Dynamics 365 Tutorials, Supply Chain and Logistics Management
Reducing the Impact of Backorders on Incoming Shipment Warehousing Discrepancies in Dynamics 365

Warehousing Discrepancies: Backorders and Incoming Shipments
Cross Docking | Batch Size | Warehouse Process | Demand Variability | Warehousing and Distribution | Backorders
Effective inventory management requires striking a balance between minimizing the expenses associated with excess inventory stock and maintaining sufficient inventory to satisfy customer demand.
Stock outs often result in lost sales and customer unhappiness, but what if a client order cannot be completed quickly but the buyer is willing to wait? Alternatively, you may send a portion of a big order to consumers who want to get available in-stock goods and are willing to wait for the remainder of the stock to arrive.
What is a Backorder?
What does backorder mean or what is a back order are the frequently asked questions in supply chain. A backorder happens when a client places an order for an item that your supplier does not now have or that your manufacturer has not yet manufactured. While this sounds similar to a stock out, there is a subtle distinction. A stock out occurs when an item is not available in your inventory. This may indicate that an item is not in stock at a company’s warehouse.
However, when an item is on backorder, it indicates that your supplier does not have it in stock. They must contact their manufacturer for more parts, resulting in even longer wait times. If you get your products straight from the manufacturer, backorder processing takes longer since the manufacturer must create additional inventory.
SUMMARY
Backorder meaning is similar to a stock out, but indicates that an item is not available in your inventory. A company’s warehouse may have an order for an item that their supplier does not have. Backorders also mean that the manufacturer must create additional inventory.
Backorders vs. Out of Stock
When a vendor does not have the item in stock and has no set date for restocking, or when the item is seasonal or limited edition, the item is considered out of stock. Backordered goods are anticipated to arrive within a reasonable amount of time.
SUMMARY
When a vendor does not have an item in stock and has no set date for restocking, or when the item is seasonal or limited edition, it is considered out of stock. Backordered goods are anticipated to arrive within a reasonable amount of time; expect them to take several weeks to arrive.
Are you ready to take your next step in career? Find all our courses here.
What is an Inventory Backorder?
When a client puts an order or makes a purchase for inventory that is not yet available, this is referred to as an inventory backorder. Backorders may arise when goods sell out due to unexpectedly strong demand and all of your safety stock has been sold. Customers may even be delighted to shop for your goods knowing that you are out of stock – for certain companies, backorders are regarded as a guarantee of sales, especially if you have a dedicated client base prepared to wait for your products. However, there is no assurance that consumers would not cancel purchases, leaving your company with the stock bought to fulfil these backorders. If prepayment is made prior to the order being completed and the supplier is unable to satisfy the order or additional delays occur, you risk the time and cost associated with refunding funds.
This may have a detrimental effect on your company via client discontent and poor word-of-mouth. The proportion of goods on backorder and the number of days on backorder are critical indicators of your company’s inventory management efficacy and customer service success.
SUMMARY
Backorders may arise when goods sell out due to unexpectedly strong demand. For certain companies, backorders are regarded as a guarantee of sales. The proportion of goods on backorder and the number of days they are on hold are critical indicators of your company’s inventory management efficacy.
We are the perfect blend of Edu-tech and enterprise software consulting company offering a unique product that offers a revolutionary training experience. Drop us an email at he**@***************on.com.
What Causes Backorders?
The first step in preventing – or at the very least minimizing – backorders is to address their sources. Consider the following frequent causes of backorders, which are all indications of insufficient inventory forecasting and may be remedied via better inventory forecasting:
Unusual demand when demand surpasses supply
Holiday seasons and other unexpected events, such as severe weather, may result in unusual buying. For instance, our current heatwave increases generator orders or a storm threat, resulting in backorders.
Inaccurate forecasting
Inaccurate predictions may result in a depleted safety supply and a greater likelihood of backorders.
Supplier or production issue
Supply chain issues, such as plant closures or raw material shortages, may result in goods being out of stock suddenly.
Orders delayed
Businesses that use safety stock formulae and need human approval of purchase orders may suffer restocking delays, followed by an unexpected spike in orders. Delays may also occur when an organization’s upstream supplier does not refill its normal supply, resulting in backorders.
Human errors
An employee may incorrectly enter an order as a backorder when the item is really available. Or, in the worst-case scenario, a merchant may accept a backorder despite the fact that the item is out of stock. This may occur as a result of a mistake or a lag in inventory updates.
