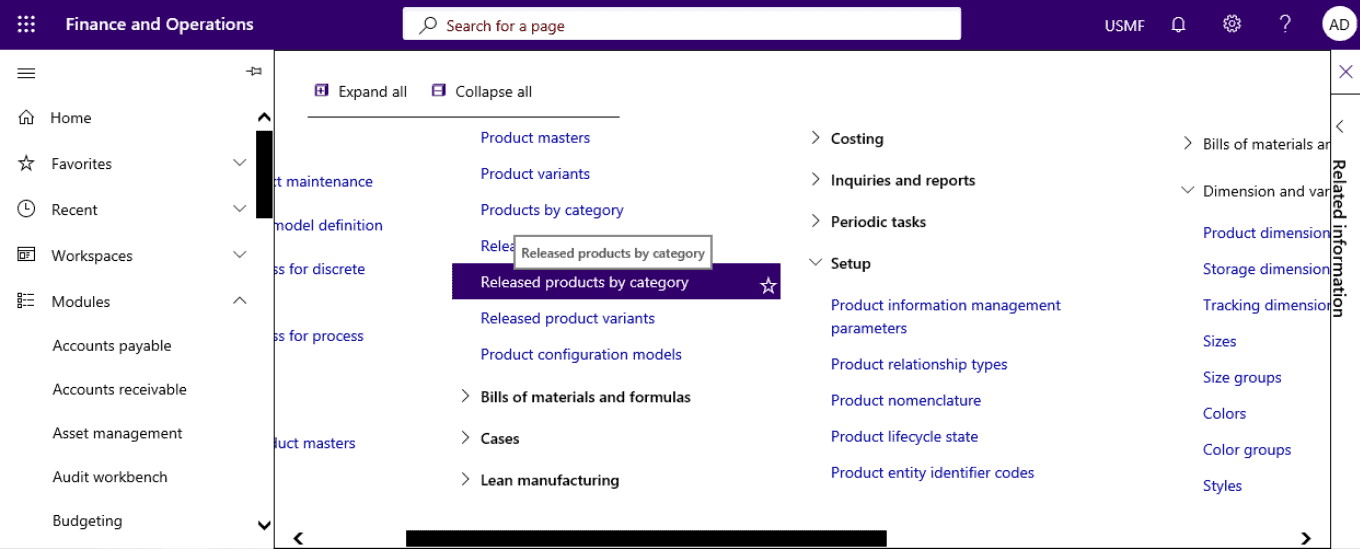
Step 9
Open Product information management > Released products.
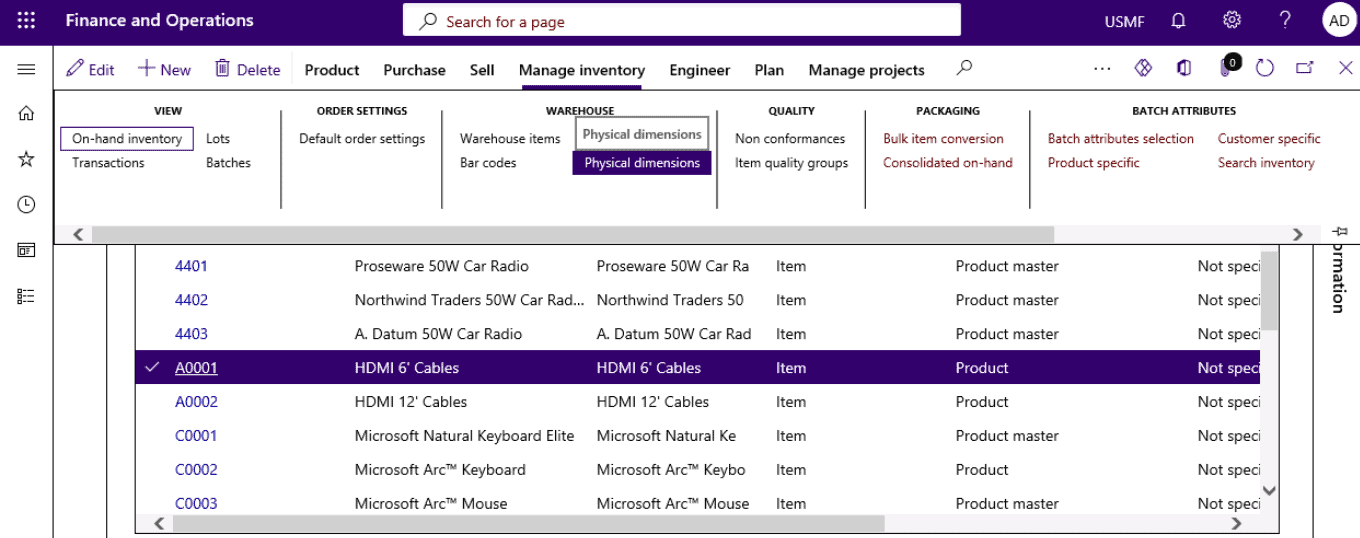
Step 10
Click on Manage inventory tab and select Physical dimensions.
