Dynamics 365 Tutorials, Dynamics Operations Training, Microsoft Dynamics 365 Developer (F&S) Training Series
Step-by-Step Guidance on Sales Tax Adjustment for Vendor Invoices Using Dynamics 365

Sales Tax Adjustment on Vendor Invoices in D365 F&O
Sales Tax | | Tax Adjustment | Dynamics 365 Finance
As your organization pursues global expansion, it will encounter challenges to keep pace with a myriad of unfolding taxation laws and ever-changing legal requirements from national tax authorities. Until about a decade ago, the only option for rising businesses to ensure international tax compliance was to hire an army of brilliant tax professionals to monitor policy variations and align your business processes with the respective functions.
However, the advancement has made the world smaller. The steady drive of digitalization and globalization has pushed through some significant winds. Regardless of massive geographic distances, it is relatively easy to communicate, connect, and trade at any instance with almost anyone. This has helped businesses and industries to expand globally to pursue a larger market, better suppliers, and higher revenue streams.
However, this new age of digitized tax regulations across the globe is more complex than ever. As a result, nearly every industry must navigate the maze of tax controls to comply with global trades.
On the bright side, the release of tax calculation by Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance has enabled the organization to deliver more value and assist in undertaking complex challenges while abiding by tax laws.
For today’s post, we decided to write on one of the most complex yet unspoken parts of digitized financing, sales tax. We see several clients getting tangled in calculating sales taxes, including tax adjustment in vendor invoices. So, let’s begin with how you can calculate and adjust your sales tax on vendor invoices using Dynamics 365 Finance, starting with basic U.S sales tax regulations.
U.S Sales Tax
Whenever you use the term “sales tax” in a generic sense, we refer to our national authorities’ tax on retail sales. Primarily, there are three types of sales taxes:
Vendor Tax
Vendor taxes are for retailers when they sell within a state. Here they have two options, either pay their tax out of their budget or pass it along to the purchaser mentioned in the vendor invoice.
Consumer Tax
As the name suggests, it is imposed on a person when a purchase is made within a state. As the tax is eventually a purchaser’s responsibility, sellers don’t have the freedom of absorbing the tax and must state the tax payment while invoicing for the purchaser.
Retail Tax
The retail tax is imposed on every retail sale transaction. Here, it is the primary liability of both seller and purchaser to pay the tax. In this tax account type, the seller collects and pays the tax, where the purchaser is responsible for paying the tax collected by the seller. In other words, it is a hybrid of the above two types of taxes. Typically, it is closer to consumer excise tax, as no seller absorbs any of it.
The Essentials of U.S. Sales Tax
The U.S does not have any national taxes. On that note, each state governs with its own tariffs. All 45 states, and its capital, Washington D.C., have taxes compulsory on every sales invoice. Washington D.C. isn’t a state, but it functions like a state to implement sales tax compliance. At the same time, the remaining five states do not impose sales tax at all.
As a businessman, you will see that several states also impose shipping taxes, a charge for the shipment of products to customers. The vital thing to notice is that your organization might have a relationship with other states to comply with all tax regulations.
The below Figure shows the structure for U.S sales tax.
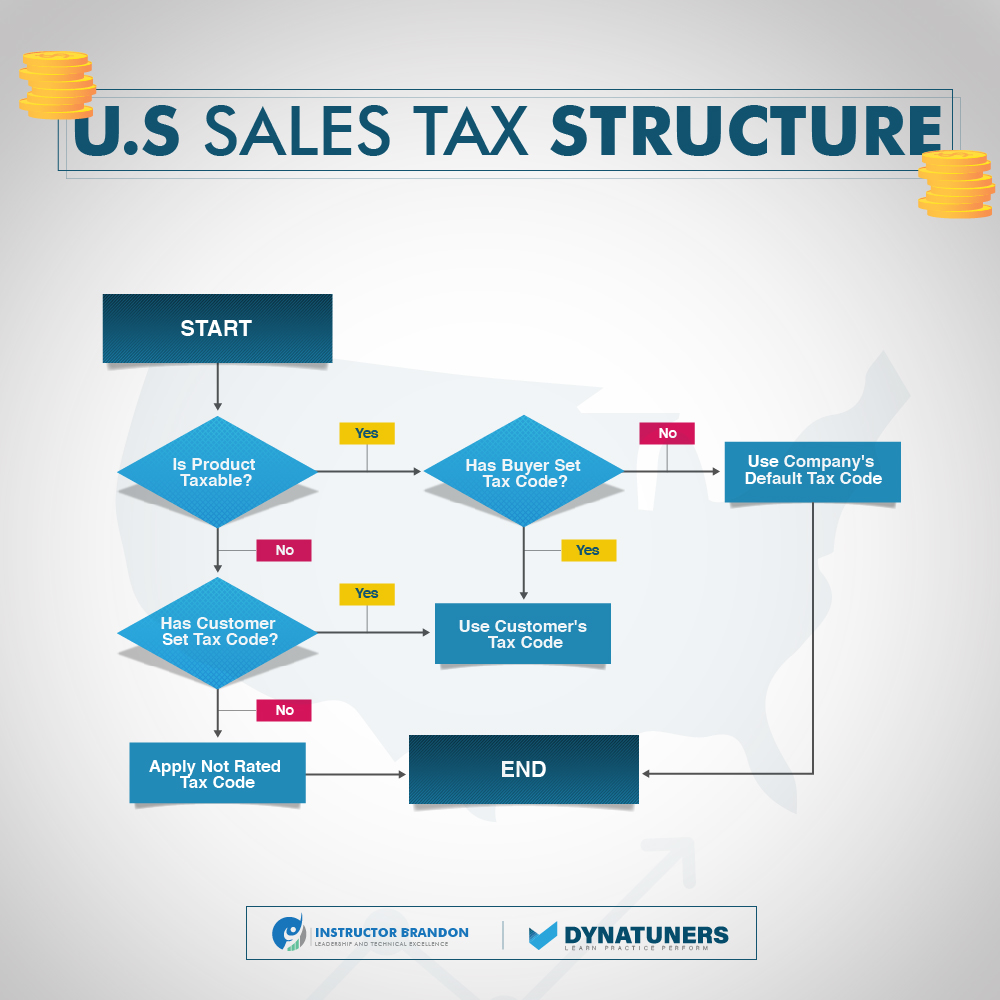
SUMMARY
Nearly every state has a consumer sales tax, where the buyer bears the burden of taxation, and the seller must collect tax for the state. Fewer states have the seller privilege tax option, but the tax is always imposed one way or the other.
