Microsoft Dynamics 365 Developer (F&S) Training Series, Supply Chain and Logistics Management
Minimize Duplicate Shipments on the same invoice through immediate posting in Dynamics 365

Invoicing Process | Sales Order | Invoice Account | Summary Order
What is Invoice?
An invoice is a document that the seller sends to the customer to collect payment. It comprises the cost of the goods or services bought by the customer. First, when you create an invoice, it contains the names of the seller and customer, the description and price of the products or services, and the conditions of payment, it may also be used as a legal document.
SUMMARY
An invoice is a payment request from the seller to the client. It includes the purchase price of the customer’s products and services. Documents including names of parties, product or service descriptions, prices and payment terms may be used as legal contracts.
Functions of invoices
To seek payment, businesses must send invoices. An invoice is a legally binding document that demonstrates both parties’ acceptance of the stated price and payment terms. Invoices, on the other hand, have additional advantages.
Keeping accurate records
The capacity to maintain a legal record of the transaction is the most significant advantage of an invoice. This allows you to determine when a product was sold, who purchased it, and who sold it.
Keep track of your payments
An invoice is a useful accounting tool. It makes it easier for both the vendor and the buyer to maintain track of their payments and outstanding balances.
Legal safeguards
A good invoice serves as legal evidence of a pricing agreement between the customer and supplier. It defends the merchant from false litigation.
Simple tax filing
All sale invoices must be recorded and maintained for the business to declare its revenue and pay the correct amount of taxes.
Business intelligence
Invoice analysis may assist companies in gaining insight into their customers’ purchasing habits and identifying trends, popular goods, peak buying periods, and more. This aids in the development of successful marketing tactics.
SUMMARY
This agreement shows both parties’ approval of the specified price and payment conditions. Undisputed price between client and supplier is legally documented by an invoice. Invoices also help businesses learn about their consumers’ buying patterns.
Duplicate Orders Overview
When supply constraints — owing to inadequate manufacturing capacity, unpredictable production yields, or supply chain faults – lead to intense distributor rivalry, order amplification occurs. The processes that lead to distributor order amplification may cause issues such as excessive manufacturing capital expenditure, inventory gluts, low-capacity utilization, and poor service, among others. When inventory is scarce, the manufacturer limits the distribution of available inventory to fulfill distributor orders, while distributors increase their orders to acquire more units. Customers have a significant influence on these dynamics as well. In certain instances, consumers may choose to place several orders with different distributors to improve the chances of receiving the goods. Customers cancel repeated orders to distributors and revert to prior ordering levels when supply eventually normalizes. As previously stated, such store ordering behavior may put pressure on manufacturers to make needless capacity expenditures, accumulate excess inventory, and suffer poor capacity utilization, all of which can result in significant financial losses.
SUMMARY
When supply constraints — owing to inadequate manufacturing capacity, unpredictable production yields, or supply chain faults — lead to intense distributor rivalry, order amplification occurs. This can cause issues such as excessive manufacturing capital expenditure, inventory gluts, low-capacity utilization, and poor service.
| 4 Billing KPIs You should be Measuring | |
| Claims denial rate by the payer | This is the percentage of total claims denied by each payer. Ideally, the denial rate for each payer should be below 5%-10%. |
| Net collection ratio | The net collections ratio is the percentage of total reimbursement collected out of the total allowed amount. This metric represents the efficiency of the revenue cycle and, thus, is the ultimate indicator of collections success. |
| Days in accounts receivable | This number indicates how long it takes to collect the money owed. Should not exceed 50 days. |
| First-pass acceptance rate | This is the percentage of claims that are paid after a practice submits them the first time. |
Issues with Duplicate Shipments
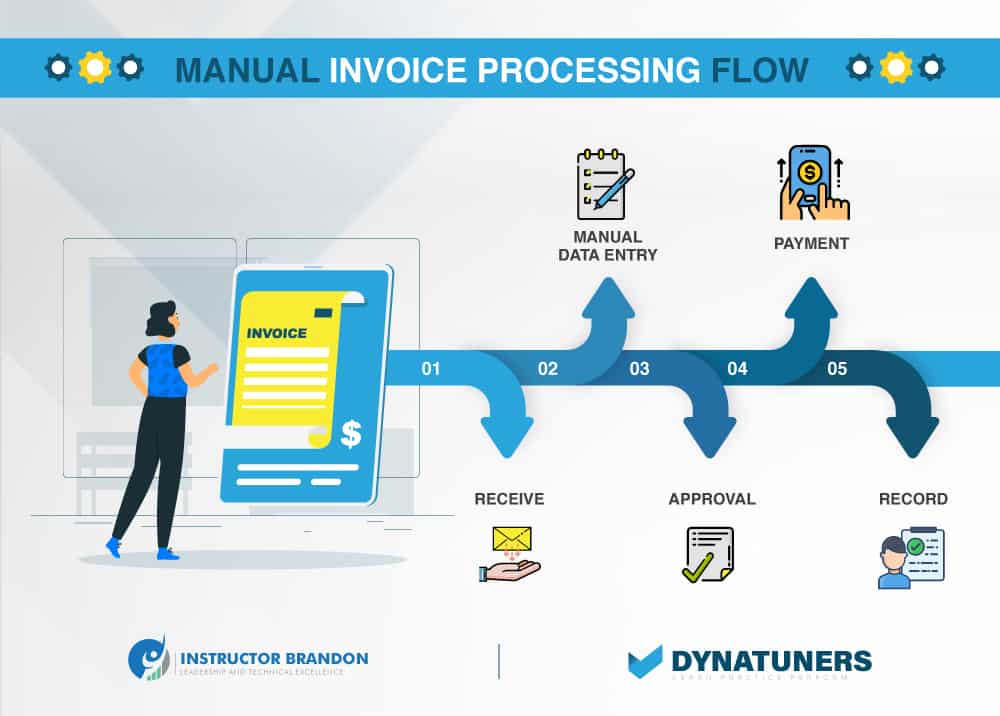
In today’s world, a typical medium-sized business loses a significant amount of money each year due to invoices that are paid twice. Most ERP systems attempt to avoid this by preventing you from entering the same invoice reference for the same vendor more than once.
What if the vendor appears in the master data twice, each with a slightly different name? Or did you make a mistake while inputting the invoice? Or does your program see a 7 as a 1?
For many businesses, this means you’re out of luck, and you may end yourself paying twice unless the accounting staff manually detects the duplicate invoice.
Inefficiencies in manufacturing occur when your company suffers or your staff does not work together as a unit. Improve the flow of information across the logistics chain, to eliminate human mistakes, and prevent repeated shipments. Ascertain that everyone in the team is aware of their duties and roles.
Want to learn something new? Read about load splitting shipments here.
SUMMARY
Every year, a typical medium-sized company loses money owing to double-paid bills. Most ERP systems try to avoid this by prohibiting duplicate invoice references for the same vendor, however this may backfire.
Shipping Audits
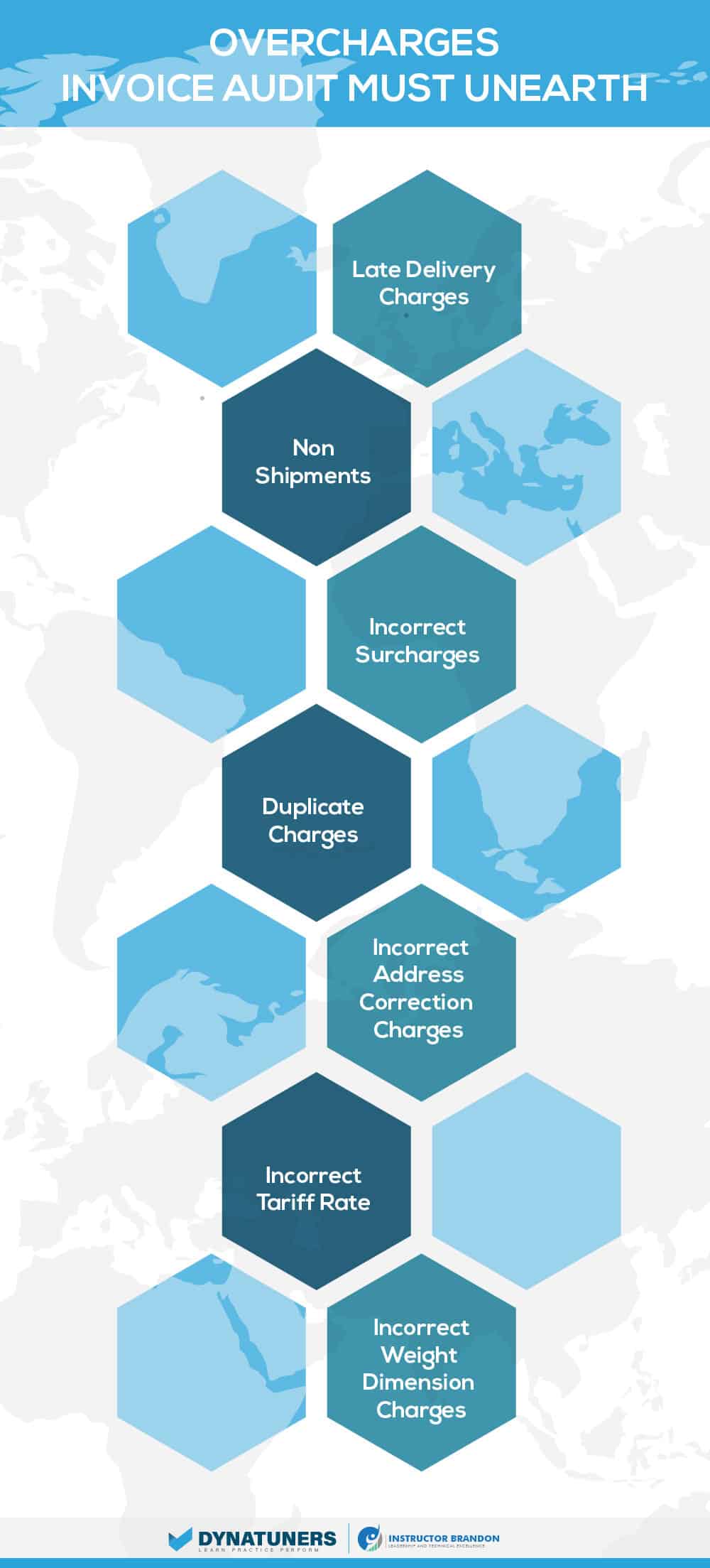
Because shipment mistakes are becoming more difficult to detect, shipping auditing services are essential. You’ll be amazed at how many mistakes appear right in front of your eyes. Late deliveries, invalid residential delivery costs, and inaccurate address rectification charges all contribute to them. Some shipments are manifested but never sent over the border. The dimensional weight may be off in certain cases. Other costs, such as duplication charges or delivery area fees, may apply. Such mistakes may be discovered via a shipment audit.