Step 11
Enter/edit product dimensions.
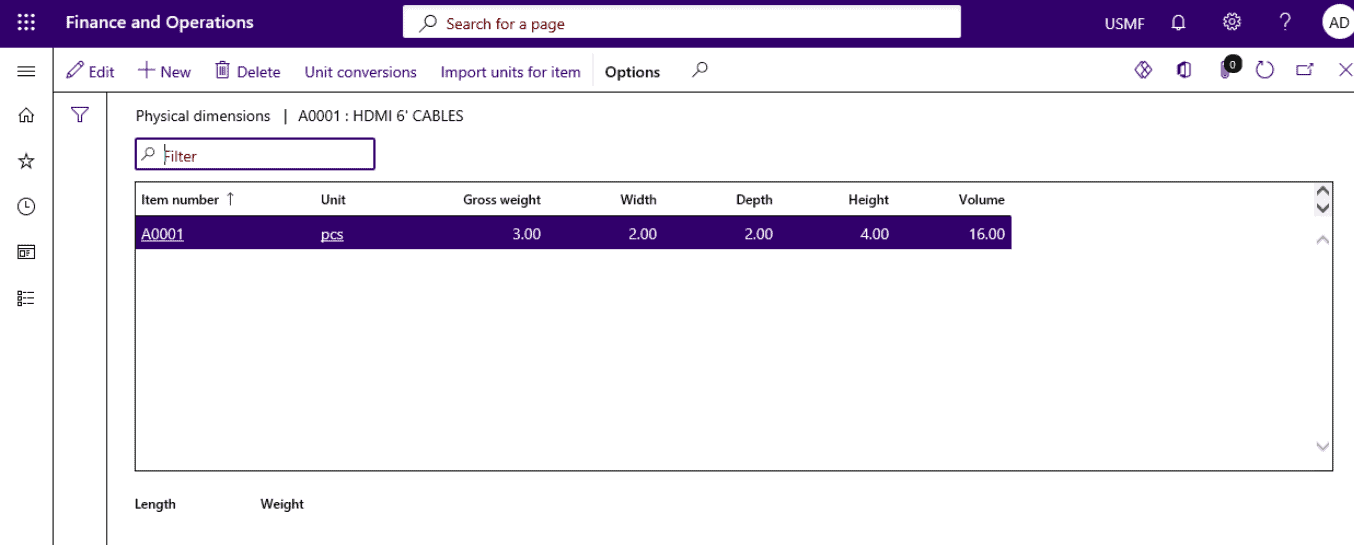
Step 12
Now Open Product information management > Products > Released products.
