Supply Chain and Logistics Management
Understanding Load Shipments & Work Templates in Dynamics 365 Supply Chain
Load Shipments | Work Templates | Dynamics 365
Load Shipments & Work Templates
Loads are made up of one or more shipments, and each shipment is made up of one or more shipping lines. Warehousing or Freight generates the loads, shipments, and shipping lines used in the shipment process. LTL shipments in Supply Chain Management are an integral aspect of the Supply Chain’s overall operation. Even more crucially, they can assist firms in improving the efficiency of their warehouse operations while also reducing total expenditures. After all, the speed with which today’s commerce (particularly e-commerce) operates forces businesses to adapt and meet customer demand more quickly while simultaneously cutting costs in order to achieve better profit margins. At the end of the day, this is what all businesses strive for: increased profits.
As e-commerce continues to grow at an astonishing rate, distribution and delivery operations require well-thought-out strategies in order to fulfil their respective goals. Talking about Microsoft Dynamics 365, work templates are vital parts of the whole process.
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management
Shipments and warehouse management play an important part in the Supply Chain at this point. Using optimal load shipments, these companies are able to satisfy their increasing demand while also overcoming the numerous obstacles they may face along the road. Additionally, by adding tools such as work templates, it is possible to import shipments into Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management. There are numerous advantages to using it to automate your operations and logistical activities. That will make things a lot easier at the end of the day, no doubt about it.
As a result, in this post, we will discuss how to configure load shipments and work templates in Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management. Let’s start by defining what a warehouse is and what it does.
WHAT IS A WAREHOUSE?
A warehouse is a planned space for storage placement and handling of goods and materials of a business. In other words, all the accounted items in a Supply Chain (Inventory) must be placed in a warehouse facility. Warehouses are usually geographic locations and serve different functions. For example, you can have a warehouse for raw materials and another one for finished goods. Warehouses can also be referred to as distribution centers. Moreover, the raw materials or finished goods come into the warehouse and get passed through the distribution chain to the final customer.
SUMMARY
In order to meet the needs of e-commerce distribution and delivery, new approaches are needed for all activities. In order to import shipments into Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management, additional tools, such as work templates, may be used. Incorporating it into your daily routines will provide many benefits, including operating your processes and logistics. This article deals with setting the different load shipping and work template configurations in Microsoft Dynamics 365.
WAREHOUSES IN DYNAMICS 365 SCM
If there is one thing that helps enhance supply chain operations, it is automation systems like Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management. But why is that the case? Well, the Warehouse management module in Supply Chain Management allows users to adjust the warehouse layout to adapt to the constant changes in the distribution process. That way, businesses can achieve optimal warehouse efficiency. Moreover, using ERP systems like D365 enhances your business’ operations strategy by automating the different processes that take place in Warehouse Management. You can control, define, and extend different workflows to reach Warehouse Management’s optimal levels.
Let’s define what a load is and what it does
Consider a load to be the object that will be used to transport the delivery. Anything from a shipping container or semi-truck to an individual package sent via postal service can be considered. These cargoes can contain a single shipment or a number of shipments. Shipments are defined as the percentage of a shipment that will be delivered to a single destination, which is typically a single client. A single shipment may contain one or more sales orders from the same customer. At this stage, treat the load and shipment as if they were an empty truck and an empty pallet, respectively.
Single Order Picking
When it comes to modest orders of things that are always in stock, Single Order Picking is the simplest fulfilment scenario. Items are picked and dispatched immediately following the establishment of the sales order, making it the most basic fulfilment scenario. As customer orders are entered, the orders must be added to a new or existing load in order to be processed. When this load is completed, a related shipment will be produced for the reserved products, as inventory needs to be reserved before shipments can be made. In the shipment will be the SO lines (items), and afterwards, a wave will be formed, processed, and released to fulfil the order.
Picking work will be generated and conveyed via a picklist once the project has been released. All of the work (including pick and pack) will be finished, and the shipment will be verified (shipped). After that, the order is on its way to the consumer.
Consider the Following Scenario
You have three orders from the same customer that have been taken throughout the day. To save time, we will combine the orders into a single shipment, wave, and following pick list, rather than three separate pick lists, one for each order, as opposed to three separate picklists for each order. Additionally, if the selected products can be packaged together, this may result in a more efficient packing process.