These mistakes may add up to a lot of money over time. As a result, invoices must be thoroughly examined. Pre or post-delivery shipping audits are possible. The objective is to guarantee that no duplicate or incorrect billing occurs. According to studies, businesses that do thorough audits save a considerable amount of money on shipping expenses. As a result of these best practices, any company, large or small, would be wise to spend time in shipping audits. Manually doing shipping audits takes a long time. However, many providers provide a one-of-a-kind solution that tracks and audits all service failures using a fully automated approach. As a consequence, your freight expenses will be lower and your shipment efficiency will increase.
What is a purchase order? Purchase orders are one of the most effective safeguards against double payments. The ability to connect payments to particular suppliers is a crucial control function of purchase orders. Seek our experts help to streamline your business processes.
SUMMARY
Thorough audits save businesses a lot on shipping costs. Late deliveries, incorrect residential delivery fees, and incorrect address correction charges all contribute. Manually auditing shipment takes time; several companies provide unique solutions.
Purchase Order Entry Errors Cause Duplicate Payments
Many businesses have experienced repeated payments as a result of invoices that were not linked to a purchase order. Because the PO was not connected to the invoice to give the required control in certain instances, the ERP system was unable to prevent repeated payments. If such problems occur regularly, the business faces an unsettling scenario.
SUMMARY
Invoices without a purchase order have caused recurring payments for several companies. This is because the PO was not linked to the invoice in certain cases. If such issues arise often, the company is in jeopardy.
What are the main causes of invoice duplication?
There is a plethora of automated payment and invoice distribution methods available today, which adds to the complexity and the possibility of problems:
- Various invoice receipt and payment methods, including outsourcing.
- Mergers, acquisitions, or siloed business processes that enable experts from different accounts payable (AP) departments to make payments without the use of strict controls to prevent duplication.
- Unethical workers or suppliers take advantage of greater possibilities to conceal repeated payments to benefit themselves at the cost of the company.
When a payer attempts to submit an invoice with the same business, vendor number, invoice number, invoice date, and dollar amount as a previously paid invoice, most enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems alert them. Unfortunately, if any of these five fields differ slightly, most ERP systems will fail to detect duplicates and will enable invoices to be submitted and paid.
The following are a few examples of frequent invoice duplication errors:
Errors in data input
Keying mistakes may be caused by a variety of factors. In most instances, the inaccuracies are the result of accidental data-entry errors made when entering hundreds of invoices each day—AP processors dealing with such a high number of invoices may quickly lose focus or get overwhelmed due to a lack of resources. The following are the most frequent keying mistakes:
- Making a blunder with a number or letter (for example 0 instead of O, or 5 instead of S)
- Number transposition (for example 56 instead of 65)
- Leaving out leading and trailing zeroes
In other instances, deliberate mistakes are created when an AP processor circumvents financial system restrictions by adding extra letters or digits to an invoice number to push an invoice into the system.
Duplicate payments may also occur as a consequence of the widespread use of Automated Clearing House (ACH) payments and the shifting of payment responsibilities away from AP departments. For most businesses, AP processors must adhere to the same procedures and standards as regular payables processing; nevertheless, this is often overlooked, resulting in repeated payments.
Duplicate vendors
Duplicate payments are most often caused by duplicate suppliers in an ERP system. Duplicates in the vendor master file are likely to arise despite extensive human efforts. When a vendor invoice is an input into an ERP system, for example, if a different vendor code is chosen, a duplicate invoice will be created. This new vendor code is the same vendor with the same or potentially different bank information; thus, any duplicate checking options will be disabled.
Requests for manual checks
Manual check generation may sometimes result in duplicate payments. Most businesses do not use numbered forms; instead, check processors produce an invoice number, which may lead to duplicate invoice numbers.
Using various source documents to pay
A duplicate payment usually often happens when two distinct source papers are filed for a single payment. When this occurs, one of the source papers for the same transaction, such as a statement or quote, is typically in a different format from the other source documents.
When duplicate bills are issued through other means, such as fax or email, double payments may occur. These repeated invoices are often sent to the payer as a reminder that the vendor has not yet been paid.
When a vendor fails to submit the correct purchase order number on an invoice, double payments may occur. When this occurs, the invoice is usually delayed in being entered into the ERP system owing to the time it takes to find the proper purchase order number. However, if the vendor has not yet been paid, he or she may provide a duplicate of the identical invoice, but this time with the purchase order number. It’s conceivable that both bills will be processed and paid in this scenario.
Invoices and reimbursements for travel and expenses
Some workers may seek reimbursement by submitting invoices for payment after filing an expense report (after paying with cash or a personal credit card). Because the cash amounts are typically modest, this kind of fraudulent behavior is difficult to monitor and manage manually.
While AP processors take shortcuts when generating vendor information, duplication may arise. External actions like mergers, acquisitions, and incoming connections from older systems may also result in duplicate suppliers.
SUMMARY
Most ERP systems fail to identify duplicates when a payer submits an invoice with the identical business, vendor, invoice number, and dollar amount. Data entry errors may occur while inputting hundreds of invoices each day. To enter an invoice into the system, an AP processor adds additional letters or digits to the invoice number. It occurs when two different source documents are submitted for a single payment. Duplicate vendors in an ERP system usually generate duplicate payments.
Invoice issues such as double paid invoices arise when vendors fail to provide the proper purchase order number. Workers may submit invoices for payment after completing an expense report. To read more on our blogs, click here.
Make a note of the vendor’s invoice and compare it to the quantity received
When you get an invoice from a vendor for products or services purchased on a purchase order, your business procedures may demand that you receive the goods or services before the invoice can be authorized for payment. Having the ability to change the invoice quantity allows you to rectify mistakes that prohibit you from publishing. Because posting errors may necessitate resubmitting the invoice to process, the ability to avoid posting errors saves time and effort for submitters and approvers.
SUMMARY
Being able to modify the invoice quantity enables you to correct errors that prevent you from publishing. This saves time and effort for submitters and approvers since posting mistakes may require resubmitting the invoice for processing. Avoiding posting mistakes saves time and work when it comes to submitting and reviewing invoices.
Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Match Vendor invoice against received quantity
When you receive an invoice from a vendor for goods or services on a purchase order, the business processes might require that the goods or services be received before the invoice can be approved for payment.
Scenario:
We will be using the PO-> 00000277: DE – T_S
Step 1
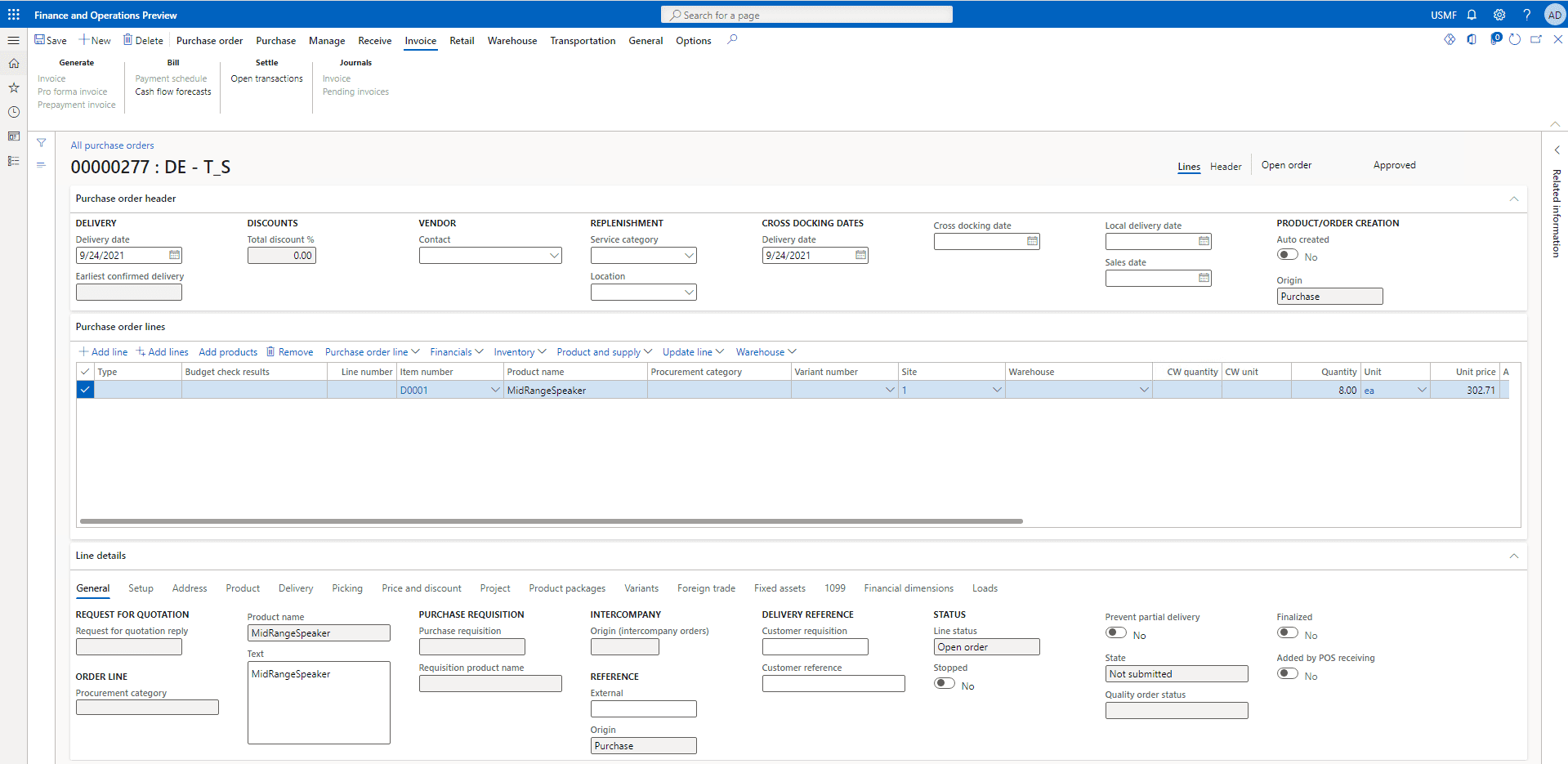
From the navigation pane head over to Accounts payable and then go to Purchase order menu and then to All purchase orders sub-menu.