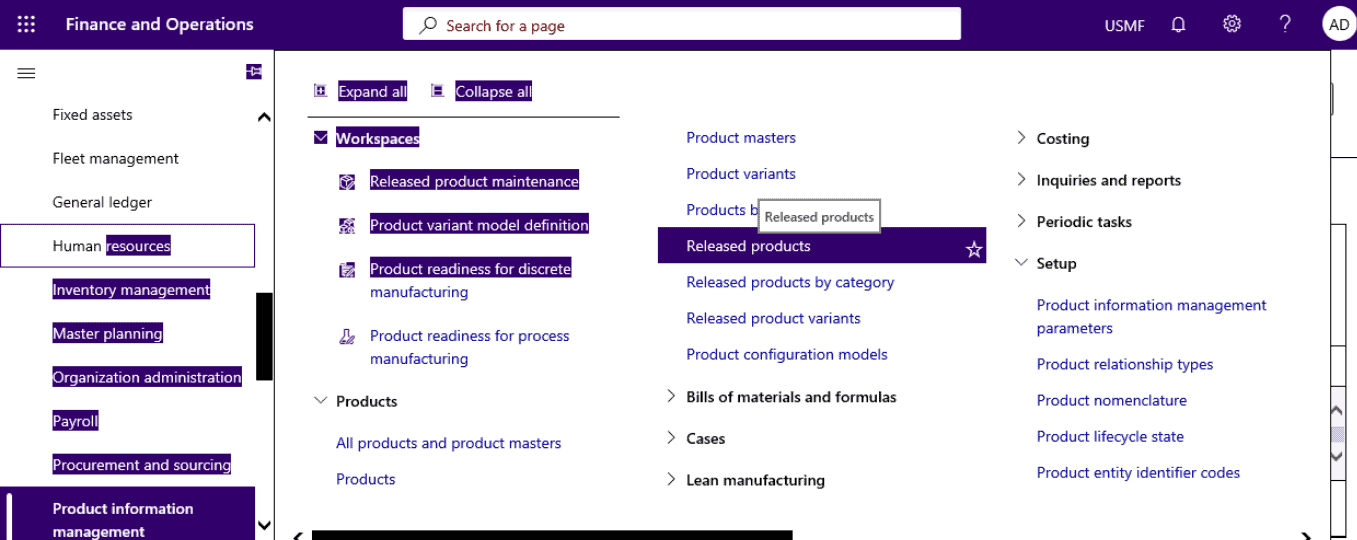
Step 13
Open Released products > Manage inventory tab > Physical product dimensions
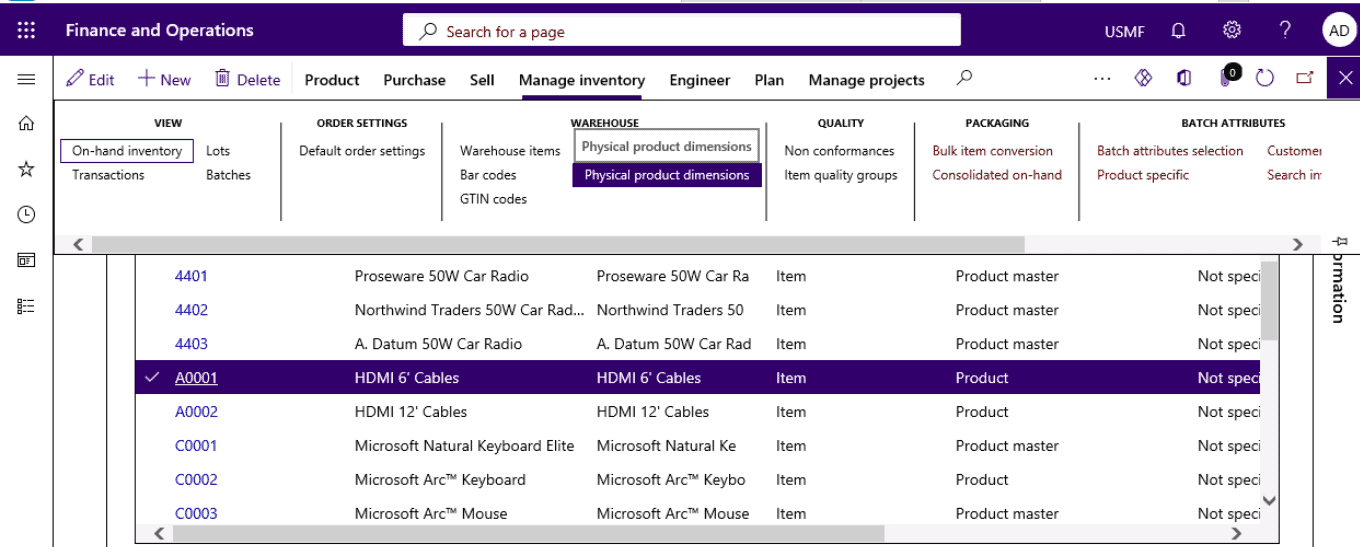
Step 14
Select the Physical dimension type.
Step 15
Enter the product dimensions.