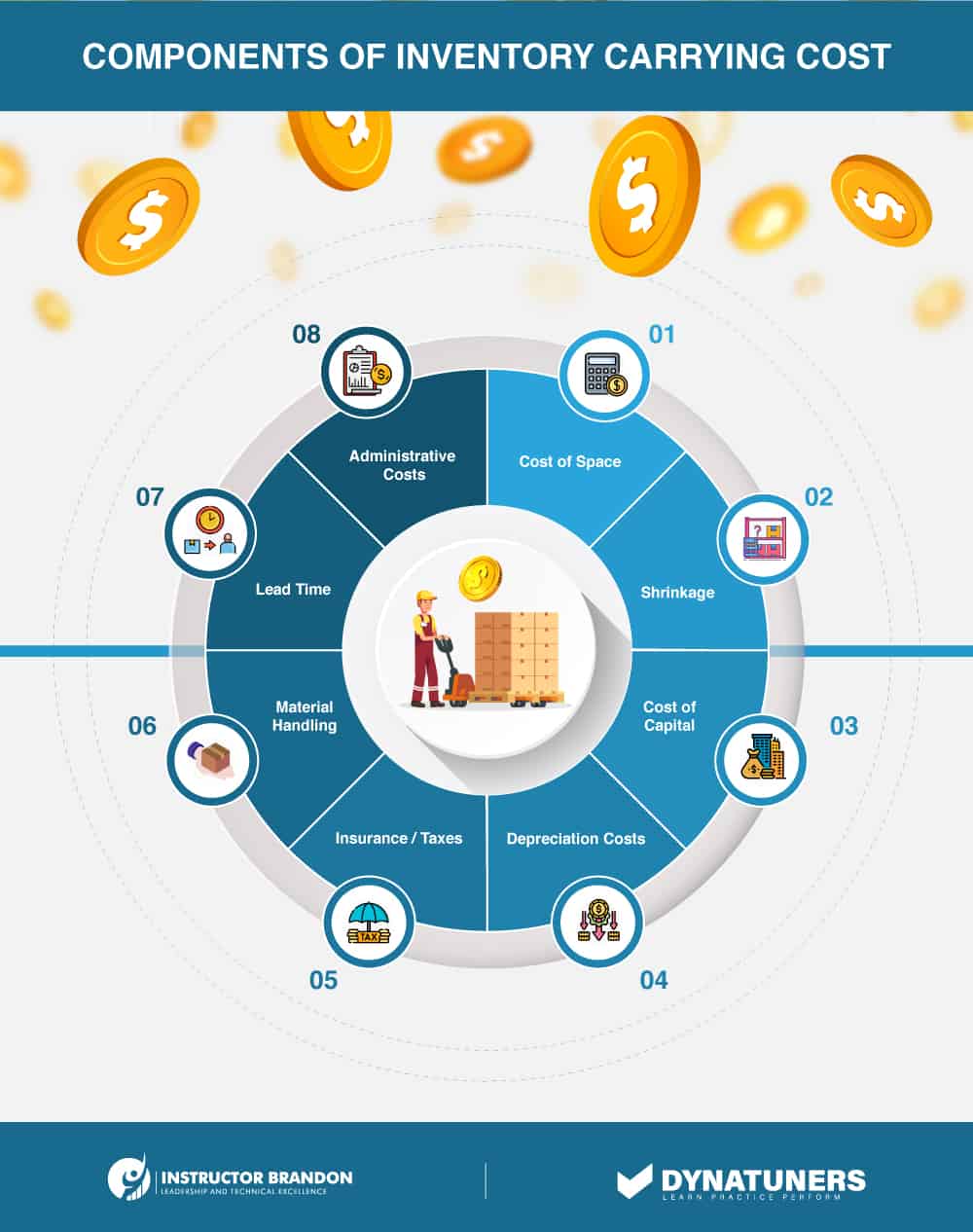
Disparities in warehouse management
The term “warehouse management” refers to all of the procedures involved in everyday warehouse operations – and there are many. A flaw in an inventory management system may result in incorrect data, or a data input error could result in goods being miscounted or lost.
SUMMARY
Backorders are a sign of insufficient inventory forecasting and may be remedied via better inventory forecasting. Businesses that use safety stock calculation formulae and need human approval of purchase orders may suffer restocking delays, followed by an unexpected spike in orders. Delays may also occur when an organization’s upstream supplier does not refill its normal supply, resulting in backorders.
How Does Backorder Processing Affect Your Supply Chain?
Backorder processing may have a significant effect on the rest of your supply chain. Indeed, backorders have been recognized as a cause of the bullwhip effect.
The bullwhip effect, also referred to as the Forrester effect, relates to a supply chain’s tendency to over- or under-react to variations in demand (also called order variability) at the customer level.
For instance, if consumer demand increases by 5%, suppliers and manufacturers across the supply chain overreact by functioning as if demand increased by 40%. This results in excess output and inventories.
On the other hand, if consumer demand is reported to have decreased by 5%, suppliers and manufacturers across the supply chain respond as if it has decreased by 40%. As a result, underproduction, stock outs, and poor customer service occur.
The bullwhip effect is best understood by considering an actual bullwhip and how a tiny stimulus at one end results in bigger waves down the whip’s length.
The client order is conveyed by a flip of the handler’s wrist. The increasing size of the waves along the whip’s length represents the upstream supply chain partners responding to the original stimulation.
SUMMARY
Backorder processing may have a significant effect on the rest of your supply chain. Backorders have been recognized as a cause of the bullwhip effect. Suppliers over- or under-react to variations in demand (also referred to as order variability) at the customer level.
The Impact of Backorders on Inventory Control
Placing backorders entails either being unable to fulfil orders or getting orders that exceed available inventory supply. You may potentially get a sales order that contains one or more out-of-stock products. For individual products, you may simply place a new purchase order and notify the client when the backordered item will arrive.
However, if you’re handling hundreds, if not thousands, of individual sales orders each week, backorders may quickly become a logistical and inventory management nightmare. If you have multiple out-of-stock goods from several suppliers, satisfying these backorders requires you to maintain track of all sales orders that include backordered items and place purchase orders for these items. Once the inventory has been received, sales orders must be matched to the appropriate purchase orders and backorders fulfilled. This becomes a huge job when dealing with a range of backordered goods across numerous orders.
Review your Inventory Management Process
If backorders are becoming more common, it may be time to review your inventory management processes. A dependable inventory control system or cloud-based inventory management system is the finest instrument for managing backorders automatically. The application may analyses previous ordering data in order to assist in determining appropriate par levels for reordering. Additionally, cloud-based inventory management solutions may automate the purchase order procedure for you. We deliver solutions through our Help Desk Services at Dynatuners that advance our clients’ success, request a demo.