Dynamics 356 for Operations provides the ability to manage outbound warehouse activities ranging from the simplest order and ship processes to the most sophisticated load planning requirements. Dynamics 356 for Operations is a Microsoft Dynamics product. D365FO makes use of a range of principles that, when combined with configuration and administration processes, provide this level of flexibility.
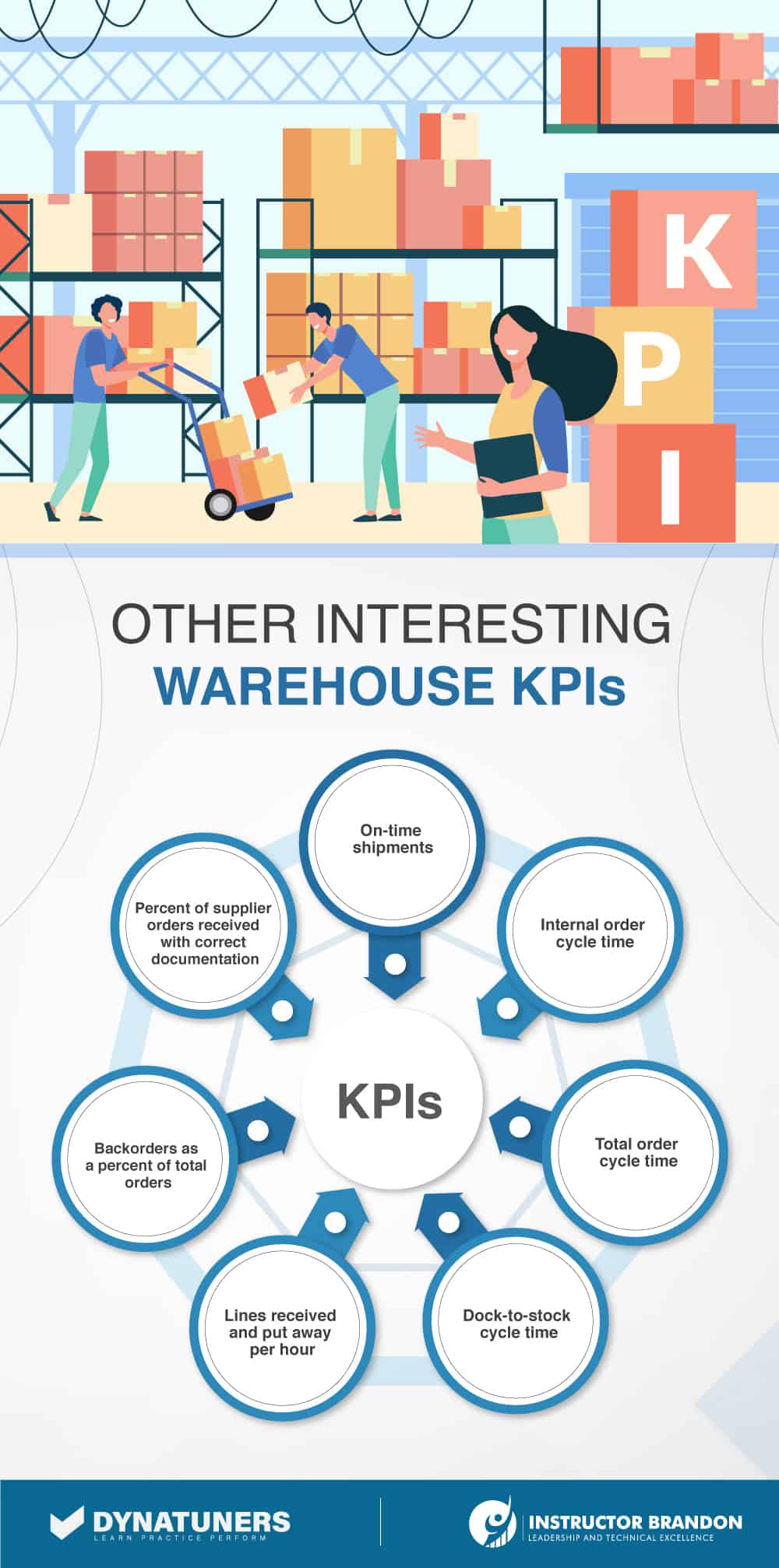
|
Order Fulfillment KPIs |
||
|
KPI |
What It Does? |
Percentage |
|
Supplier On-time Delivery |
This KPI provides important information on deliveries that were on time and how many arrived late. |
Best in class is ≥ 99.8 percent, median 98.5 percent. |
|
Internal Order Cycle Time |
This KPI is measured from the time an order is placed to the moment it gets shipped. It is used to measure the pick-pack-ship efficiency of the warehouse. The objective is to minimize the percentage. |
Best in class is < 3 hrs., median 13 hrs. |
|
Dock-To-Stock Cycle Time |
This cycle time measures the time from the start of a receipt to the time that Putaway is complete. This is an important KPI to measure the performance of inbound activities. |
Best in class is < 2 hrs., median 6 hrs. |
|
Order Picking Accuracy |
Order picking is the costliest and labor-intensive function in a warehouse. This measurement is critical to monitor the success of warehouse operations. It is also an important factor when delivering high customer service. It is the percentage of pick lines picked without errors, and the objective is to maximize the percentage |
Best in class is ≥ 99.9 percent, median 99.5 percent. |
|
Lines Picked and Shipped per Hour |
This KPI is also important to measure to ensure high customer service. It is based on the number of lines picked and packed/total labor warehouse hours. |
Best in class is ≥ 74.2 percent, median 28 percent. |
|
Order Fill Rate |
This KPI percentage is based on the number of items ordered to the items shipped. The fill rate can be calculated on numerous items, such as SKU, case or on a value basis. |
The best in class for items ordered to shipped is≥ 99.8 percent, median 98.3 percent. |
|
Peak Warehouse Capacity |
This KPI measures the amount of warehouse capacity used during a peak season. It is expressed as a percentage of storage space that has products in them |
Best in class is ≥ 100.0 percent, the median is 95 percent, but it also depends on how the product is received. The best in class for average warehouse capacity is ≥ 91.2 percent, median 84.9 percent. |
SUMMARY