All of this is nothing more than the tip of the iceberg for calculating sales taxes. If you still haven’t moved towards tax calculation automation, here are some of the reasons for you to start implementing finance automation.
Why Automate Tax Calculation?
With Dynamics 365 Finance and operations, several ERP solutions are changing this baffling situation for organizations with timely and intelligent solutions like auto tax calculation. It does not only help you unify data relevant to tax and power automate to turn such a tedious process into an efficient one. Further, such assistance also minimizes the risk of being non-compliant by reducing the chances of errors.
We at Instructor Brandon provide services to simplify and improve the tax calculation process for global businesses. In addition, we assist our clients to:
Integrate Tax Compliance into Business Apps
D365 tax solutions interface is the most reliable solution and provides an open API, allowing you to manage your tax compliance from a single dashboard.
You can make your pending acquisition public and have the flexibility to bring in a new revenue stream, integrate with your existing ERP solution, and get accurate finances right away.
Reduce Tax Risk
State requirements are vast and increasingly complex. The rates, taxability rules, and tax regulations are continuously in flux. Without any assistance from a well-implemented ERP system, your organization may take an unnecessary audit risk.
By implementing auto-updates on rates and machine-supported rules, Dynamics 365 Financial Management can increase operational efficiency of your sales tariffs.
Expand Business
Increased tax amounts might be a result of a company’s expansion. For example, entering new markets and adding sales channels, staff, products, and/or services can result in new registration and filing duties in other locations.
Expansion into international markets has the same effect. Global sales bring more complicated tax standards and a new range of tax jurisdictions. For example, the goods and services tax (GST) and the value-added tax (VAT) are applied differently from the United States sales tax. And each country’s tax laws are unique.
Here is a basic formula if you wondering how to calculate sales tax:
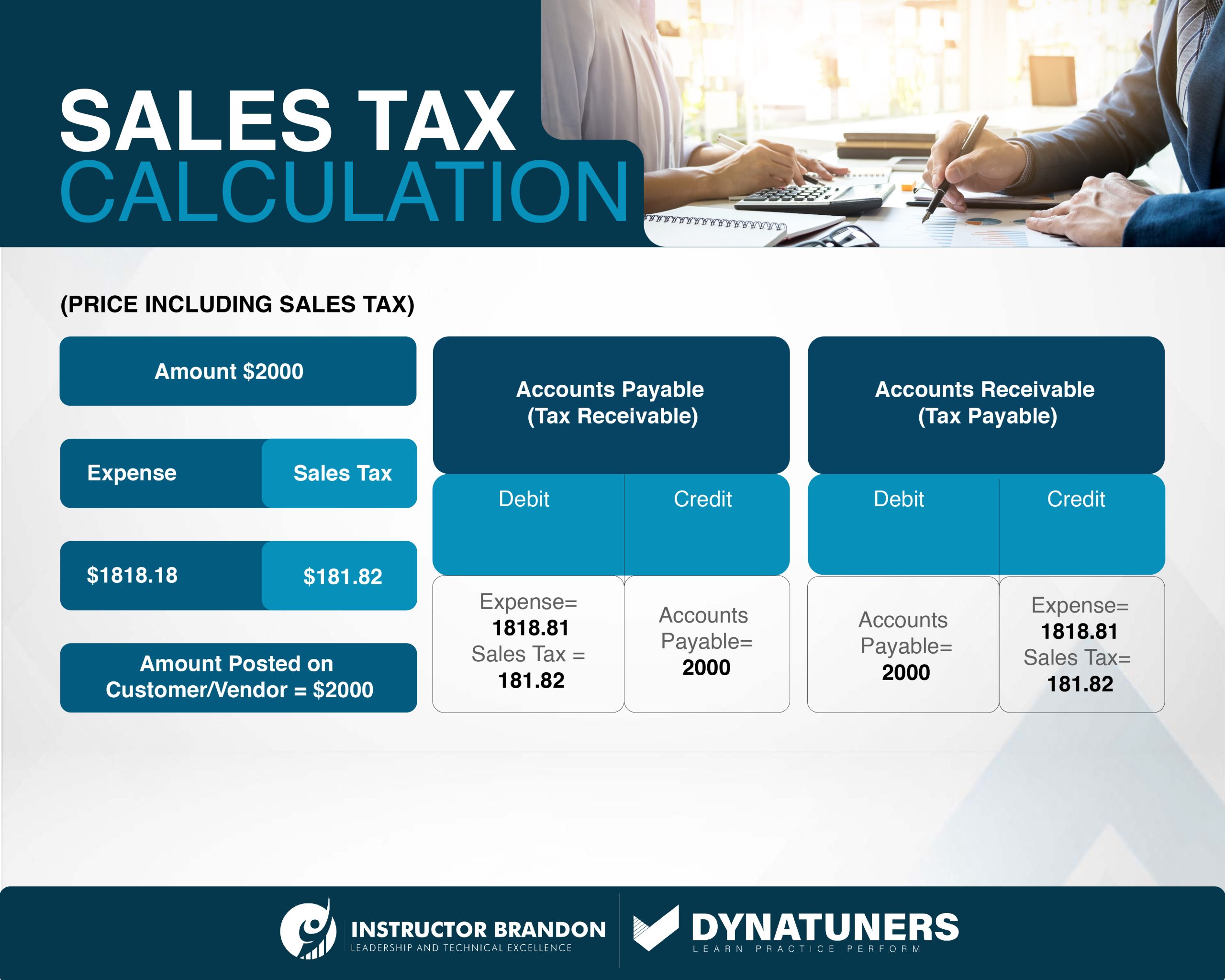
SUMMARY
The tax information complexity that often comes with corporate growth is reduced by automation. When you do business across the majority of the United States, the work required to maintain compliance in a few states is substantially different. Selling to other nations adds even another layer of complications for handling accounts payable.