SUMMARY
You may potentially get a sales order that contains one or more out-of-stock products. Maintaining track of all sales orders that include backordered items is a huge job. A dependable inventory control system or cloud-based inventory management system is the finest instrument for managing backorders automatically.
Managing Inventory Backorders
The most critical element of managing inventory backorders is to manage client expectations carefully. When you are unable to meet your clients’ demands instantly or foresee a delay, tell this to them promptly and give a revised anticipated delivery date. Instantly update your website so that consumers understand why the product is unavailable and the steps you’re taking to fix the problem. Ascertain that your contact information is clearly posted on your website and keep your customer service staff informed of prospective customers’ calls and emails about the backordered goods.
Evaluate the turnaround time for backorder fulfilment – how fast can suppliers supply fresh goods to you? Can orders be fulfilled through drop shipping? Drop shipping backorders implies that your supplier will fulfil them straight to your consumers, reducing their wait time even more.
With a dependable inventory management system, you can simply monitor and handle backorders, ensuring that your clients are not kept waiting for extended periods of time. Even better, with cloud-based inventory management solutions, you can prevent inventory backorders in the first place.
SUMMARY
With a dependable inventory management system, you can simply monitor and handle backorders, ensuring that your clients are not kept waiting for extended periods of time. Cloud-based inventory management solutions can prevent inventory backorders in the first place.
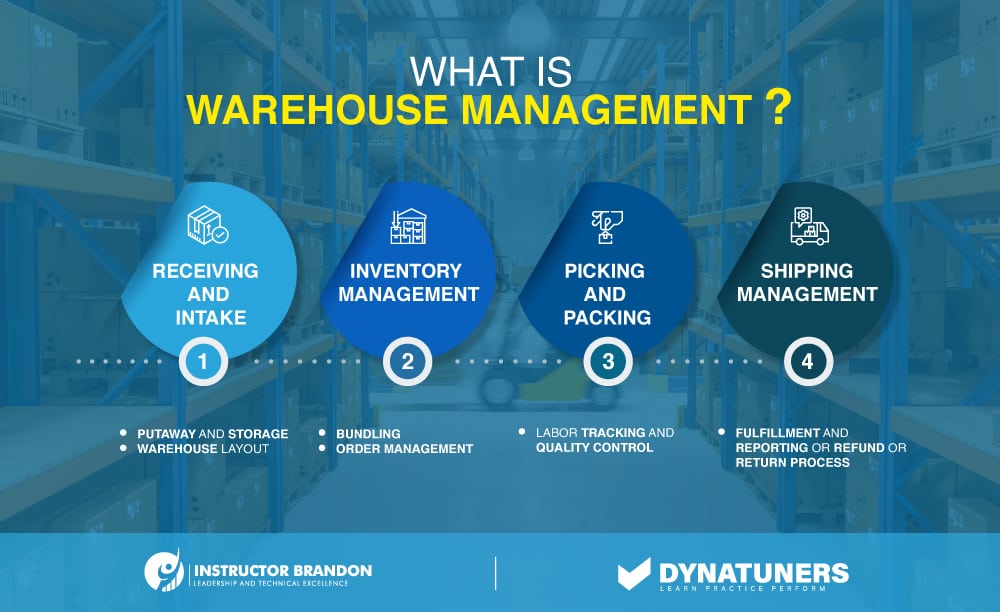
The type of the order and the quantity of goods awaiting shipment will influence the time required to deliver the product to the client. This demonstrates the critical importance of digitizing warehouse operations in order to priorities orders based on their urgency.
A really well backorder plan may provide a significant competitive edge. However, backorders provide unique inventory optimization problems since they enable the system to accept orders for items that are out of stock and instantly request the item from the relevant supplier. The whole procedure must be simplified and error-free in order to expedite the delivery of products to end consumers.
To do this, contemporary installations use warehouse management systems, such as Easy WMS, that connect with enterprise resource planning systems (ERPs) to handle all supply chain operations. The WMS monitors and maintains inventory levels at different points throughout the supply chain, generating precise forecasts about upcoming orders, depleted SKUs, and low stock levels. Thus, in order to effectively implement a backorder plan, the usage of software – specifically, a warehouse management system (WMS) – is critical.
SUMMARY
Backorders provide unique inventory optimization problems since they enable the system to accept orders for items that are out of stock. The whole procedure must be simplified and error-free in order to expedite the delivery of products to end consumers. In order to effectively implement a backorder plan, the usage of software – specifically, a warehouse management system – is critical.