The Warehouse management module in Supply Chain Management helps organizations make continuous adjustments to their distribution processes by enabling them to modify warehouse layouts. Improving your company operations strategy by using ERP systems like D365 is made easier with the systems’ ability to automate the various activities that are performed in Warehouse Management. You are able to customize, create, and extend processes to bring about the optimum levels of Warehouse Management. D365O uses a mix of concepts to offer this degree of flexibility.
WORK TEMPLATES IN D365 SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT
In order to complete the setup procedure, you must enable work templates that are appropriate for the needs and specifications of your organization. This means that before you can begin using work templates, temporary work transactions, and Shipment ID, you must first set them up in your system. Begin with Work Templates and work our way up to the rest of the site.
Work Template
In the context of work, a work template is a template that defines the “what” and “how” of the work that is performed. They enumerate all of the prerequisites for the project to be completed. It may be necessary to identify the locations linked with these work templates in order to determine where the work is being performed. Pick operations and Put operations, which are used to drive the fundamental process of transferring on-hand inventory from one location to another, must be included in each template. Each template must also have at least one Put operation.
Warehouse Management Process
When it comes to the Warehouse Management process, Work Templates in Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Finance and Operations are crucial pieces of the puzzle to put together. In order to make the process of establishing work templates simple, templates are used to construct “Work” that must be performed for a variety of operations. A “Work” Pick/Put Pair contains two steps: at least one that comprises the “Work” and a location directive that specifies where the “Work” Put must be performed. After then, the “Work” will be performed through the client user interface or on a mobile device (by creating Mobile Device Menu Items and Menus).
Wave Templates and Work Templates
Both Wave Templates and Work Templates have Sequenced settings, which are sequenced in the same way as Wave Templates and Work Templates. When generating the Work of an object, the first template that fits the data is chosen and utilized to construct it (sales order, purchase order, etc.). This Work Template Query contains the criteria for assigning a Work Template and generating a Work based on these parameters. Work Templates assist in estimating how long tasks on the system will take.