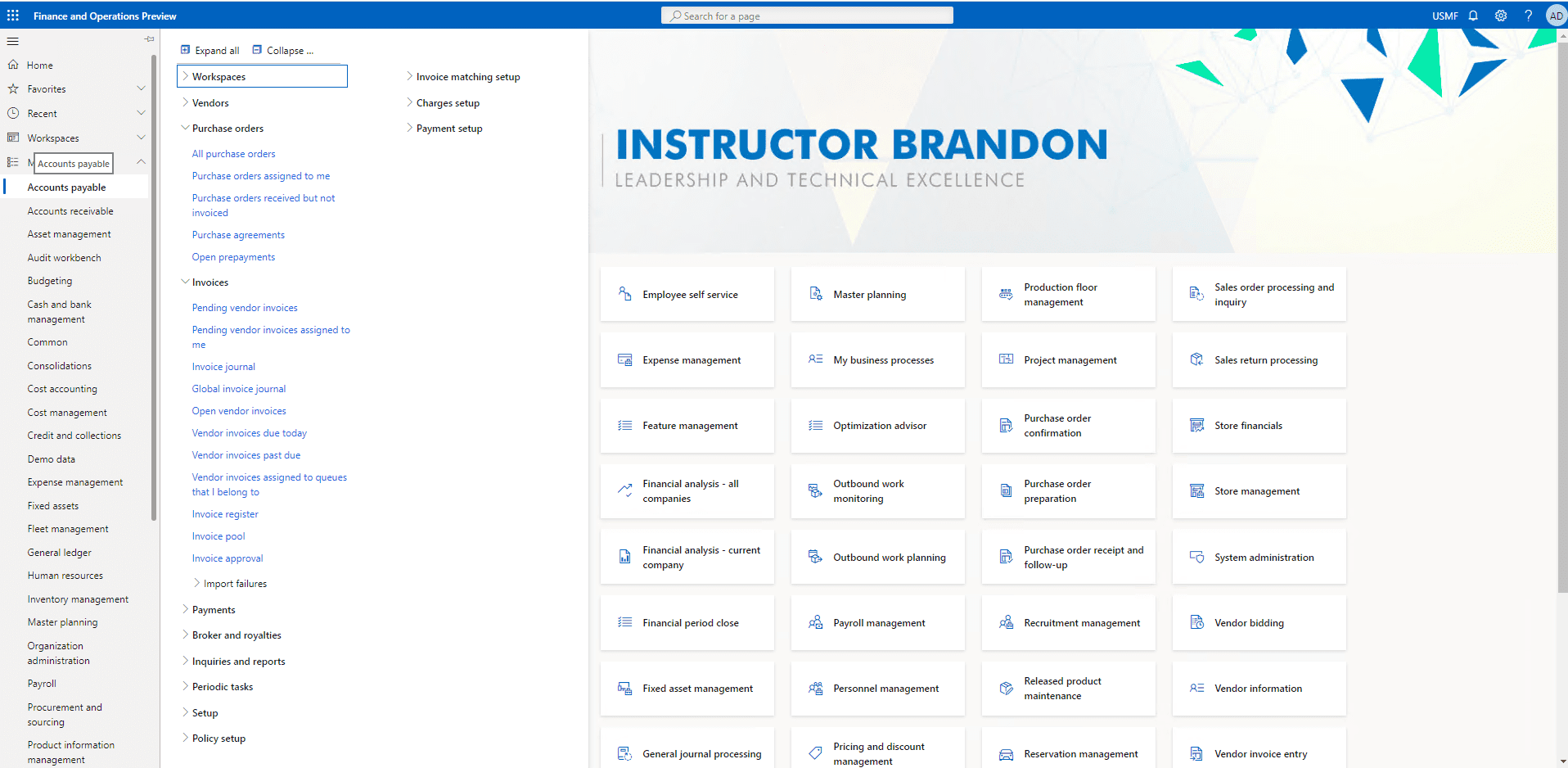
Step 2
Go to our purchase order: 00000277 and open it.
Step 3
Click on Add lines and select the item number D0001 from the drop-down and click enter. Then change the Quantity to 8 items and also set the warehouses to 11 from the dropdown and hit enter.
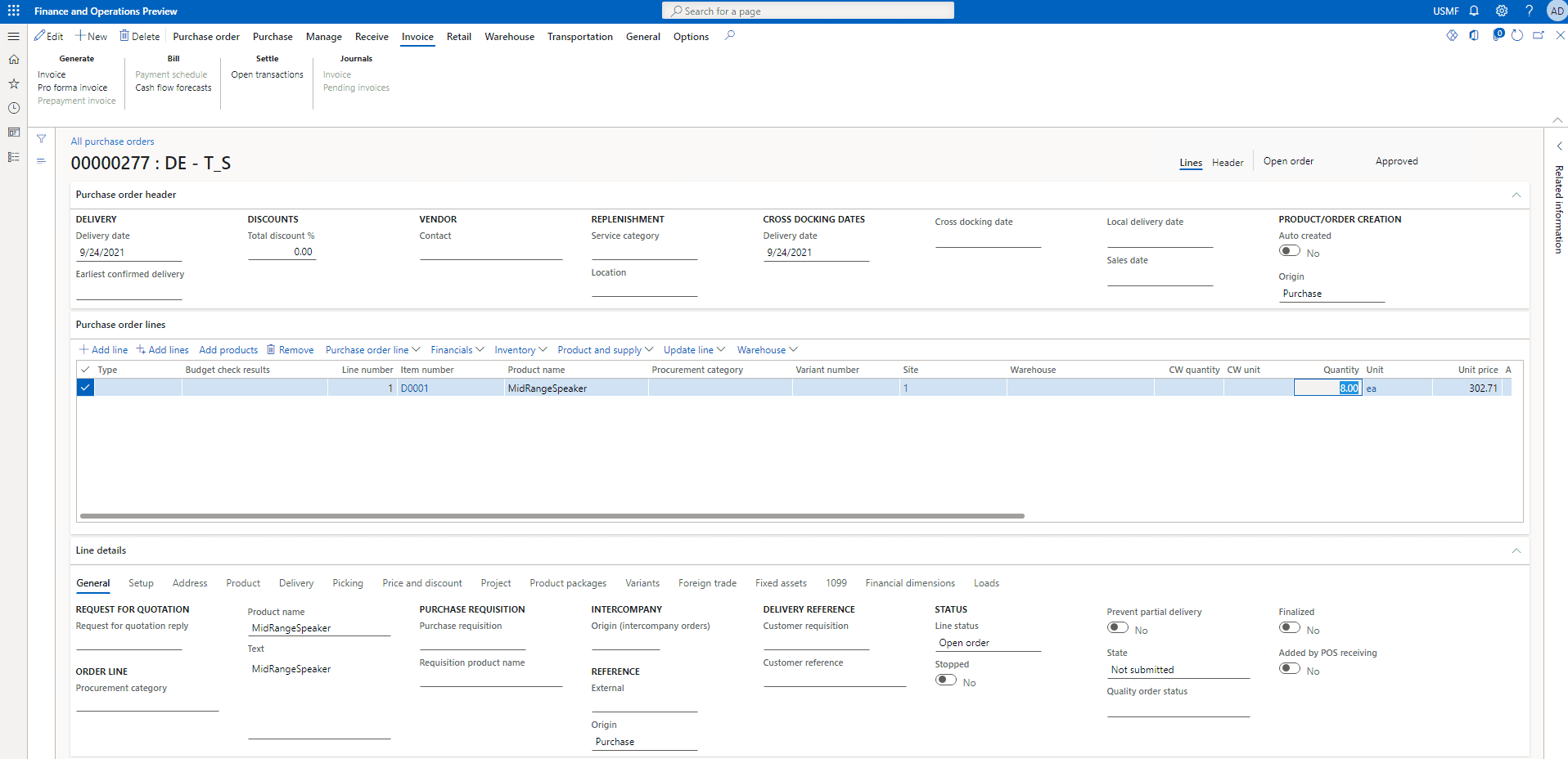
Step 4
Go to the Purchase tab and click on Confirm under the Actions tab to confirm the purchase order.