|
Sr. |
Warehouse KPIs to measure warehouse performance and efficiency |
||
| KPI | Description | Accuracy/Formula | |
|
1. |
Picking accuracy | This KPI tells you how accurately items are being picked from your warehouse for customer orders. | (Total number of orders – Incorrect item returns) / Total number of orders |
|
2. |
Total order cycle time | Total order cycle time refers to the average time it takes an order to be shipped, starting from the moment the customer places the order. | The shorter this time, the better the chance of you retaining your customers |
|
3. |
Order lead time | Order lead time is the average time it takes an order to reach a customer after they’ve placed it. | it’s better for your business if your order lead times are short. |
|
4. |
Backorder Rate | Backorder rates compare the number of backorders you have placed to your total orders. | Total backorders / Total orders |
|
5. |
Fulfillment accuracy rate | This KPI calculates the number of orders that have been successfully fulfilled from start to finish, out of the total number of customer orders received. | Orders completed without issues / Total orders received |
|
6. |
On time shipping rate | This indicator tells you how efficient your shipping processes are. | Number of orders that have been shipped on time or in advance / Total number of orders shipped |
|
7. |
Cost per order | This KPI tells you how much it costs to fulfill one of your customer orders, from the moment the order is placed to the time it reaches the customer. | Total fulfillment costs / Total number of orders |
|
8. |
Rate of returns | The rate of returns tells you the percentage of customers that have returned their items, whether because of factors you can fix (like damaged products, incorrect item sent, or late delivery) or factors out of your control (such as fraud or problems with the product after delivery). | (Items returns / Items sold) * 100 |
Back orders in Microsoft Dynamics 365
Backorders are either purchase orders from a vendor that have not yet been fulfilled or sales orders that have not yet been fulfilled by a client.
It is critical to monitor backorders. For instance, if suppliers’ goods are delayed, you may need to adjust the date of delivery to consumers and notify them of the change. Utilize one of the following categories to check the status of backorders: products, customers, or suppliers.
-
Backorders may be seen by item
When viewing backorders by item, you may monitor the anticipated future flow of transactions for a particular item. For instance, you may verify:
- How many sales orders are generated for a certain item?
- Whether goods delivery from suppliers are still delayed.
- Whether more goods should be purchased to ensure timely delivery of all sales orders.
The overview enables you to respond to client inquiries about delivery times. Additionally, you may priorities sales backorders and divide available inventory across orders. See View backorders by item for more information.
-
View customer-specific backorders
You may see the status of a customer’s remaining orders while viewing backorders by customer. This is advantageous when responding to inquiries from consumers who are awaiting delivery of goods that have been delayed. For more information, visit View customer backorders.
-
View vendor-specific backorders
When you examine backorders by vendor, you can keep track of late deliveries and estimated delivery dates.
When goods come from suppliers and sales orders must be selected for delivery, the overview is also beneficial for prioritizing. More information is available at View backorders by seller.
SUMMARY
Backorders are either purchase orders from a vendor that have not yet been fulfilled or sales orders that haven’t been fulfilled by a client. Utilize one of the following categories to check the status of backorders: products, customers, or suppliers. View backorders by item to monitor anticipated future flow of transactions for a particular item.
Backorders: Functional Walkthrough in Microsoft Dynamics 365
Step 1
Navigate to Procurement and sourcing > Vendors > All vendors.
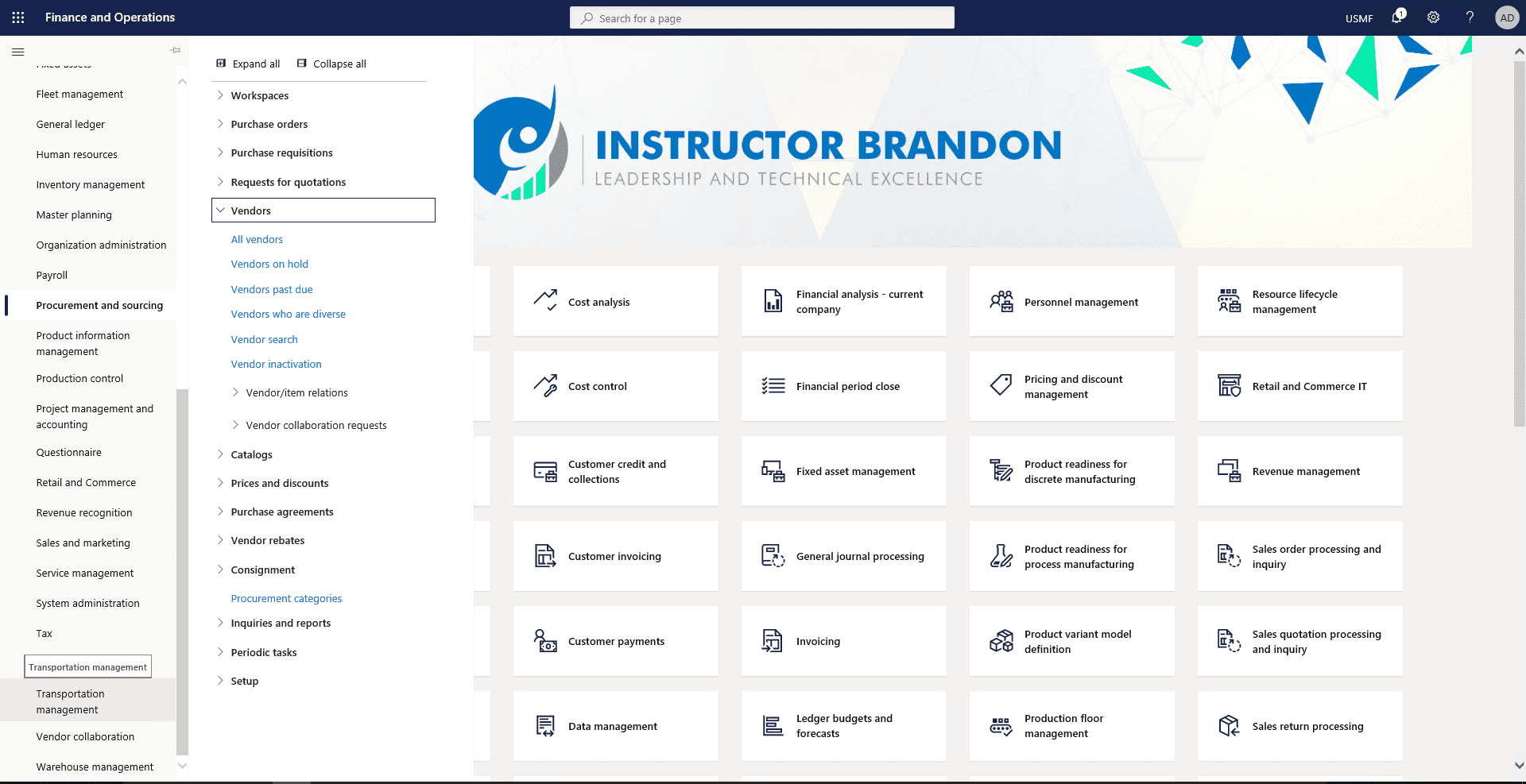
Step 2
Select the vendor to view backorders for.