To help us differentiate some prominent benefits of automation over manual processing and calculation of taxes, here is a table:
|
Manual Vs. Automated Tax Calculation |
||
|
|
Manual |
Automated |
| Registration |
|
|
| Calculations |
|
|
| Returns & Reporting |
|
|
| Compliance Documents Management |
|
|
How Dynamics 365 Finance Caters to Tax Calculation
The tax payment and calculation process is an extraordinarily flexible and multitenant service that enables organizations to industrialize and simplify the method with the help of a global tax engine. You can customize Dynamics 365 Tax engine according to your needs.
This is where we step in. With our services, you can customize taxable data models, tax applicability matrices, tax codes, and tax calculation formulas. Initially, the Dynamics tax engine runs the Azure core service platform and enables modern technology and exponential scalability.
However, the tax calculation eventually integrates with Dynamics 365 Finance Supply Chain Management. In the longer run, you will also have its integrations with project operations, commerce, and other first or third-party applications.
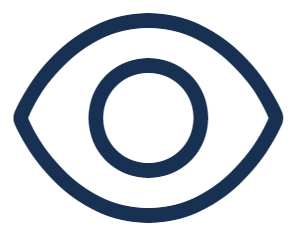
Calculate and Adjust Sales Tax on Vendor Invoice using Dynamics 365 Finance
Step 1
In the navigation pane, go to Modules > Accounts payable > Invoices > Invoice journal.
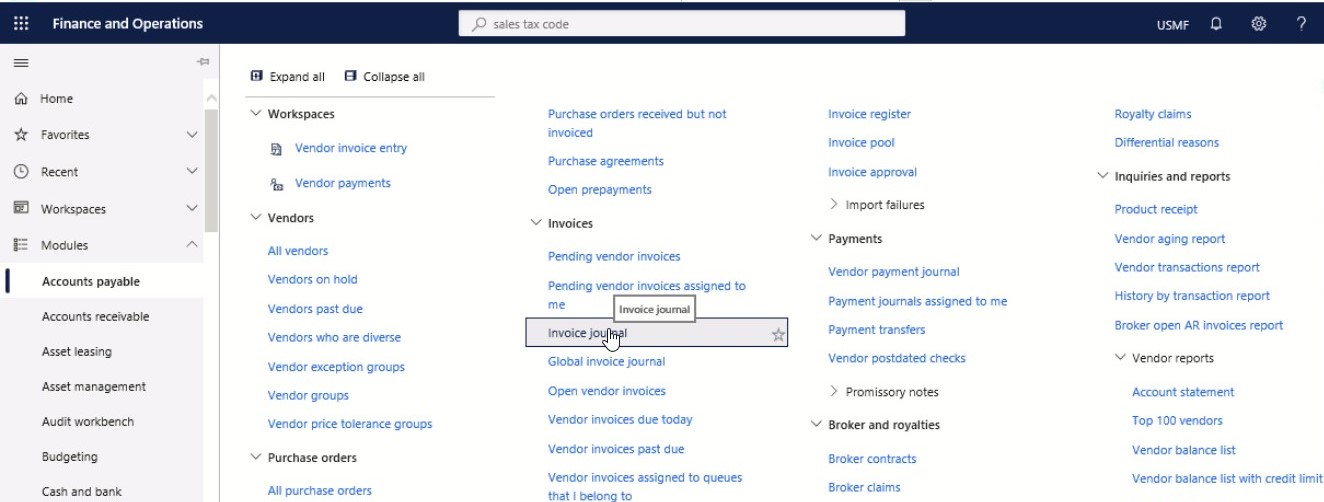
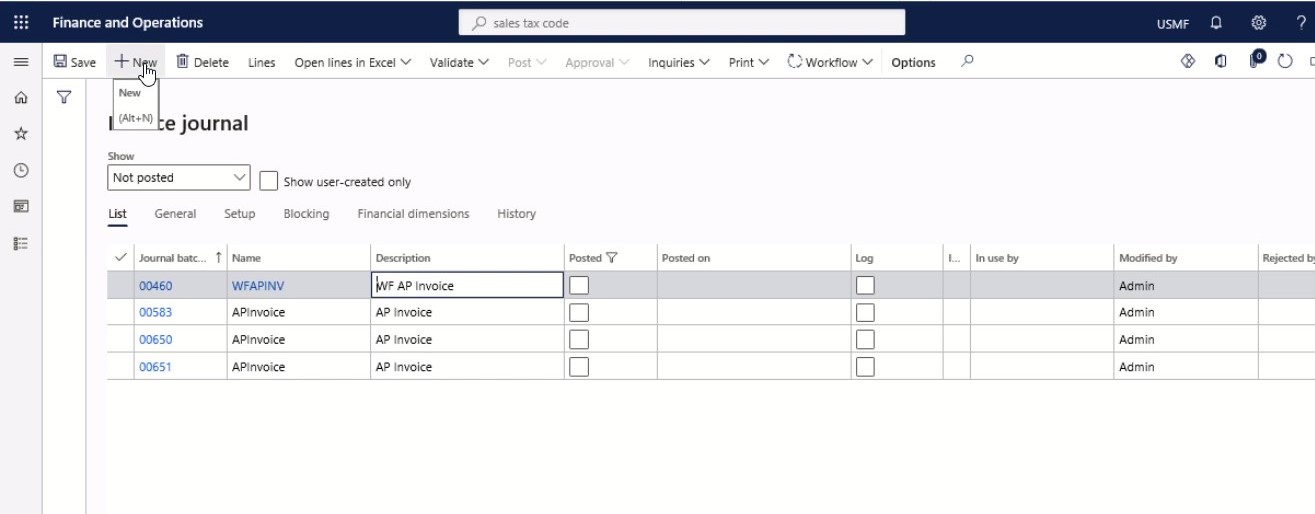
Step 2
Select New.