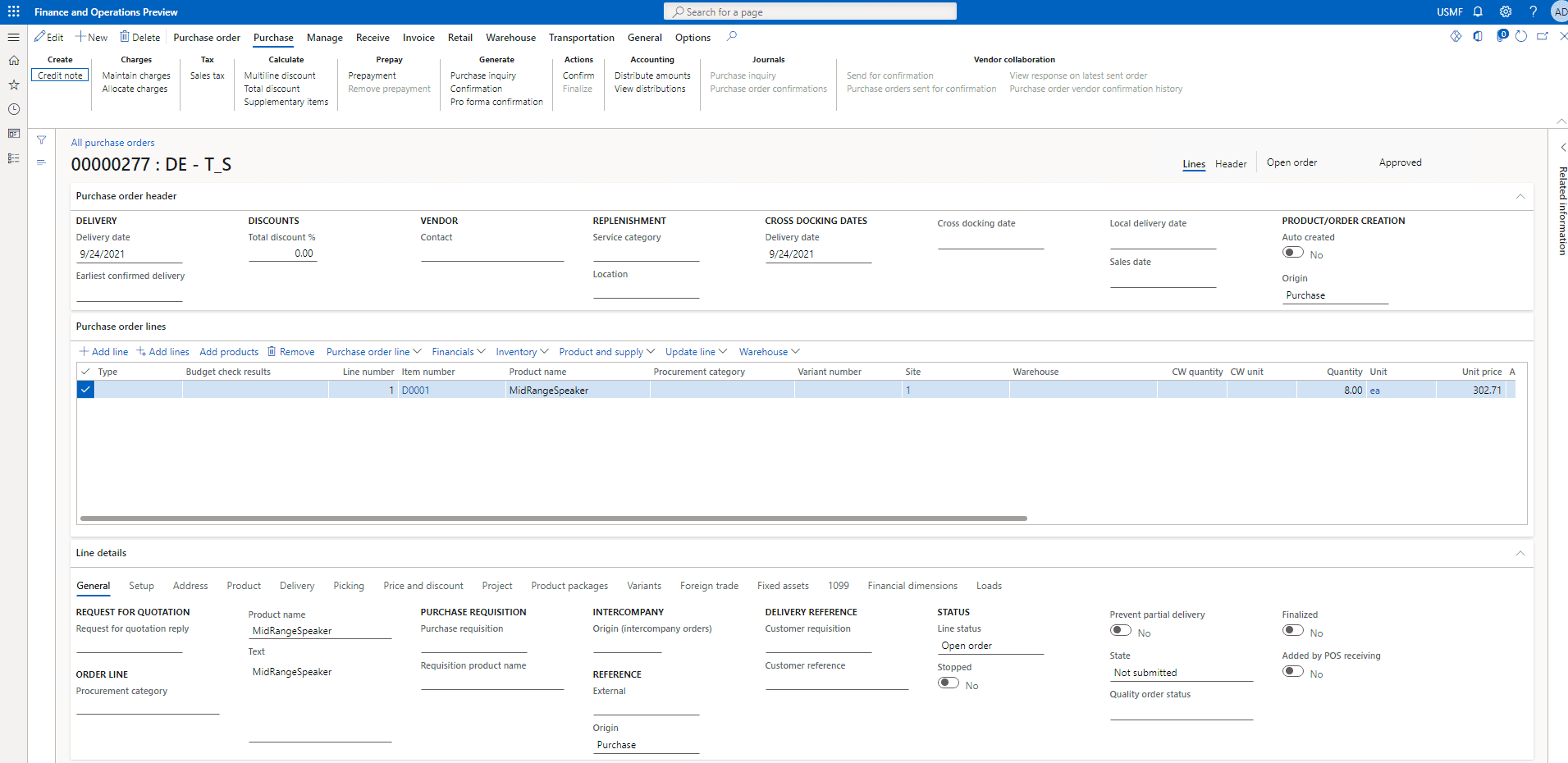
The process of confirming the PO is running and looks like this
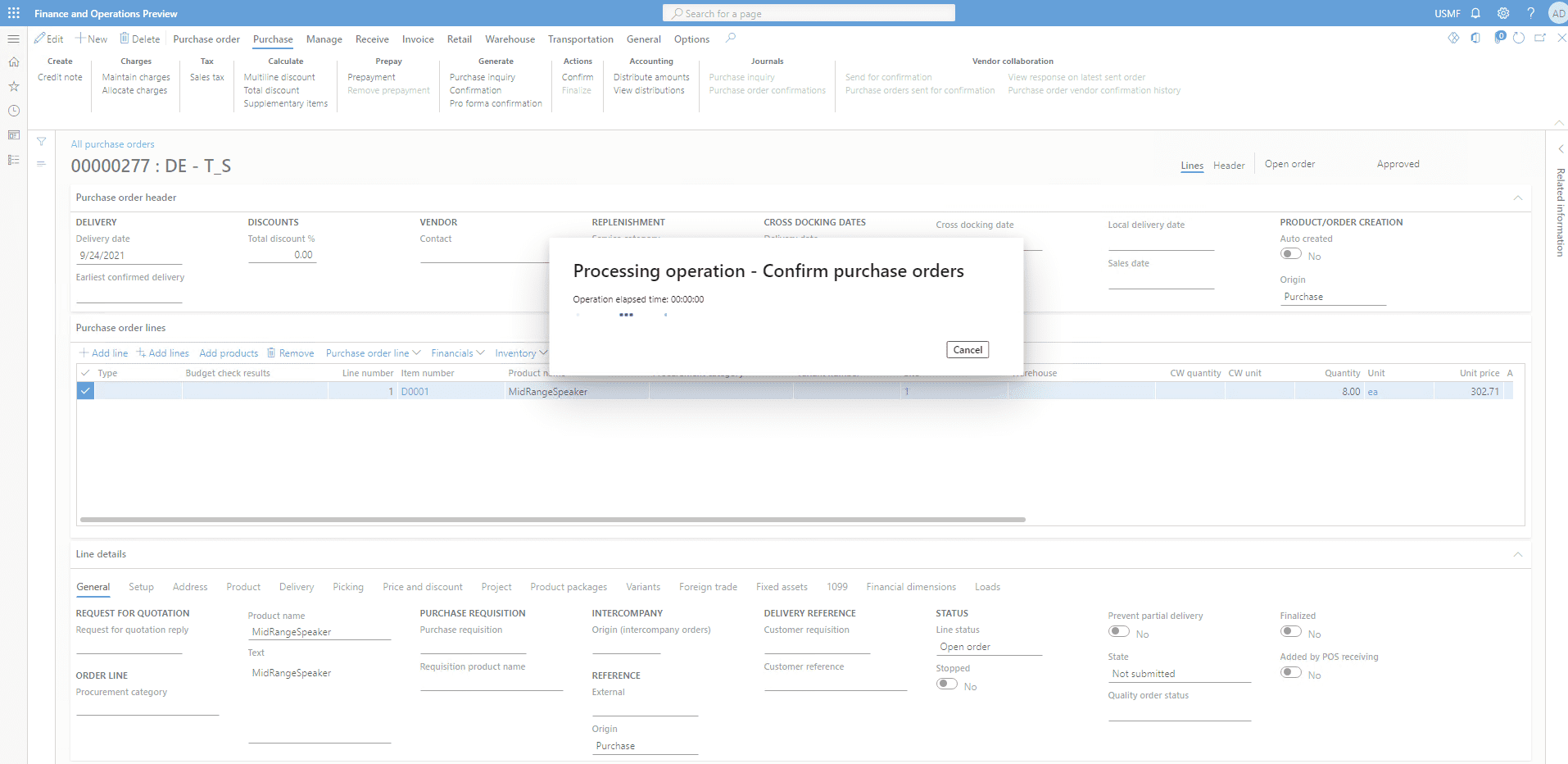
Step 5
Once the order has been confirmed On the Action Pane, click Receive and then Click on Product receipt.