Step 3
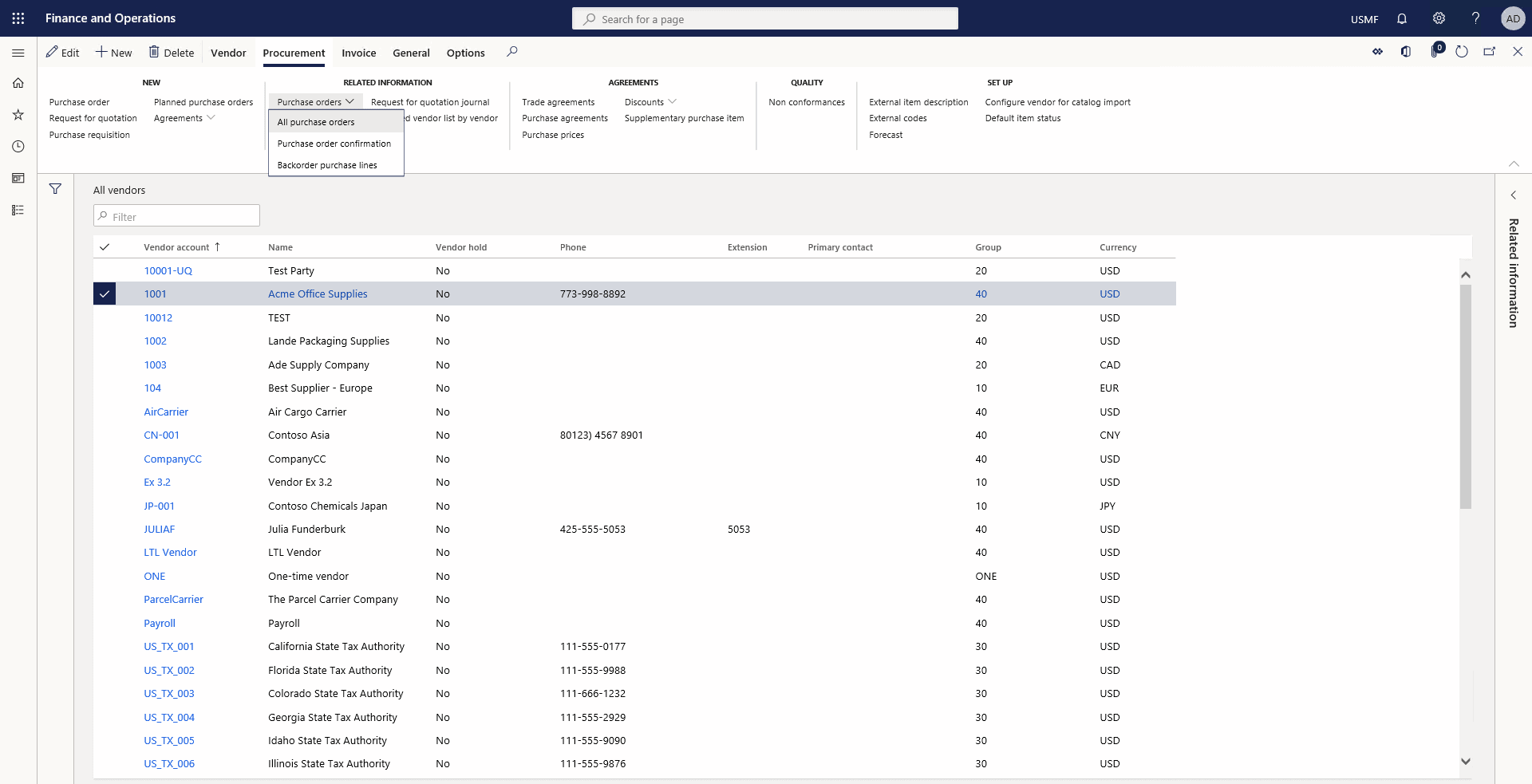
On the Action Pane, click the Procurement tab. In the Related information group, click Purchase orders > Backorder purchase lines.