Step 3
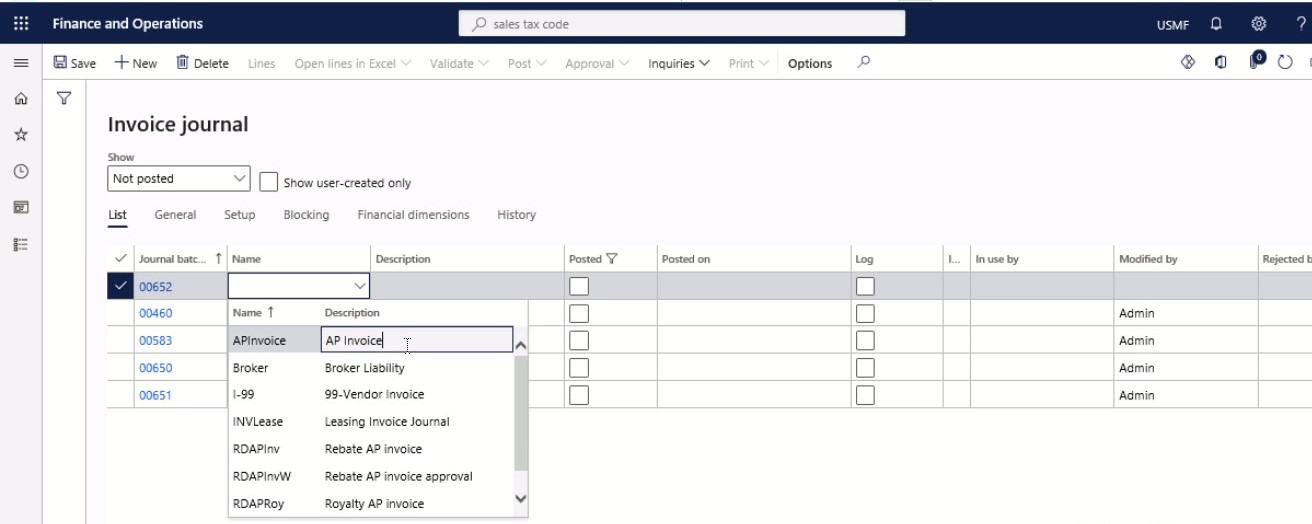
In the Name field of the new row, select an option in the drop-down menu.
Step 4
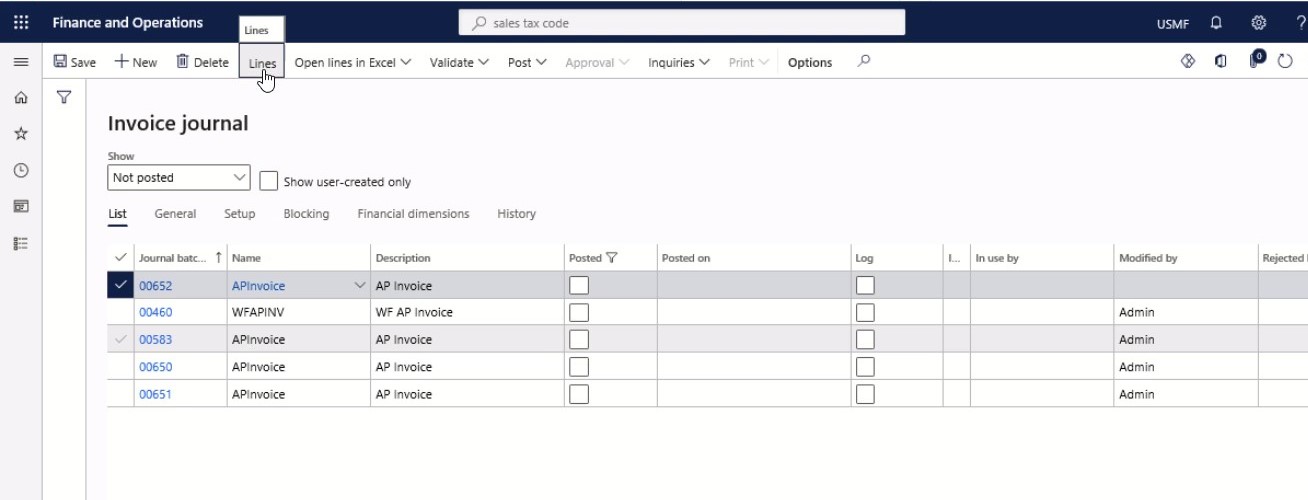
In the Action Pane, select Lines.