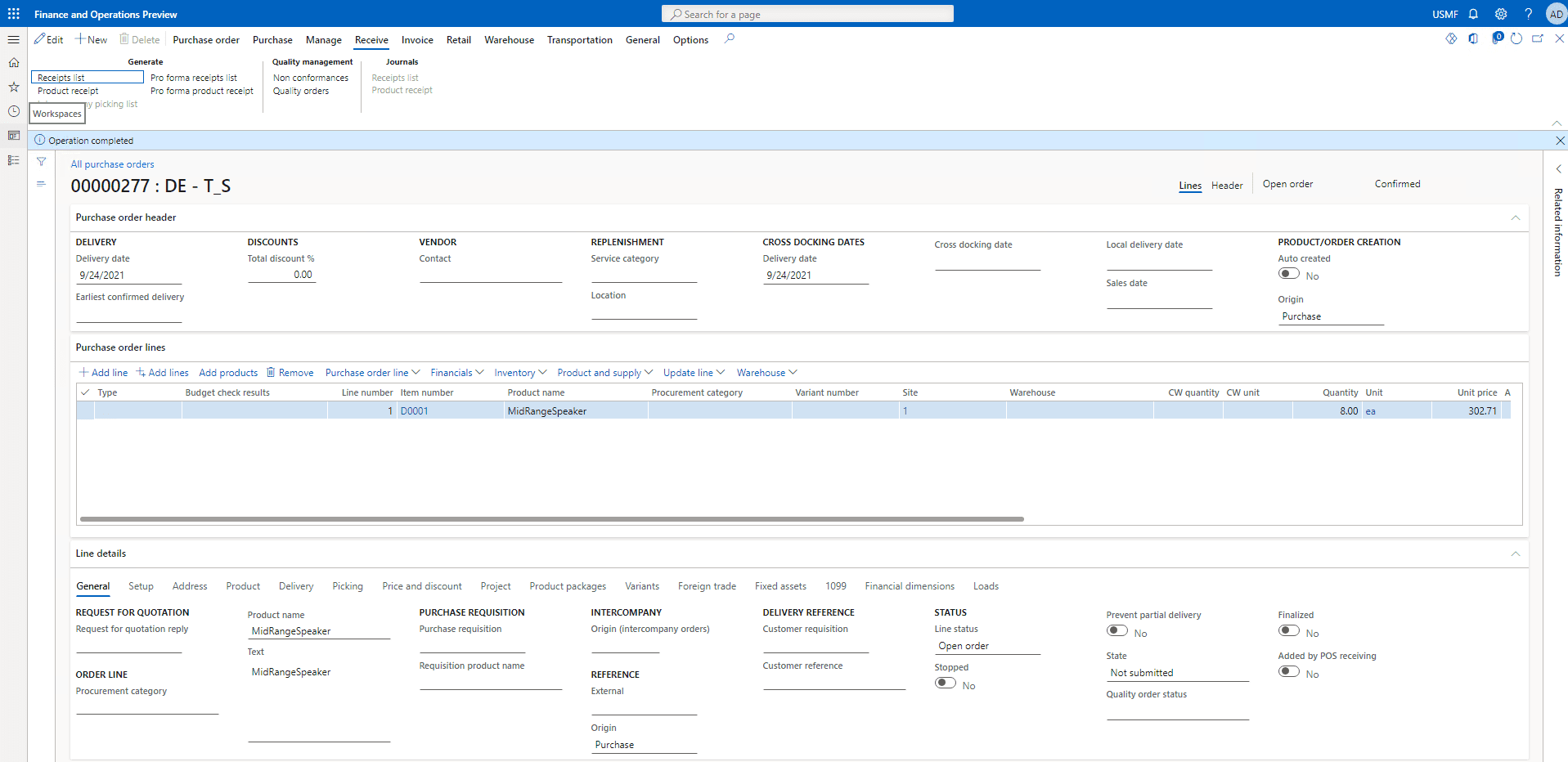
Step 6
Enter a Product Receipt 4567 and click on OK
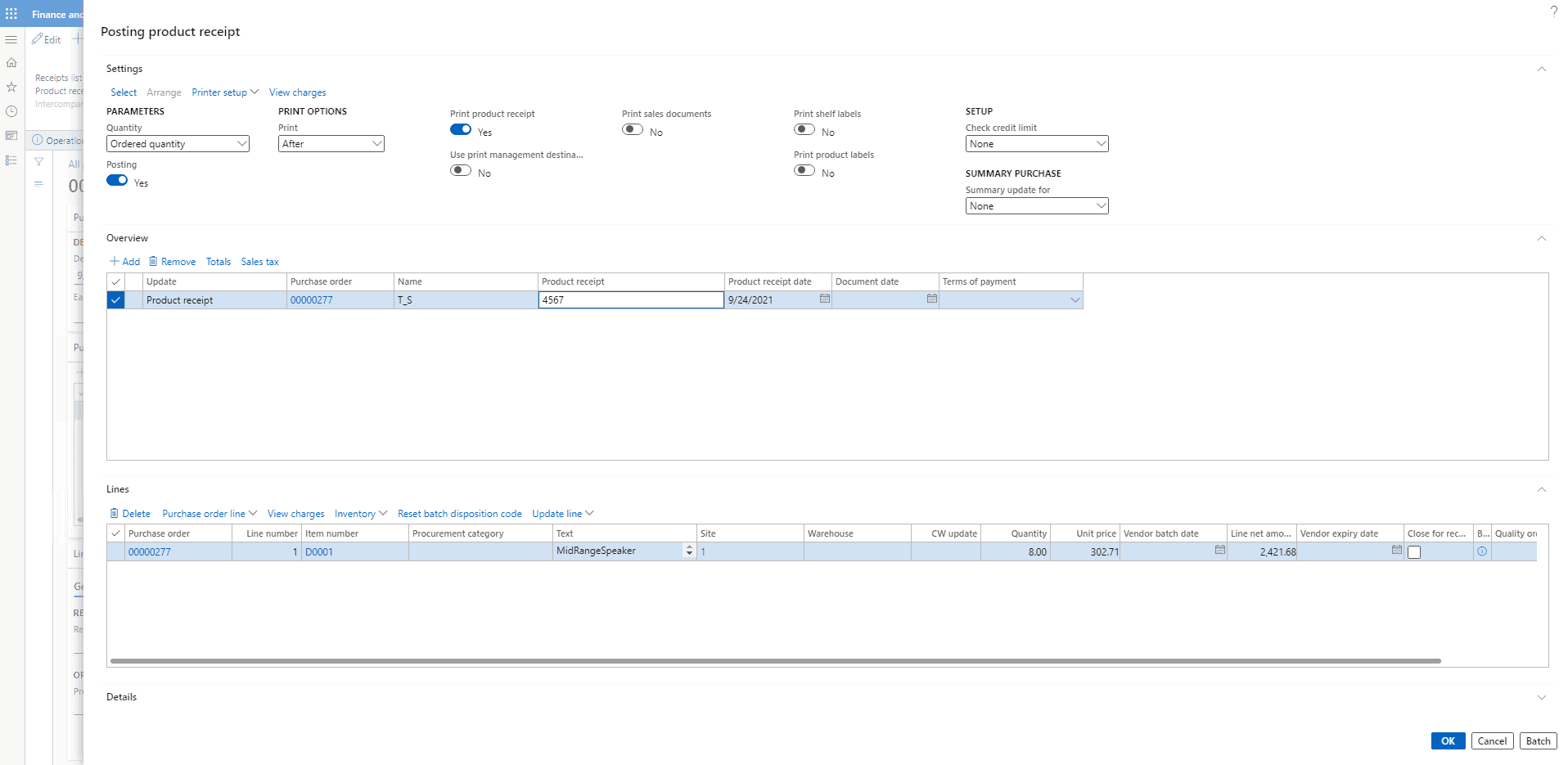
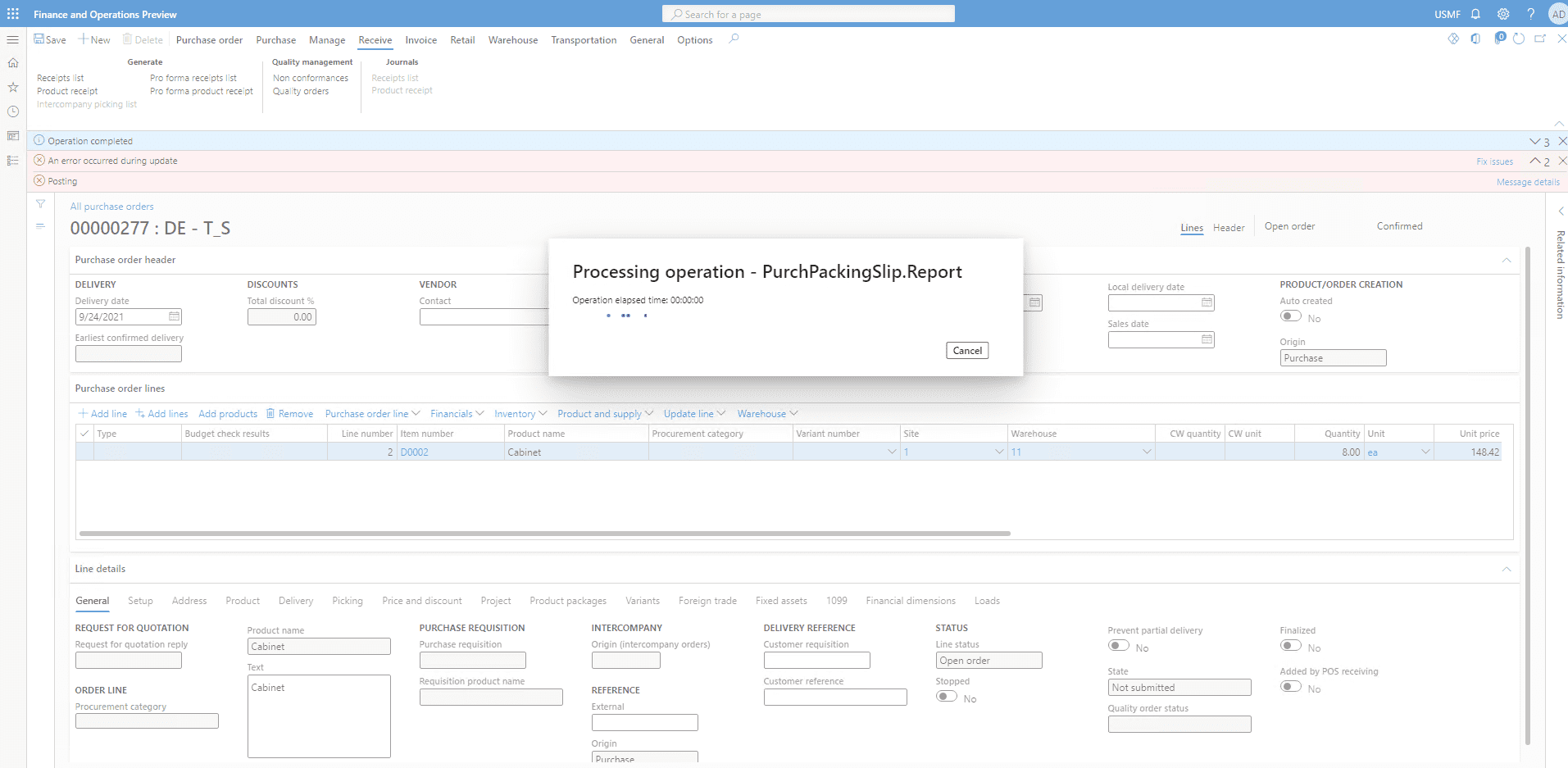
The generated product receipt looks like shown below.