Tasks may be assigned to individual resources or groups of resources. Examine the client user interface while evaluating progress on the Work (UI). The book may be judged as a whole, or each chapter can be looked upon separately. Work history log problems should be addressed if you’re experiencing trouble generating work. Any exceptions that occur during the execution of the job are recorded in the Work Exceptions Log. You may reduce the time it takes to create new templates by copying and pasting templates into new ones. Work Templates are grouped into various categories of work, called work order types:
- Sales Orders
- Purchase Orders
- Finished Good Put Away
- Co-Product/By-Product Put Away
- Inventory Movements
- Inventory Transfers
- Cycle Counting
- Replenishments
- Returns
- Kanban movements
- Raw Material Picking
You can create a work template for the following types of warehouse-related activities:
- Inbound transactions
- Picking of inventory items
- Production tasks such as picking or putting of raw materials
- Inventory transfers
- Movement of inventory items between locations
- Replenishment of locations
Once again, the order in which the Work Templates are presented is essential in determining how the Work Templates are ultimately picked. To see whether the newly generated Work Template is genuine, be sure to choose the checkbox labelled “Valid” in the “Valid” column. By giving Work Templates individual names that identify the requirements they fulfil, it is easier to identify and utilize them. It is possible to provide the criteria for the template by selecting the Query tab and then choosing Edit Query from the Template drop-down menu. This lets you create table joins and sorting requirements. The Work Priority function may be used to place specific tasks above other work. You may reallocate certain Work Templates by providing the associated Work Pool ID into the relevant Work Pool field.
Setting up a work template
- Work order type
- Work Template Header
- Sequence Number – A sequence number is given to each work template. This is the order in which the system evaluates each template to decide which one should be allocated to anything.
- Work Template ID – each work template has its own unique ID.
- Valid – Once the Work Template has been produced and contains all of the required components, it will be recognized with a Valid checkmark.
- Work Pool ID – ID established to collect work into particular groups for processing • Automatically Process – choose whether the work should
Work Template Details
- Work Kind – The type of work to be performed. • Line Number – The sequence number for processing the work in the template.
- Custom work type – only utilized if Work Type is set to Custom.
- Required – is the step in the process that must be completed?
- Halt work – stop the work so that it may be taken up by another user or picked up later.
- Freeze
- Code of directives
- Work Class ID – Use this ID to set up the mobile device’s interface.
- Query for Work Template
Once again, the order in which the Work Templates are picked is crucial in determining how they are chosen. The second most essential aspect is to double-check if the newly generated Work Template is valid by looking for a checkmark in the “Valid” column. For simplicity of usage and recognition, each Work Template will be given a name that identifies the template’s requirements. By selecting Edit Query, you may provide the template’s criteria, which include any database joins needed to access the data as well as any sorting requirements. By giving a greater priority to certain templates, the Work Priority may be utilized to prioritize specific tasks above other work. By assigning a Work Pool ID to a certain Work Template, it may be preset to be allocated to a group of employees.
SUMMARY
In Microsoft’s Dynamics 365 for Finance and Operations, Microsoft Work Templates are vital parts of the whole process. A work template is used to build work that must be completed for various activities. To drive the basic process of moving on-hand inventory from one place to another, each template must contain at least one Pick/Put activity. Work templates help the system predict how long a job will take. Work order types are used to identify different kinds of work. The template’s name will reflect the criteria it fulfils. You may enter search criteria in the Edit Query dialogue box by choosing Edit Query from the Template drop-down menu. You may set the assignment of Work Pool IDs to a particular group of employees using the settings of a Work Pool. The Work Template sequence is very essential in deciding which templates are chosen. To aid in usage and identifiability, each Work Template will have a name that reflects the requirements of the template. To prioritize particular work above other work, create Work Priorities for each kind of work and give a greater priority to the templates for that type of work.
HOW DO YOU CREATE WORK TEMPLATES IN D365 SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT?