Step 4
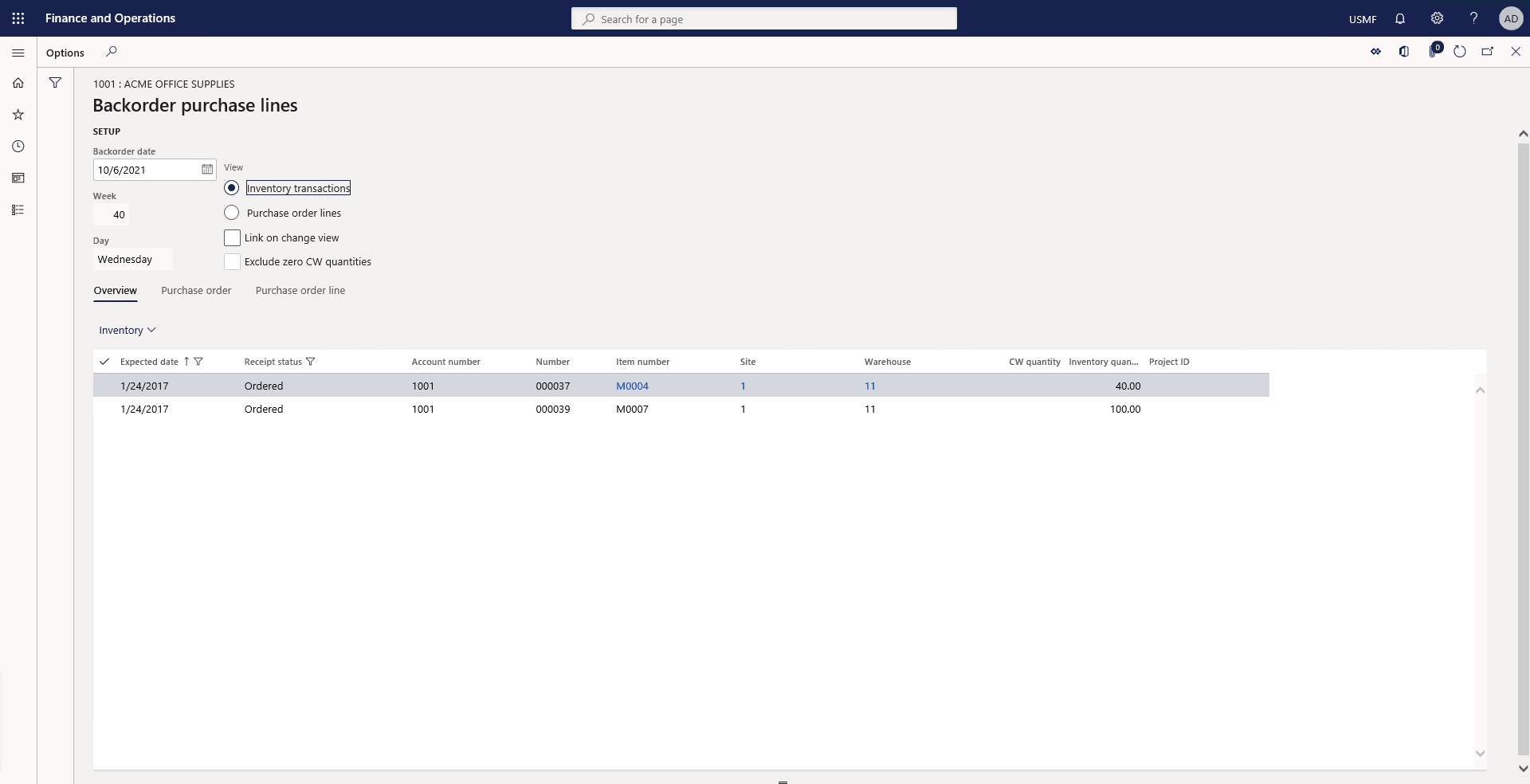
In the Backorder purchase lines form, select the Inventory transactions option to view the inventory transactions for the vendor’s backorders.
Step 6
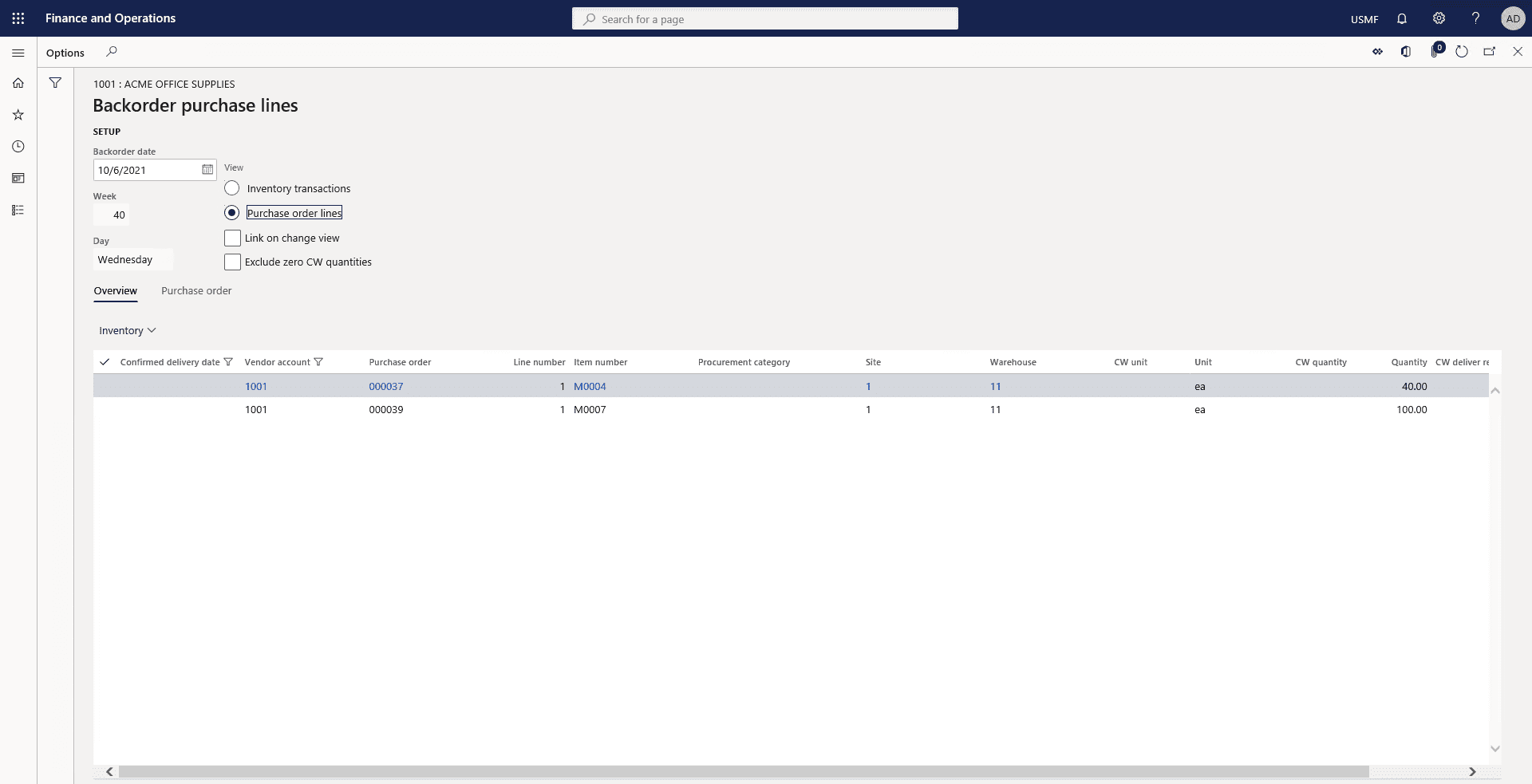
Select the Purchase order lines option to view the remaining open order lines for the vendor.
SUMMARY
Follow the instructions to view backorders for vendors.