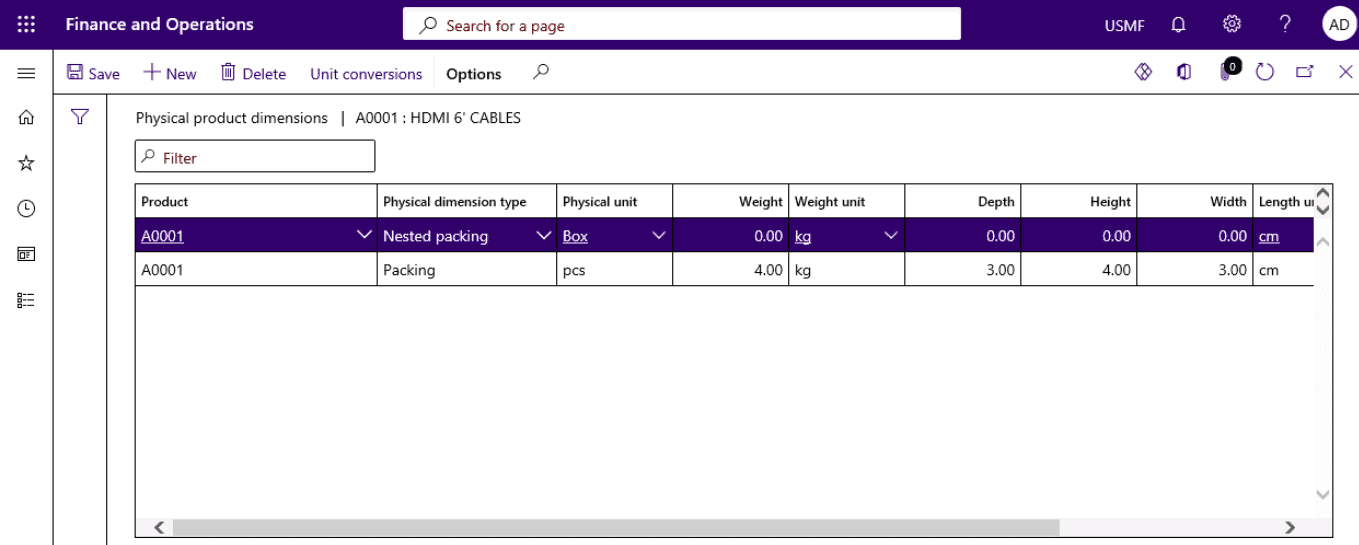
SUMMARY
Following the above steps, you can create direct deliveries in Dynamics 365.
Stock Control Systems – Keeping Track Manually
Stocktaking compiles an inventory or list of all available merchandise and records, its location and worth. It’s often a yearly activity – a kind of audit to determine the stock’s value as part of the accounting process.
While codes, especially barcodes, may significantly simplify the procedure, they can still be rather time-consuming. By doing more regular stock checks and implementing rolling inventory strategy, you may avoid a tremendous yearly effort, but it requires ongoing attention throughout the year. RFID tagging with portable readers may be a simple and effective method to keep an eye on inventories in real-time.
Any inventory management system must allow you to:
- Keep inventory
- Make orders
- Issue stocks
The stock book is the most straightforward manual approach and is ideal for small enterprises with few stock items. It allows you to maintain a record of every good received and issued. It may be used in conjunction with a simple reordering mechanism. For instance, the two-bin system is comprised of two containers containing stock products. When one becomes empty, it’s time to begin utilizing the second bin and place an order for more goods to replenish the empty one.
Direct delivery results
For increasingly complicated systems, stock cards are employed. Each class of stock has an accompanying card that contains information such as:
- Description
- Value
- Location
- Stock levels, quantities, and lead times for reorders (if this method is used)
- Information about the provider
- Historical data on stock prices
More complex manual methods identify objects using coding. For example, codes may show the stock’s worth, location, and the batch number, which is beneficial for quality control.
SUMMARY
Stocktaking compiles an inventory or list of all available merchandise and records its location and worth. It’s often a yearly activity – a kind of audit to determine the stock’s value as part of the accounting process. RFID tagging with portable readers may be a simple and effective method to keep an eye on inventories in real-time.
Using RFID for Inventory Control, Stock Security and Quality Management
RFID enables businesses to identify and monitor individual items and components across the supply chain, from manufacturing to point-of-sale.