Step 5
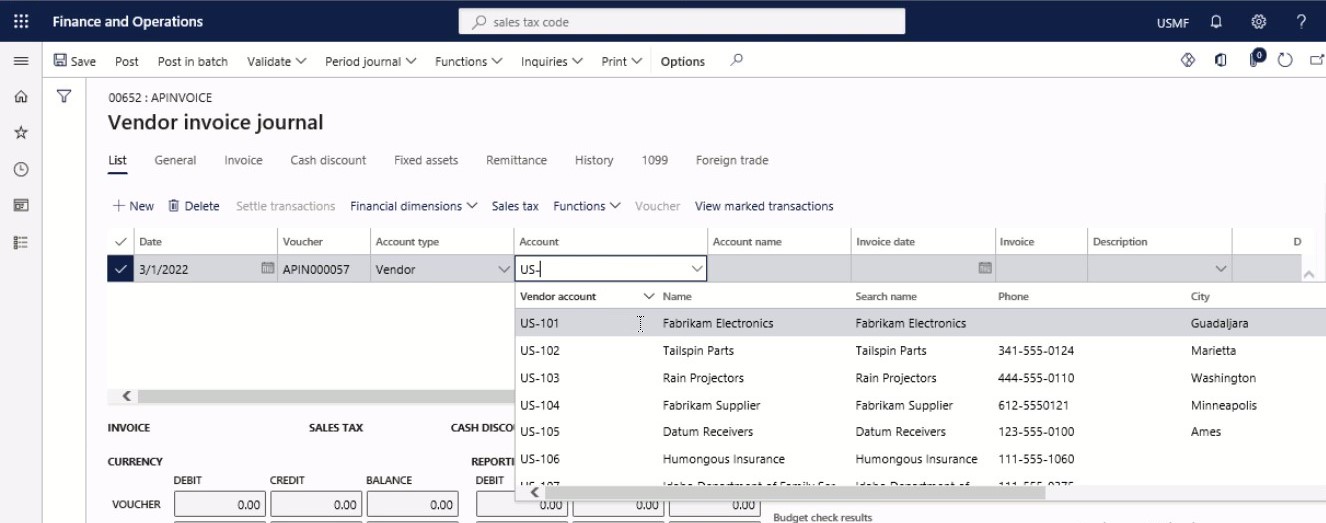
In the Account field, specify the desired values.
Step 6
In the Invoice field, type a value.
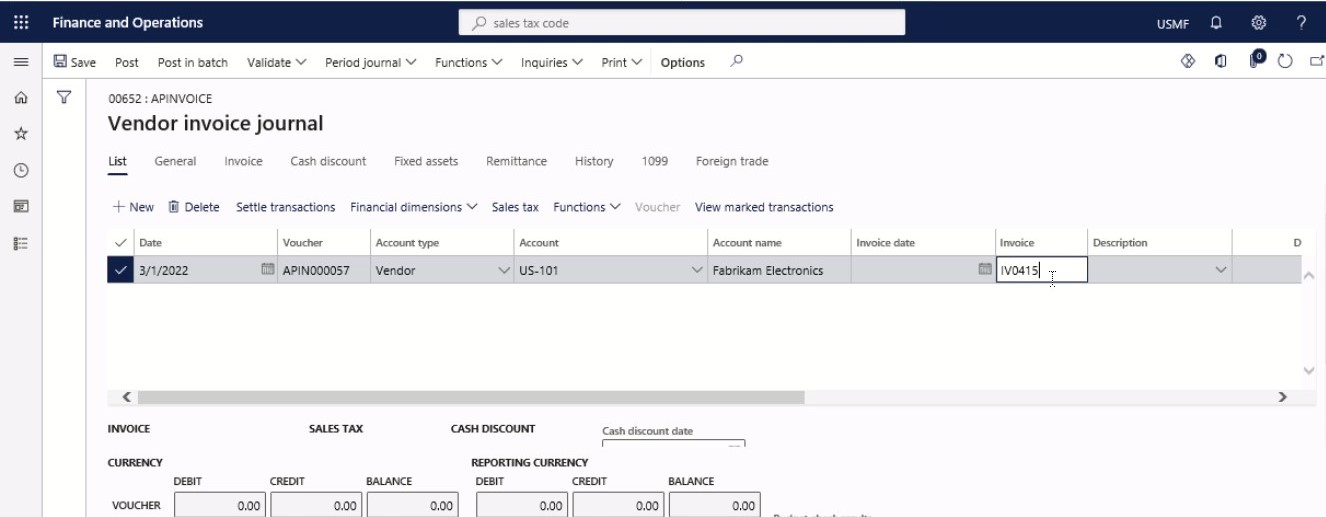
Step 7
In the Credit field, enter a number.
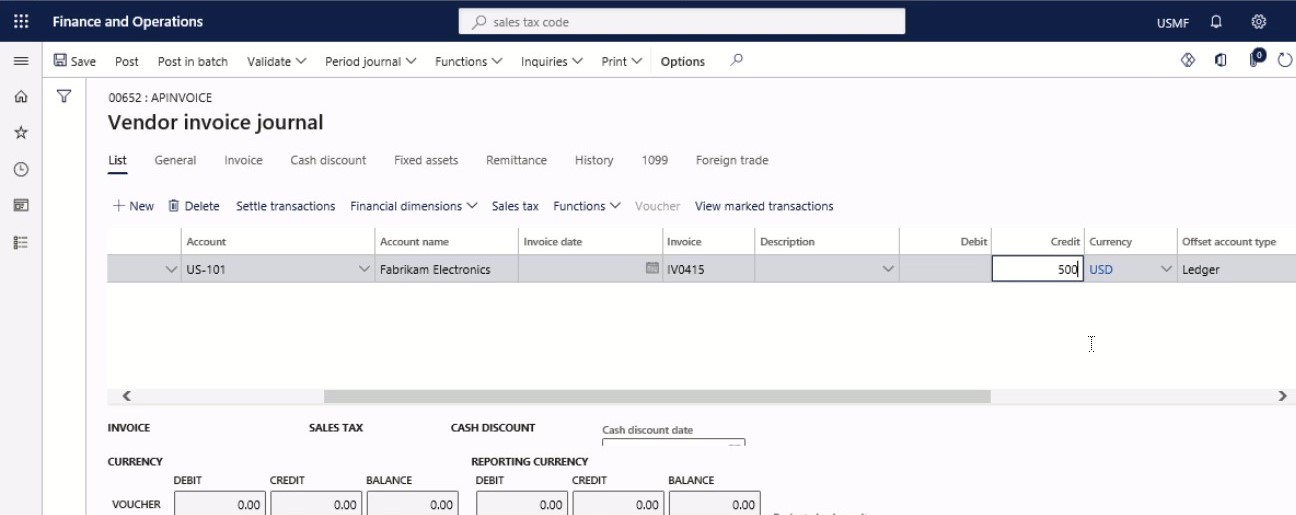
Step 8
In the Offset account field, specify the desired values.