How to Manage Backorders in the Supply Chain?
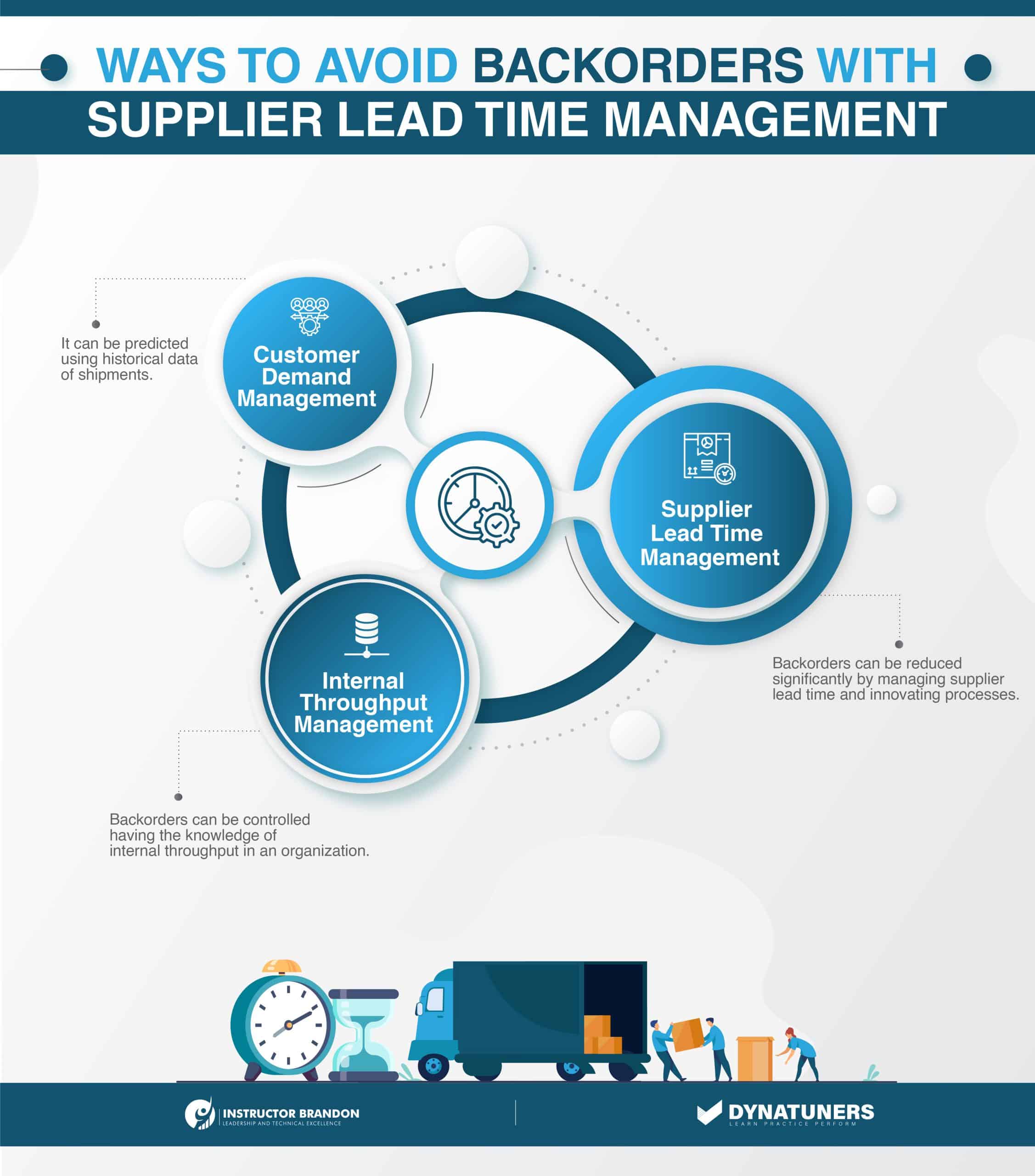
The most effective method to handle backorders is to eliminate the need for them entirely via the use of inventory management systems and best practices. If backorders become required, following best practices will aid in preventing supply chain overcorrections and safeguarding future profits.