Step 1
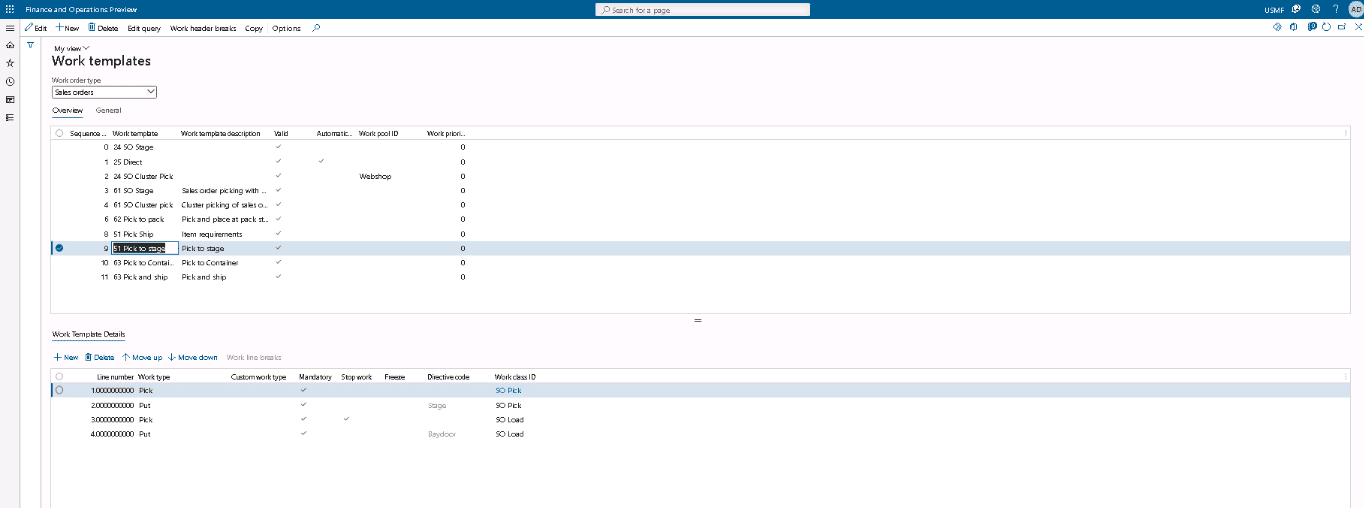
Go to Warehouse management > Setup > Work > Work templates.
Step 2
In the grid in the upper part of the page, select an existing work template where you want to set up the Confirm and transfer feature. (If you’re working with the USMF demo data, select the 51 Pick to stage work template.) Alternatively, create a new work template. The following screenshot shows the result of the above 2 steps:
Step 3
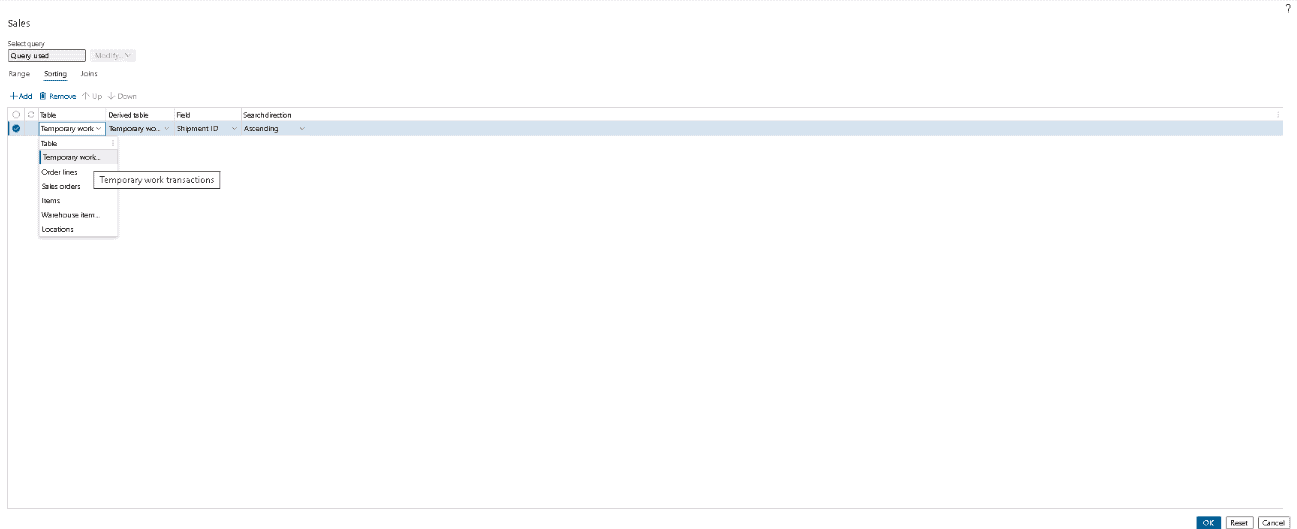
On the Action Pane, select Edit query to open the Sales dialog box.
Step 4
In the Sales dialog box, on the Sorting tab, select Add to add a row to the grid.
Step 5
In the new row, set the following values:
- Table: Temporary work transactions
- Derived table: Temporary work transactions
- Field: Shipment ID
- Search direction: Ascending
Step 6
Select OK to save your settings and close the Sales dialog box.