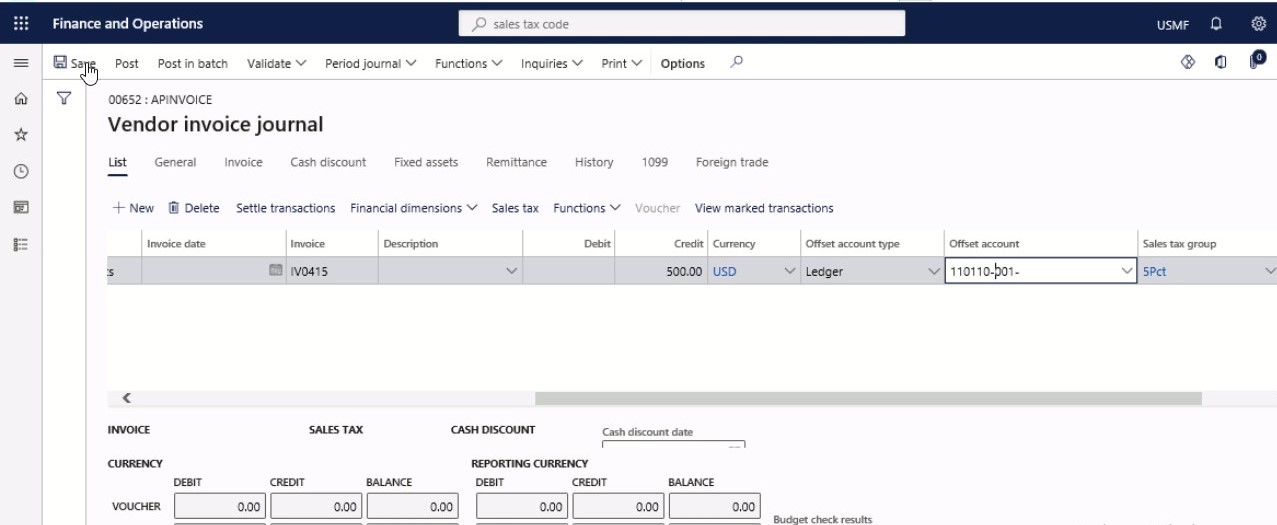
Step 9
Select Sales tax.
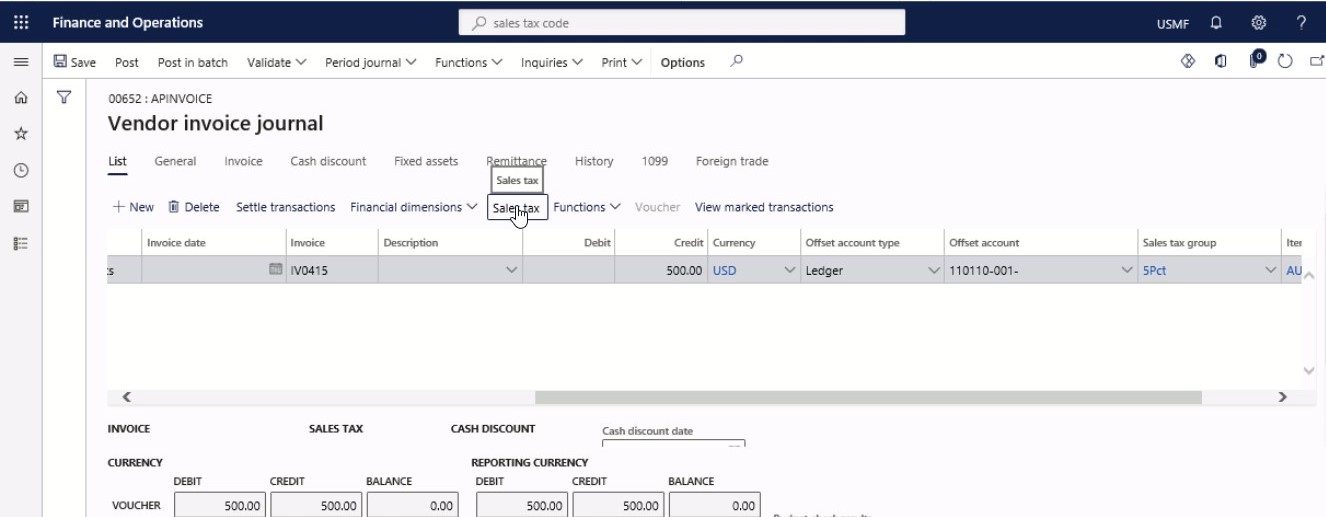
Step 10
In the Total actual sales tax amount field, enter a number.