RFID tags are comprised of a small microprocessor and a small antenna that may store a variety of digital data about the thing being tracked. Tags are encased in plastic, paper, or some similar substance attached to the product or its packaging, a pallet or container, or even a van or delivery vehicle.
An RFID reader interrogates the tag by transmitting and receiving radio signals to and from it. Readers may vary in size from a small handheld device to a large “portal” through which many tagged objects can be carried simultaneously, for example, on a pallet. The reader’s information is compiled and processed using specialized computer software. For example, readers may be positioned throughout a plant or warehouse to indicate when products are moved, allowing continuous inventory management.
RFID Tagging
RFID tagging has various benefits over traditional stock management technologies such as barcodes:
- Tags can be read remotely, frequently from a distance of several meters.
- Multiple tags can be read simultaneously, allowing an entire pallet load of products to be checked concurrently.
- Tags can be assigned unique identification codes, allowing individual products to be tracked.
- Certain types of tags can be overwritten, allowing information about items to be updated, for example, when they are moved from one factory area to another.
RFID tagging may be used:
- To prevent over-or under-stocking of a product or component for stock security by placing tag readers at high-risk locations, such as exits and triggering alarms.
- For quality control purposes, primarily if you manufacture or store commodities with a short shelf life.
The prices of RFID tagging have decreased significantly in recent years and continue to do so, bringing the procedure within the grasp of an increasing number of organizations. In addition, the advantages of increased stock management and security make it especially appealing to retailers, wholesalers, and distributors who carry a diverse range of things and manufacturers that generate big runs of products for various consumers. Discover case studies of our successfully implemented solutions for a variety of business performance concerns for leading corporations worldwide.
SUMMARY
RFID tags are comprised of a small microprocessor and a small antenna that may store a variety of digital data about the thing being tracked. Tags are encased in plastic, paper, or some similar substance attached to a product or its packaging, a pallet or container, or even a van or delivery vehicle. An RFID reader interrogates the tag by transmitting and receiving radio signals to and from it.
Control the Quality of your Stock
Quality control is a critical component of stock control, all the more so when it comes to the safety of consumers and the completed product’s quality.
Effective stock control should combine both stock monitoring and batch tracking. This entails being able to track an item backward or forward from the source to the completed product and identify the batch’s other components.
Goods should be inspected for quality systematically, flaws found, and the afflicted batch weeded out. This enables you to address any issues with your supplier while also demonstrating the safety and quality of your goods.
This kind of tracking is pretty simple with an intelligent computerized stock management system. Additionally, manual stock management systems may use codes to streamline monitoring and make it simpler to trace specific batches.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology may be used to record information on the manufacture date of a product or component, ensuring that it is sold or processed on time. Additionally, the technology may be used to swiftly and effectively track down problematic items. Get in touch with us as Dynatuners offers a cutting-edge help desk solution for resolving all of your Microsoft Stack technical issues.
SUMMARY
Effective stock control should combine both stock monitoring and batch tracking. This entails being able to track an item backward or forwards from the source to the completed product. Goods should be inspected for quality systematically, flaws found, and afflicted batches weeded out.
At Instructor Brandon | Dynatuners, we always seek innovative methods to improve your competitiveness and suit your Microsoft Dynamics 365 requirements. Our offerings are founded on defined procedures, industry experience, and product understanding. If you’re interested in consulting with our specialists on how to effectively use direct deliveries to overcome stocking issues in your operations, don’t hesitate to Contact Us.
[sc_fs_multi_faq headline-0=”h2″ question-0=”What is D365’s direct delivery? ” answer-0=”Direct deliveries are those made straight from a vendor to a client. Direct deliveries shorten delivery times and save inventory costs, since you do not store the items in your warehouse before shipping them to the consumer. ” image-0=”” headline-1=”h2″ question-1=”What is the difference between direct and indirect delivery in routing?” answer-1=”The packet’s ultimate destination is a host linked to the same physical network as the deliverer in a direct delivery. In an indirect delivery, the packet travels from router to router until it reaches the one that is physically linked to the ultimate destination. ” image-1=”” headline-2=”h2″ question-2=”What are the various methods of forwarding? ” answer-2=”The three most often utilized forwarding strategies today are next-hop, network-specific, and default. The routing database for the next-hop approach contains simply the address of the next hop for each destination. ” image-2=”” count=”3″ html=”true” css_class=””]
 4418
4418