Step 7
If you receive a message stating that grouping will be reset, select Yes to continue. The above settings are shown in the below screenshot:
Step 8
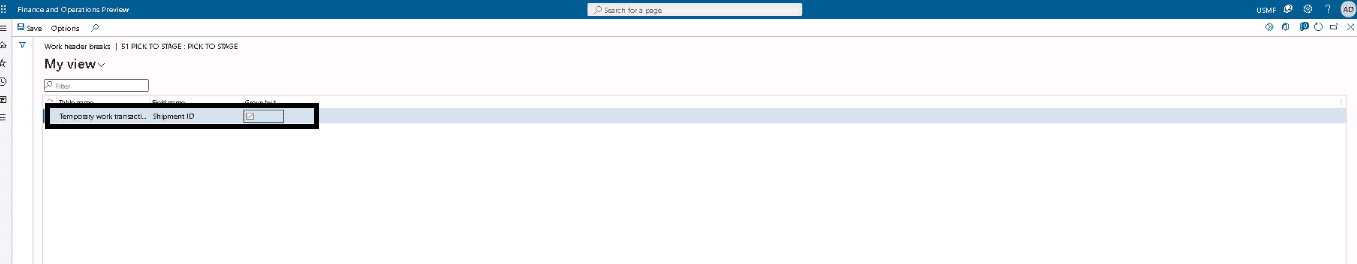
In the grid in the upper part of the Work templates page, select the template that you just edited, and then, on the Action Pane, select Work header breaks.
Step 9
On the Action Pane, select Edit to put the page into edit mode.
Step 10
In the grid, set the following values:
- Table name: Temporary work transactions
- Field name: Shipment ID
- Group by this field: Select this check box.
- On the Action Pane, select Save.
Step 11
Close the page.
HOW DOES LOAD SHIPMENT AND WORK TEMPLATES IN D365 HELP TO BOOST THE COMPANY’S EFFICIENCY?
There are a lot of ways in which optimal shipments can contribute to the profitability of a business. With an efficient Warehouse Management System, you can:
- Make/load template contains information about equipment and measures such as height, width, depth, and volume of the load. It can be used to define the capacity of a container that carries goods. The system can also update if the defined template capacity is less than the carrying goods.
- Load planning workbench basically provides a platform where we can create a load for the inbound and outbound process.
Are you in need of specialized supply chain solution creation for the load shipment process? If so, please get in touch with us. We love developing solutions that improve the load shipment functionality in Dynamics 365.
Thank you for taking the time to read this blog post. Keep an eye out for our next blogs, in which we will go into greater detail on this and other relevant subjects.
SUMMARY
The Make/Load Template includes information on the kind of equipment and measurements that may be relevant for the load, such as height, breadth, depth, and volume. In usage, the capacity of a container that carries products may be described as “It can be used to specify the capacity of a container.” We enjoy coming up with improvements to Dynamics 365’s shipping and load capabilities. Do you require supply chain strategy development? Please contact us if you can. If you want to speak to us right away, leave a remark below and we will respond as soon as possible.
At Instructor Brandon | Dynatuners, we always seek innovative methods to improve your competitiveness and suit your Microsoft Dynamics 365 requirements. Our offerings are founded on defined procedures, industry experience, and product understanding. If you’re interested to consult with our specialists on how it may benefit you to achieve your business efficiency targets, don’t hesitate to Contact Us.
[sc_fs_multi_faq headline-0=”h2″ question-0=”What is Warehousing? ” answer-0=”The importance of warehousing in your retail supply chain cannot be overstated. While it may not be the most exciting topic, warehousing and inventory storage impact everything from procuring raw materials to properly managing inventory to sending orders to consumers on time. ” image-0=”” headline-1=”h2″ question-1=”How Warehouse Management helps Organizations? ” answer-1=”Inventory management becomes faster, easier, and more efficient with Warehouse Management. Warehouse Management provides immediate, accurate feedback based on updated information in real-time, allowing businesses to respond faster to client requests. At all times, wholesalers and distributors know exactly what is in the warehouse, where it is stored, and when it needs to be refilled. ” image-1=”” headline-2=”h2″ question-2=”What are Work Templates in Microsoft Dynamics 365? ” answer-2=”The Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management work templates define warehouse operations and tasks that decide warehouse workers’ instructions on their devices. Work templates specify how each warehouse process is carried out. ” image-2=”” count=”3″ html=”true” css_class=””]
 6677
6677