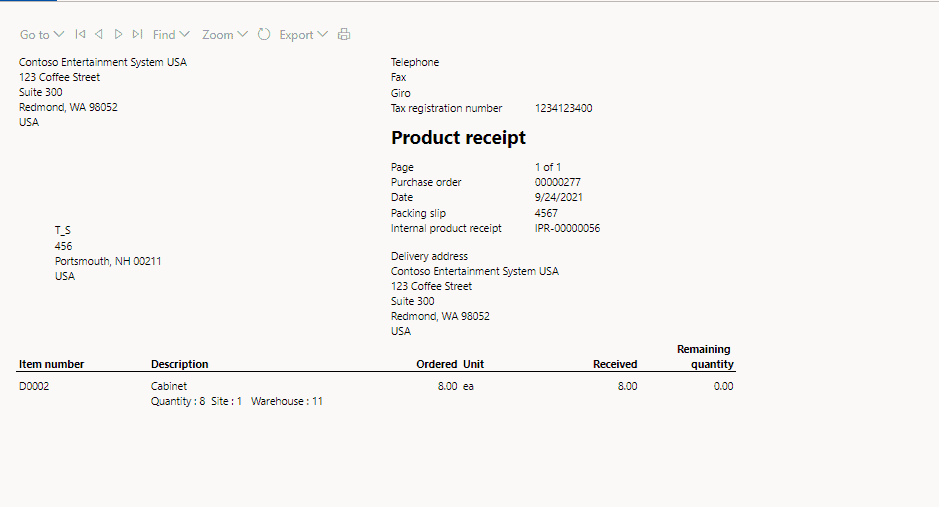
Step 7
Now click on the Invoice tab and then go to Invoice under Generate.
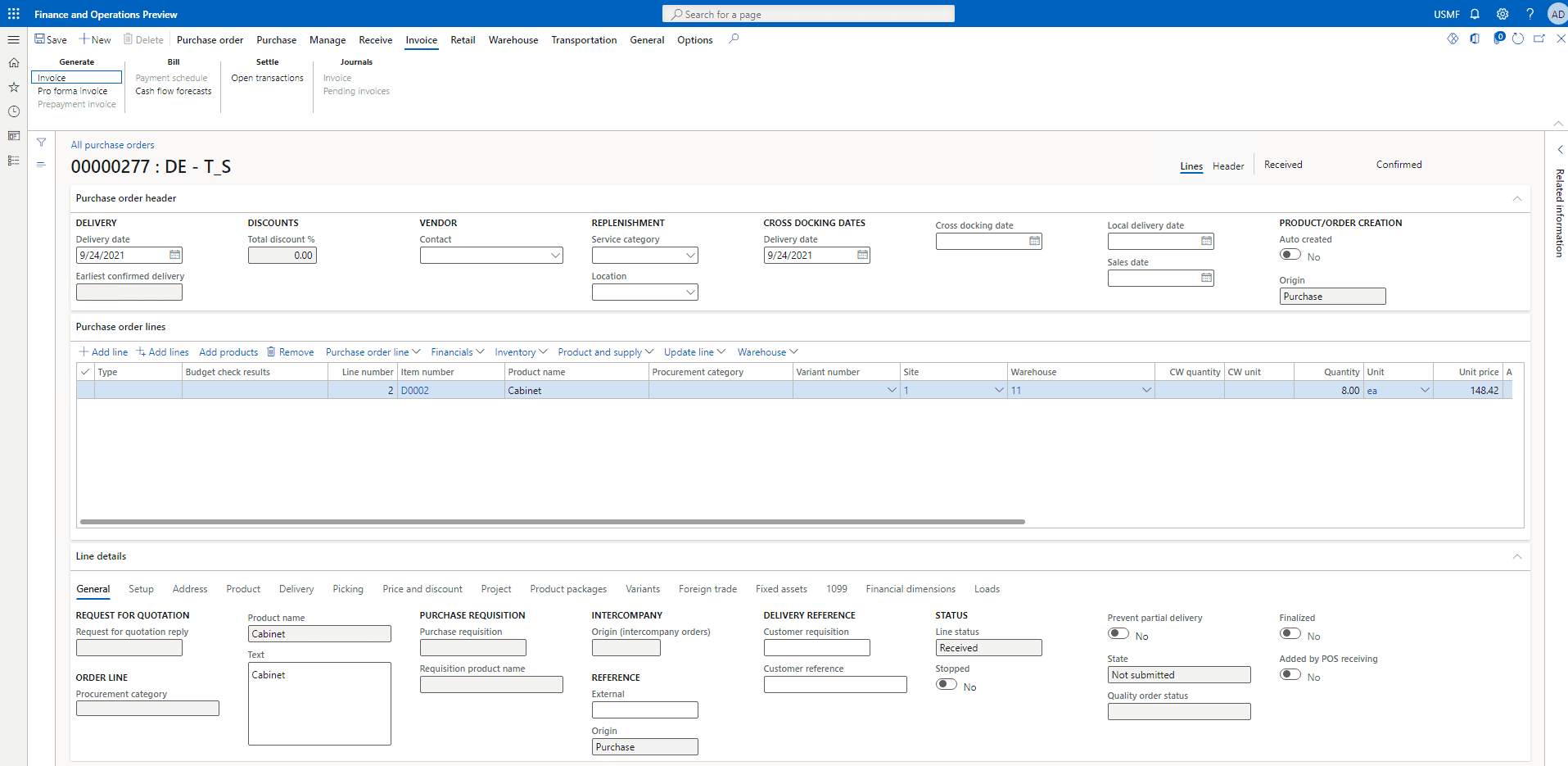
Step 8
Input a number in the Number field as 345
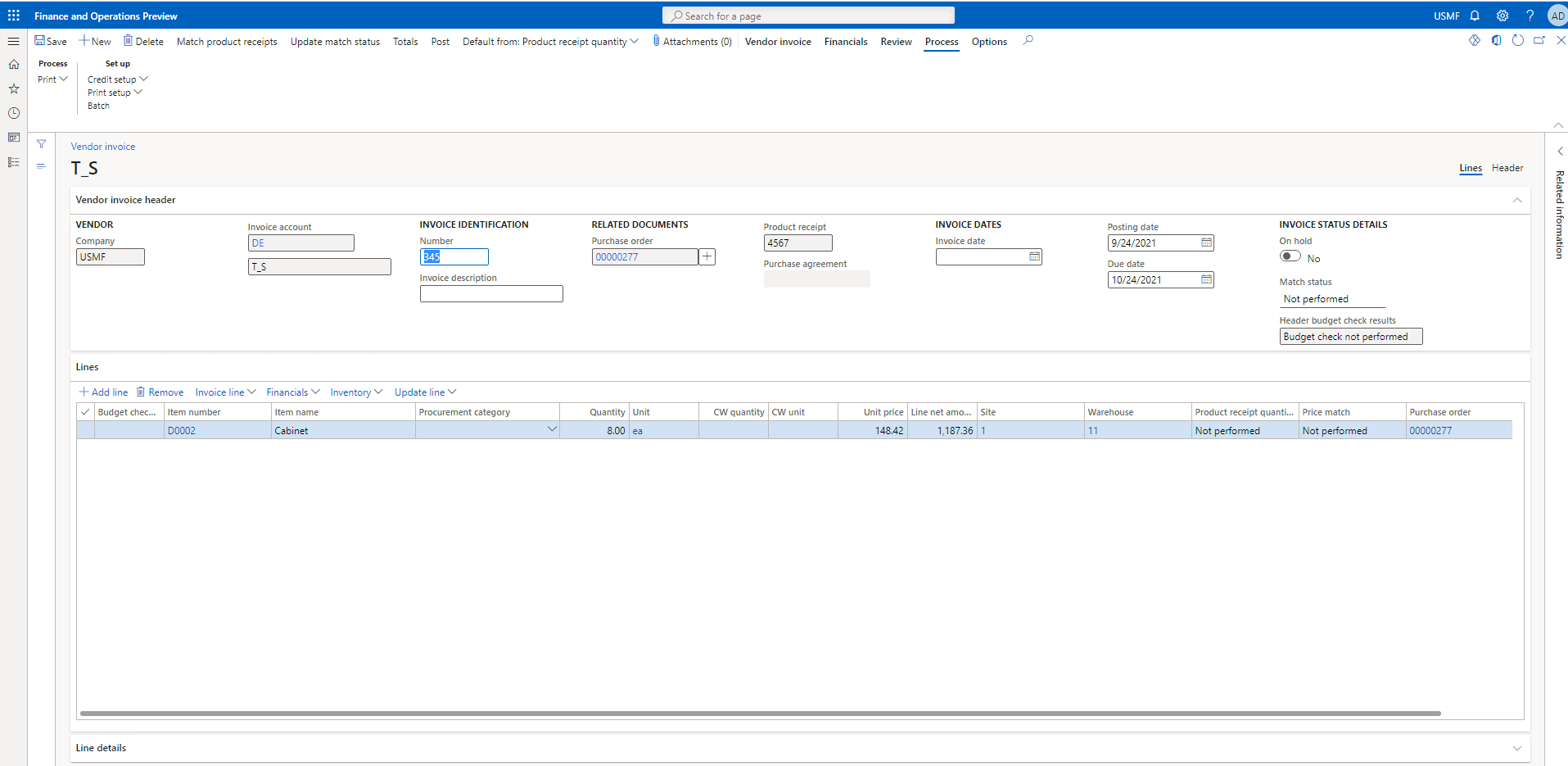
Step 9
Once that is done from the top click on Default from Product receipt quantity and select Ordered Quantity from the list.