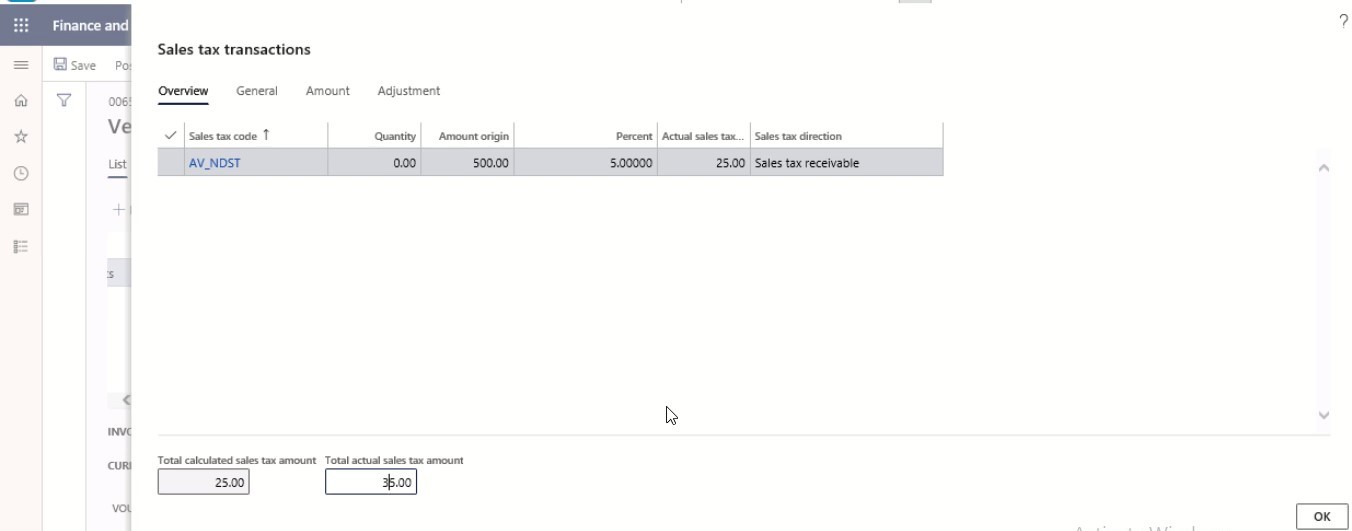
Step 11
On the Adjustment tab, the sales tax amounts can be adjusted per sales tax code.
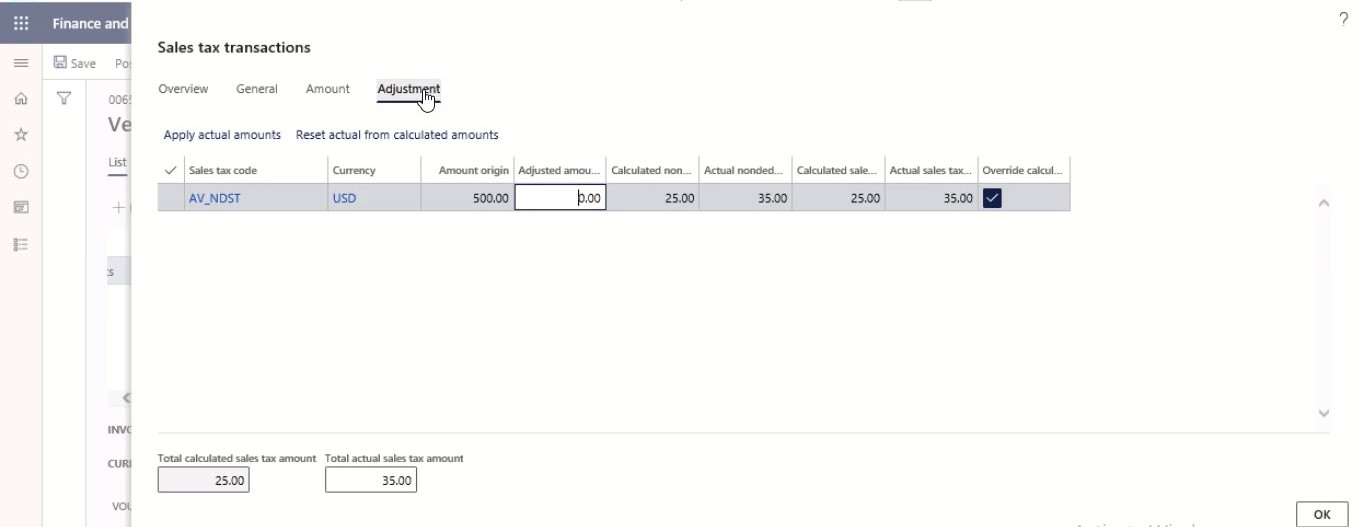
Step 12
Select Reset actual from calculated amounts.
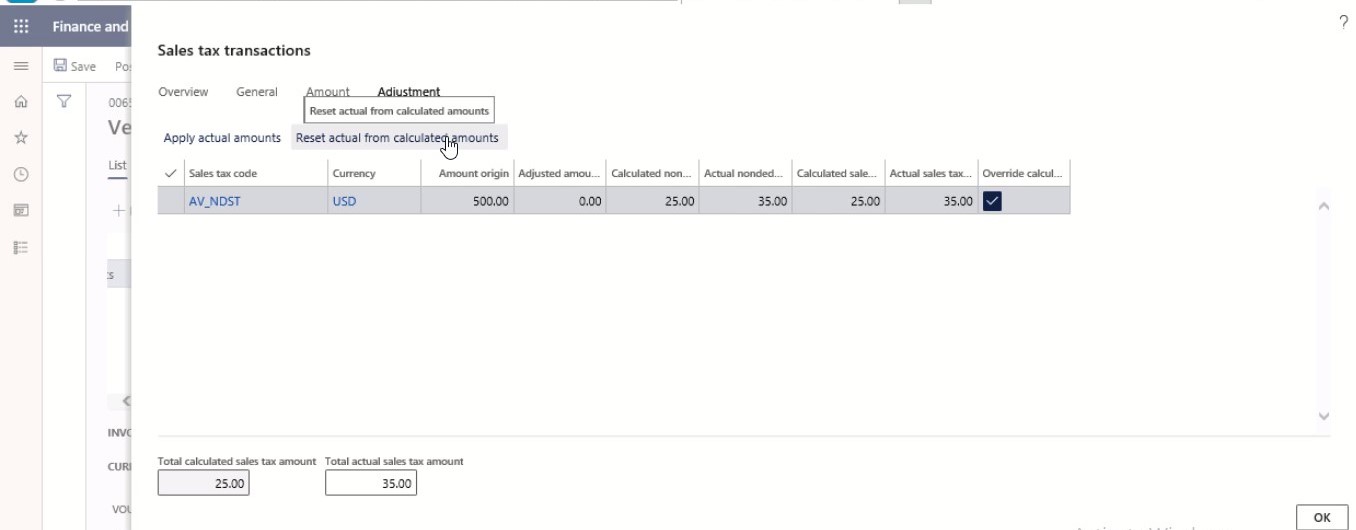
Step 13
Select OK.