-
Best practice for backorders: Communication
Supply chain best practices include open communication between all parties to help you avoid backorders in the first place. When retailers communicate effectively about supply levels and customer demand, wholesalers and suppliers are better informed, allowing them to maintain consistent stock levels and avoid the need for backorders.
If inventory shortages are inevitable, a strong channel of communication between retailer, supplier, and manufacturer will assist in preventing an excessive amount of buffer stock from being purchased, which will hurt future sales.
-
Best practice for backorders: Data-driven Inventory Management
Without data-driven inventory management, reorders may be received too late to prevent stock disruptions. By adopting data-driven inventory management systems, demand and real-time inventory visibility will clearly define reorder points, eliminating the requirement for backorders.
-
Best practice for backorders: Warehouse Inventory Accuracy
Accurate inventory management is critical for avoiding supply chain interruptions. Integrating warehouse management systems with inventory data sources enables the collection of all incoming and outgoing receipts and orders, thus increasing insight into inventory levels.
Additionally, warehouse inventory management processes such as first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory allocation guarantee that goods does not slip through the gaps.
SUMMARY
If backorders become required, following best practices will aid in preventing supply chain overcorrections and safeguarding future profits. Data-driven inventory management systems, demand and real-time inventory visibility will clearly define reorder points, eliminating the requirement for backorders. Integrating warehouse management systems with inventory data sources enables the collection of all incoming and outgoing receipts and orders, thus increasing insight into inventory levels.
Final Thoughts: Backorders
Efficient fulfilment processes mitigate the danger of goods selling out and necessitating backorders thus to optimize fulfilment operations and minimizing backorders or out of stock items you should do as follows:
-
Utilize demand forecasting
Demand forecasting is the process of using historical data and market research to anticipate demand fluctuations, allowing you to determine the precise amount of stock to purchase.
-
Establish reorder points
A reorder point is a specified stock amount below which a reorder is triggered. When you reach a reorder point, the assumption is that you still have enough stock to satisfy demand until your supplier delivers more goods. To establish reorder points, you must do demand forecasting, be familiar with your supplier’s lead times, and use inventory software to notify you when stock levels fall below a certain level.
-
Inventory efficiency
Inventory efficiency refers to the practice of maintaining sufficient stock in the appropriate locations to fulfil demand without straining your overhead. This is critical for multi-channel merchants, since they may run out of supply on one channel while maintaining stock on another. To circumvent this issue and increase inventory efficiency, distribute your goods via a single network capable of serving orders from all of your channels. This manner, all of your sales channels will have access to your complete inventory.
-
Diversify your supply network
A diversified supply chain minimizes the risk of supply chain interruptions and delays by using numerous suppliers from different regions. If you are unable to locate suppliers located in distinct nations, search for goods in distinct areas through distinct shipping routes.
-
Collaborate with a third-party fulfilment provider
A third-party fulfilment business has the technology, tools, and experience necessary to assist you in increasing fulfilment efficiency and avoiding backorders. This includes the following:
- Inventory management systems capable of forecasting demand and establishing reorder point
- Multi-channel connections that ensure that all inventory is accessible across all channels.
- Increased fulfilment capacity and warehousing
Presently, warehouse management systems’ predictive algorithms, automation, and sophisticated technologies enable effective backorder management. Should you like to read more on our latest blogs, click here.
SUMMARY
Efficient fulfilment processes mitigate the danger of goods selling out and necessitating backorders. To optimize fulfilment operations and minimize backorders or stock shortages you should do as follows. Demand forecasting is the process of using historical data and market research to anticipate how well your goods will sell in the future. Establish reorder points, be familiar with your supplier’s lead times, and use inventory software to notify you when stock levels fall below a certain level.
At Instructor Brandon | Dynatuners, we always seek innovative methods to improve your competitiveness and suit your Microsoft Dynamics 365 requirements. Our offerings are founded on defined procedures, industry experience, and product understanding. If you’re interested to consult with our specialists to minimize shipment discrepancies, don’t hesitate to Contact Us.
[sc_fs_multi_faq headline-0=”h2″ question-0=”What factors contribute to backorders?” answer-0=”A backorder happens when a client places an order for an item that your supplier does not now have or that your manufacturer has not yet manufactured. If you get your products directly from the manufacturer, the processing of backorders takes longer since you must wait for the manufacturer to restock. ” image-0=”” headline-1=”h2″ question-1=”Are backorders a problem? ” answer-1=”Backorders are not always a negative thing. It is entirely dependent on their management. They may arise for a variety of causes, including the following: Unexpected Demand – An unusual demand is a frequent cause of backorders. ” image-1=”” headline-2=”h2″ question-2=”What are the warehousing-related issues? ” answer-2=”Common warehouse issues such as duplicate procedures, inefficient facility architecture, seasonality in demand, high labour costs, and incorrect inventory information need strong systems that keep management aware of changes and critical gaps. ” image-2=”” count=”3″ html=”true” css_class=””]
 4302
4302