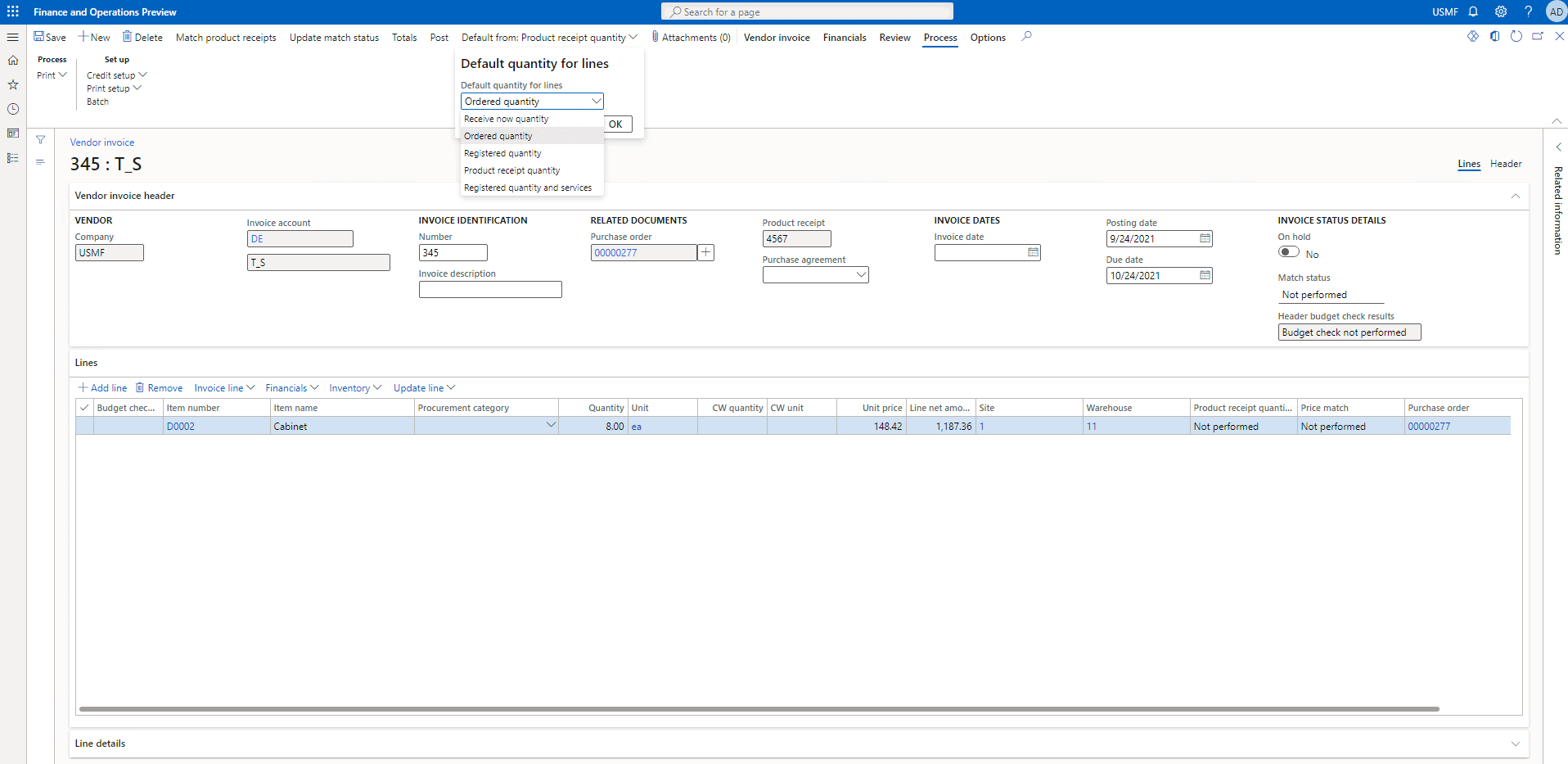
Step 10
Now click on Match product receipts.
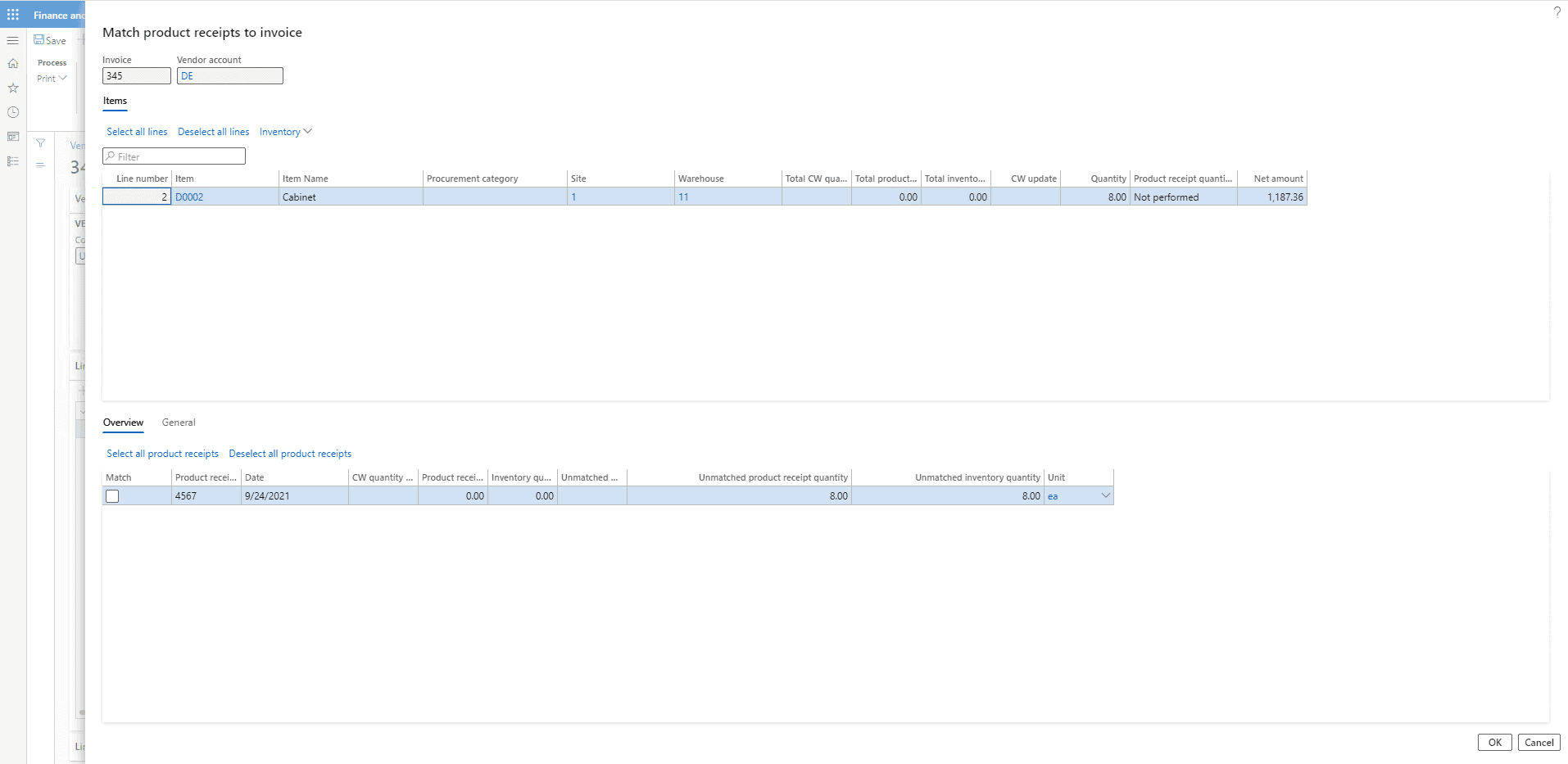
Then click on OK.
Now click on Review and then click on Matching details
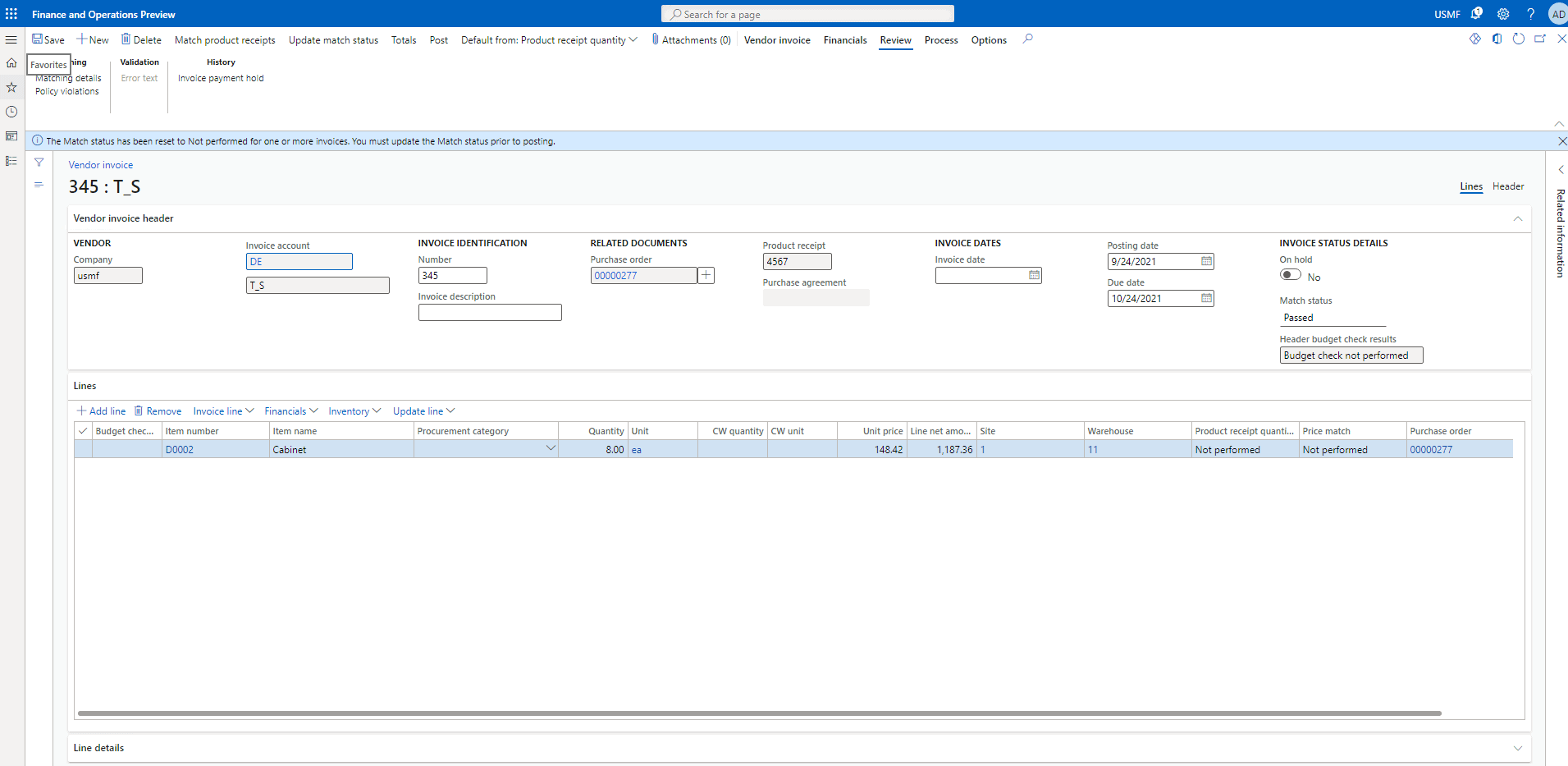
Here are the details for the invoice matching.