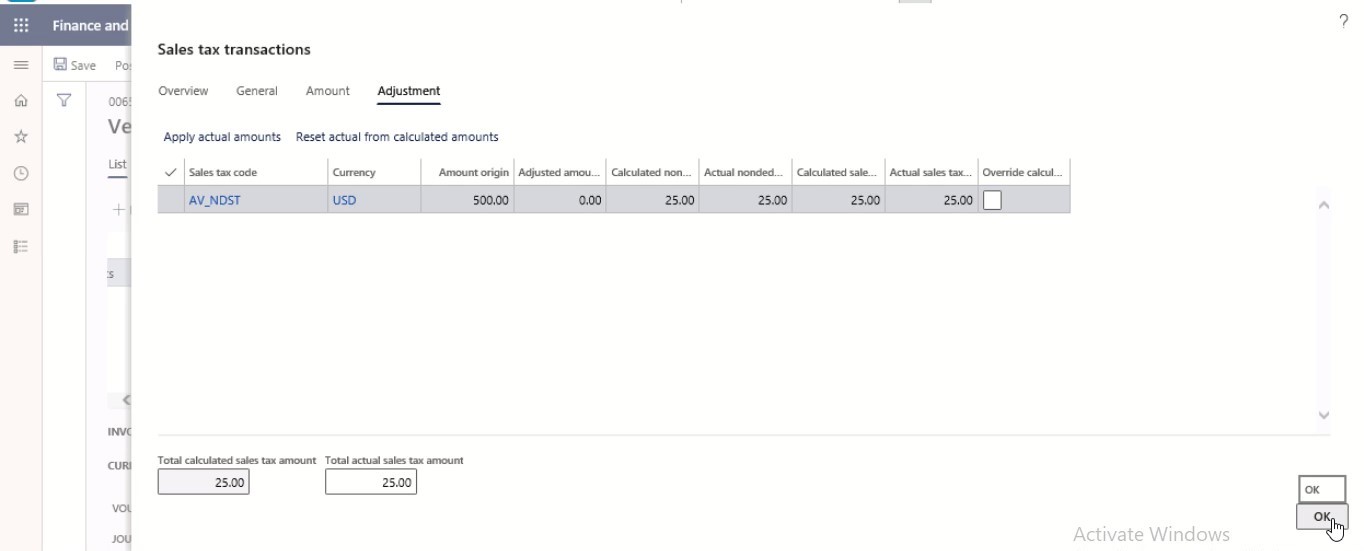
Step 14
Select Save.
SUMMARY
When you activate Tax Calculation, some activities on associated data may be executed in a data center other than the ones that keeps your service data. The tax is registered for both customer and vendor, which settles international suppliers by showing different tax rates for the same item. The system also accumulates both of these taxes as project level to process the sales transaction successfully.
NOTE: Before enabling Tax Calculation, read the Terms and Conditions.

Implementation with Instructor Brandon
If you choose Microsoft Dynamics 365, it’s a good idea to bring in a solution provider who can bring in experienced tax professionals early on in the ERP implementation process to boost your chances of success and prevent typical pitfalls and mistakes.
Your ERP transformation would follow our Powered Enterprise transformation methodology with a Microsoft Certified Partner along your side:
- Validate & Vision
- Build and Deploy
- Evolve
Instead of seeing transition as a negative event, you might now see it as an opportunity. Our team will offer proven expertise and experience to implementations, allowing you to successfully steer your business into the digital future. Make certain you’re prepared for the next task.
At Instructor Brandon | Dynatuners, we always seek innovative methods to improve your competitiveness and suit your Microsoft Dynamics 365 requirements. Our offerings are founded on defined procedures, industry experience, and product understanding. If you’re interested to consult with our technical solutions experts on how to calculate and adjust sales tax using Dynamics 365 Finance, feel free to Contact Us and get more information on it.
[sc_fs_multi_faq headline-0=”h2″ question-0=”Why automate Sales Tax Compliance? ” answer-0=”Automated tax checking establishes a procedure for creating, scheduling, and performing compliance checks in real-time to manage and minimize risks. It would assist management in identifying compliance concerns, correcting them, and implementing mitigation solutions promptly. ” image-0=”” headline-1=”h2″ question-1=”What is remittance of sales tax? ” answer-1=”Businesses collect sales tax from customers and then send it to their respective state monthly or quarterly. Failure to remit sales tax payments in time might result in significant penalties. ” image-1=”” headline-2=”h2″ question-2=”Is there a direct or indirect sales tax? ” answer-2=”Indirect taxes that are applied to the sale of goods and services include sales tax, excise tax, value-added tax (VAT), and goods and services tax (GST). ” image-2=”” count=”3″ html=”true” css_class=””]
 7447
7447