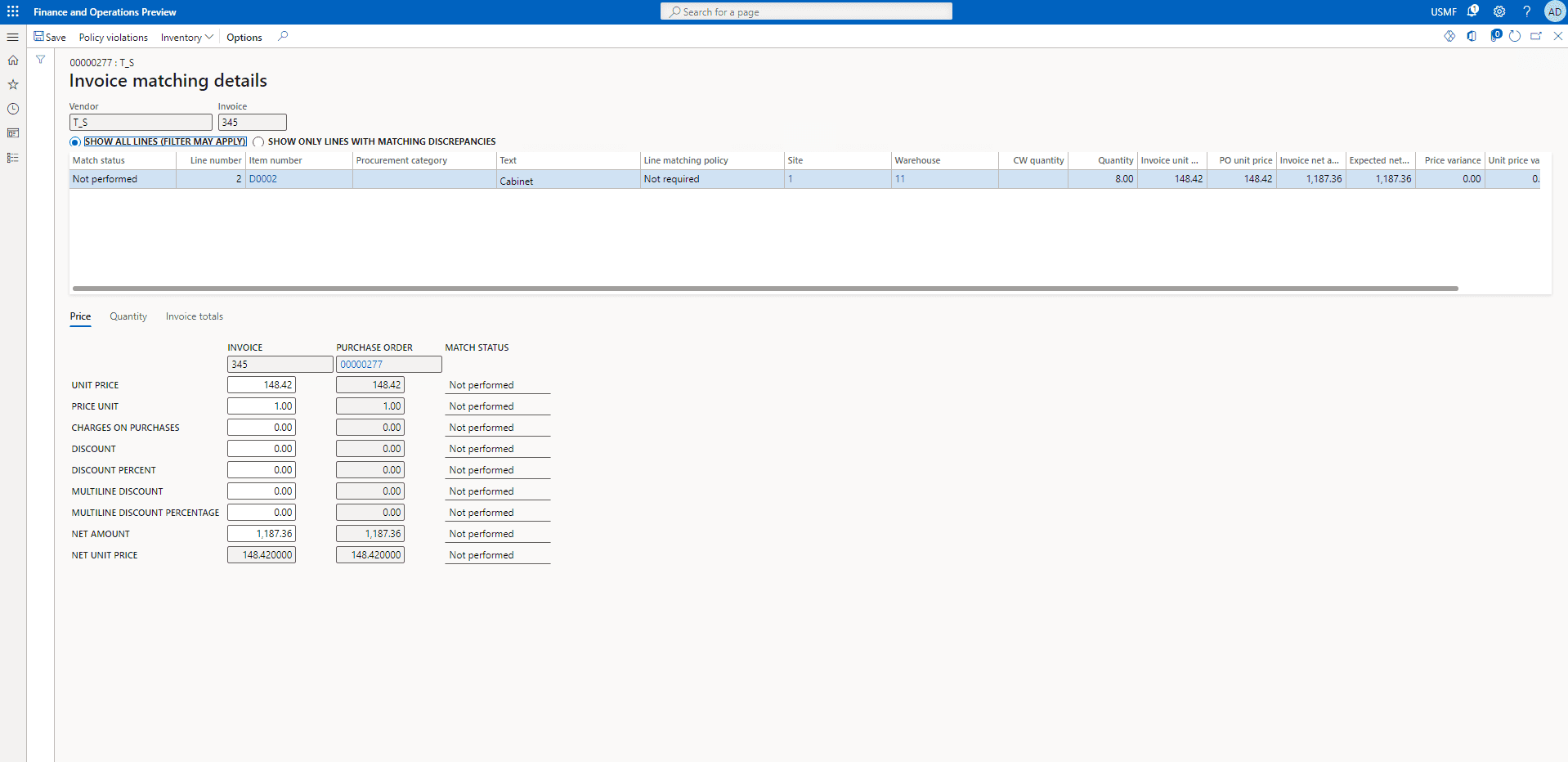
SUMMARY
Follow the above steps to Review and then Match details.
Want to get a real-world hands-on learning experience through our custom-designed courses? Enroll now.
Simple ways to cut down on repeated payments
Following are some managerial best practices to follow:
- Conduct regular reviews of vendor master files.
- Restrict manual check requests to situations in which there is no genuine invoice. Forms for check requests may still be filled out and submitted numerous times. End users should be taught not to submit the same check request more than once. Use automated invoice processing.
- Create a uniform invoice numbering policy for the whole business. When an invoice number already exists, this policy should provide clear standards for entering it, as well as capitalization and punctuation requirements. You should try to enforce the policy as much as feasible inside your financial system. The policy should also specify how an invoice number is created if one does not already exist.
- Adopt a vendor payment policy that requires an official invoice with a reference to an order schedule or contract number, as well as an invoice number.
- Use continuous monitoring technology to look for duplicate invoices before a check run is processed.
SUMMARY
Managers should examine vendor master files on a regular basis. Create an invoice numbering policy that applies to the whole company. Before a check is completed, use continuous monitoring technologies to search for duplicate invoices. Adopt a vendor payment policy that necessitates the submission of an official invoice referencing an order schedule or contract number.
Tips to Prevent Duplicate Payments using Purchase Orders
The following pointers will assist businesses in avoiding repeated payments by properly utilizing Purchase Orders.
- Instead of blanket Purchase Orders, use itemized Purchase Orders.
- In addition to other pertinent information, ensure that Purchase Orders contain the following
- Item Description
- Number of Items
- Quantity
- Unit Cost
As many invoices as feasible should be linked to Purchase Orders. The ERP system is unable to avoid duplicate invoices when invoices are not connected to Purchase Orders. Duplicate invoice payments happen a lot more than most companies realize. On average, around 0.1 percent to 0.05 percent of invoices paid are duplicate payments, which may result in a $300,000 loss for a medium-sized company with yearly expenditures of $100 million over three years. Many duplicate invoice payments are detected when high-integrity vendors discover the error, while many others require costly recovery audits and/or time-consuming manual procedures. Many of them go unnoticed or unresolved. “64 percent of companies still depend mainly on manual control testing to identify control breaches such as duplicate invoice payments,” according to a 2012 KPMG survey.
SUMMARY
Duplicate payments account for up to 0.05 percent of invoice payments, resulting in a $300,000 loss for a medium-sized business. When high-integrity suppliers find the mistake, they notice a large number of duplicate invoice payments. Others require time-consuming manual processes and/or expensive recovery audits.
Duplicate detection rules in Dynamics 365
If your company uses Dynamics 365, you’ll almost certainly run across duplicate entries or out-of-date data that has to be handled at some time. To begin, it’s essential to remember that just because you’ve put up duplicate detection criteria to limit the number of duplicate entries in your CRM doesn’t mean they can’t be created. As a result, once you’ve set up your duplicate detection criteria, it’s a good idea to set up frequent routines to assist you to identify duplicates before reviewing and removing them from your CRM.
SUMMARY
If your company uses Dynamics 365, you’ll almost certainly run across duplicate entries or out-of-date data. Just because you’ve put up duplicate detection criteria doesn’t mean they can’t be created. It’s a good idea to set up frequent routines to assist you to identify duplicates.
At Instructor Brandon | Dynatuners, we always seek innovative methods to improve your competitiveness and suit your Microsoft Dynamics 365 requirements. Our offerings are founded on defined procedures, industry experience, and product understanding. If you’re interested to consult with our specialists on how to eliminate invoicing issues, don’t hesitate to Contact Us.
[sc_fs_multi_faq headline-0=”h2″ question-0=”What does it mean to have multiple orders?” answer-0=”Duplicate medication orders (duplicates) were defined as two or more active orders for the same medicine, regardless of dose, for the purposes of the study. The duplicate order was assigned to the second order entered. ” image-0=”” headline-1=”h2″ question-1=”How do you keep duplicate orders at bay? ” answer-1=”The following pointers will assist organisations in avoiding multiple payments by properly using Purchase Orders. Instead of blanket Purchase Orders, use itemized Purchase Orders. You can also use Item Description to guarantee that Purchase Orders include the following, in addition to other important information. Number of items, quantity, and price per unit. ” image-1=”” headline-2=”h2″ question-2=”Is it possible to have numerous invoices on a sales order?” answer-2=”Yes, there is a possibility. If you have a number of un-invoiced sales orders, you can combine them into a single invoice. Prerequisite: All invoiced sales orders must be associated with the same customer, and all invoiced sales orders must be in the Confirmed status. ” image-2=”” count=”3″ html=”true” css_class=””]
 2629
2629